Compound Measures Worksheets
Distance Speed Time (A)
Year groups: 8, 9
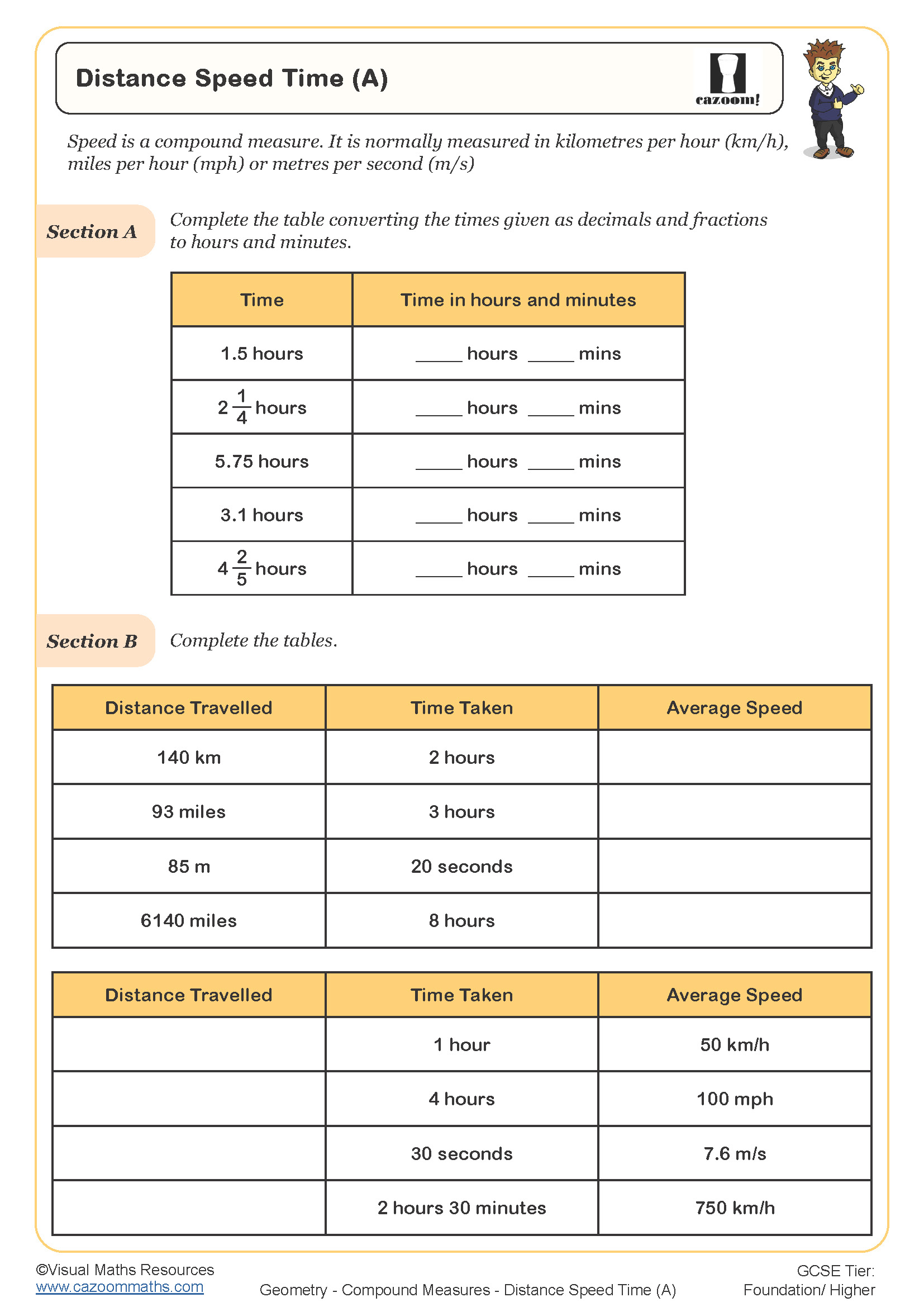
Distance Speed Time (B)
Year groups: 8, 9
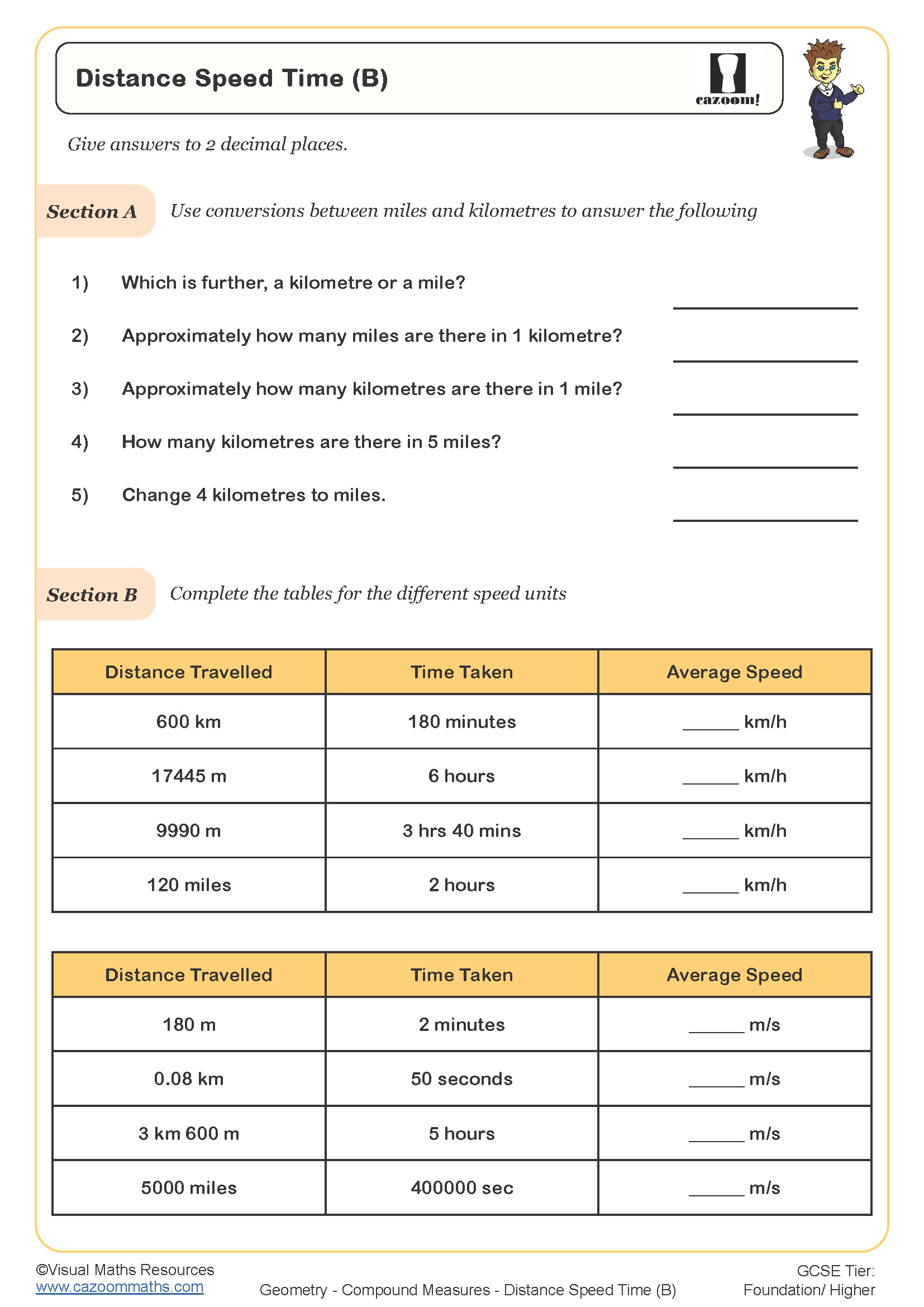
Speed
Year groups: 8, 9
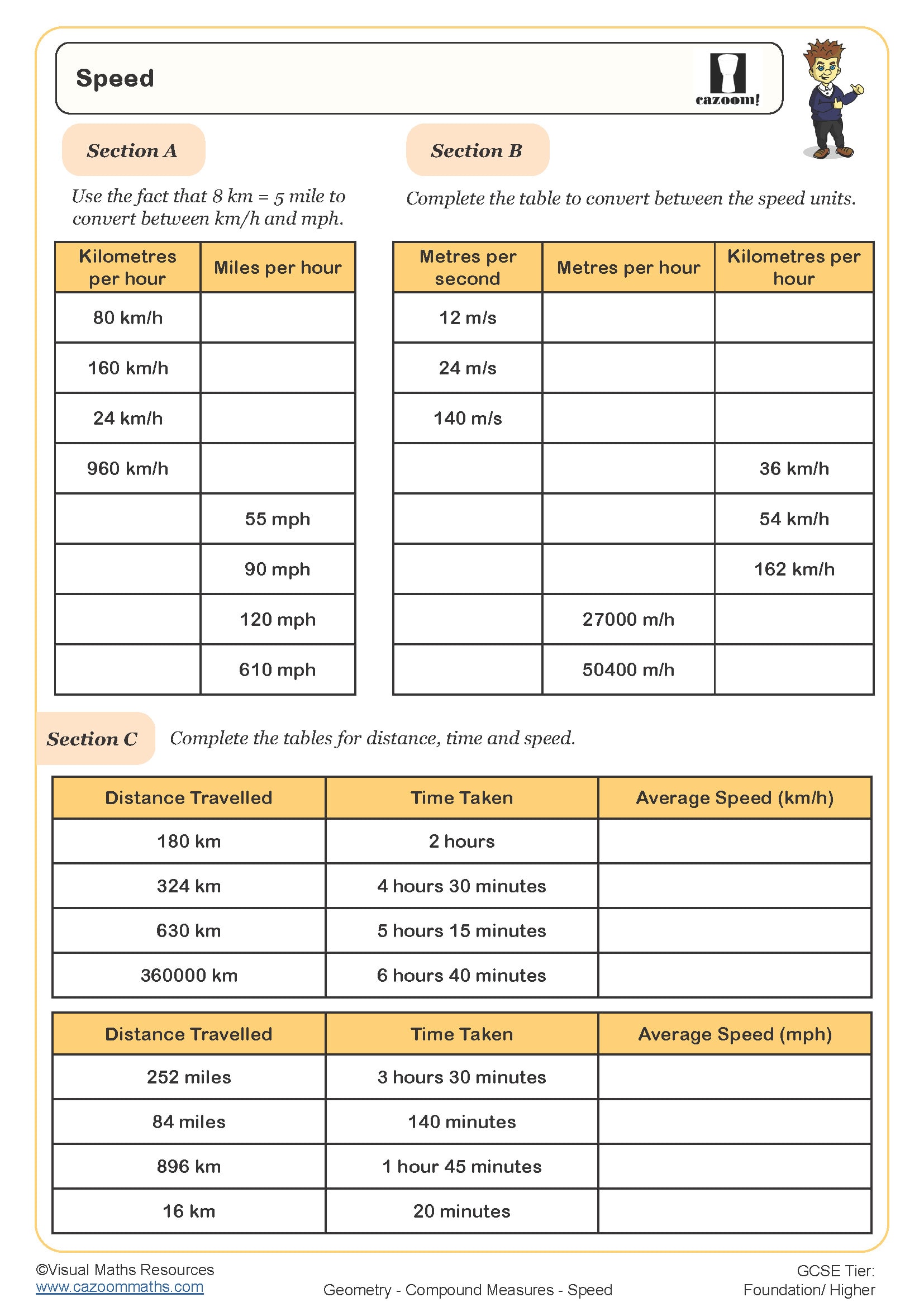
Density, Mass and Volume (A)
Year groups: 9, 10
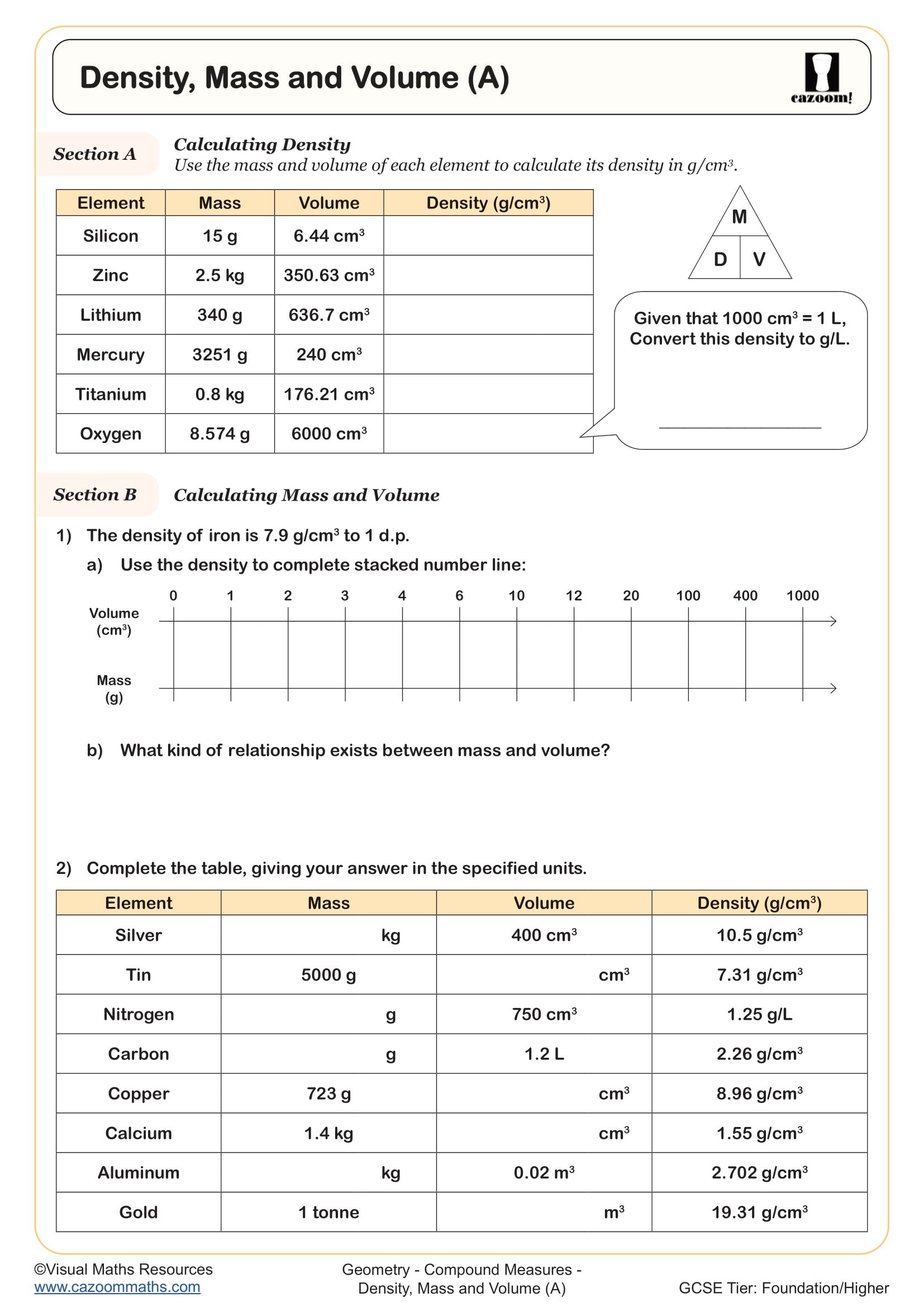
Density, Mass and Volume (B)
Year groups: 9, 10
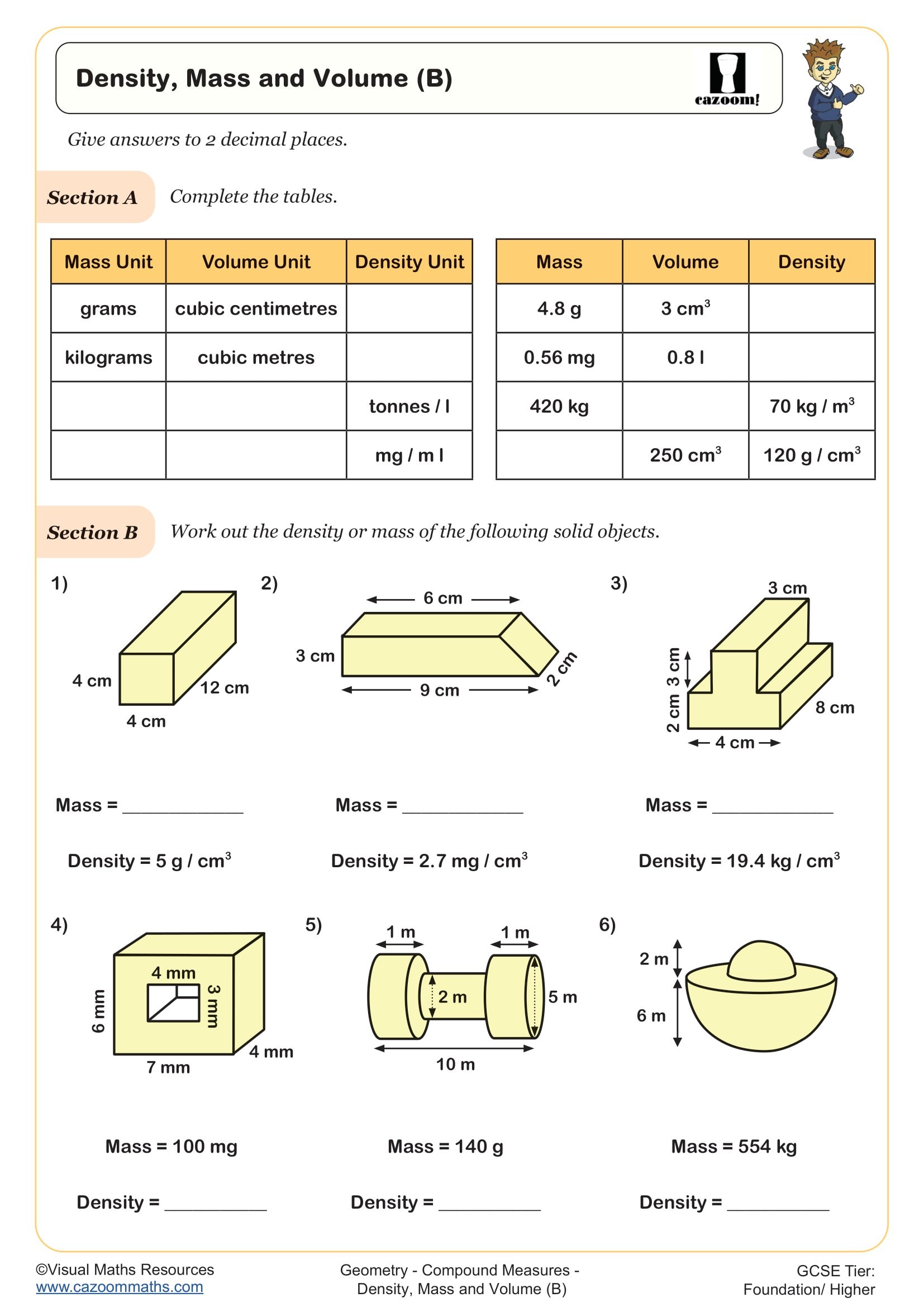
Population Density
Year groups: 9, 10
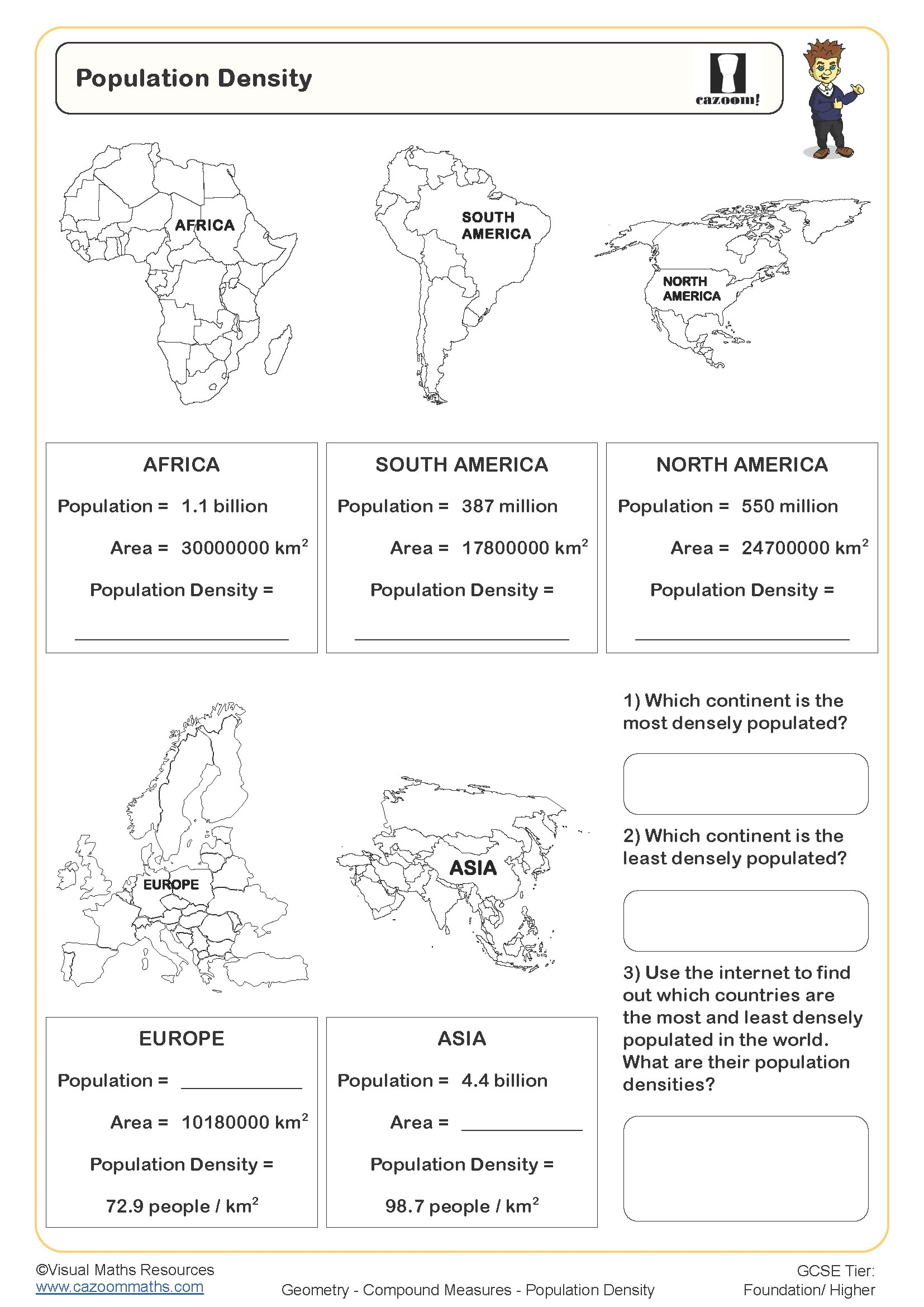
Speed, Distance, Time - Multi Stage Journeys
Year groups: 9, 10, 11
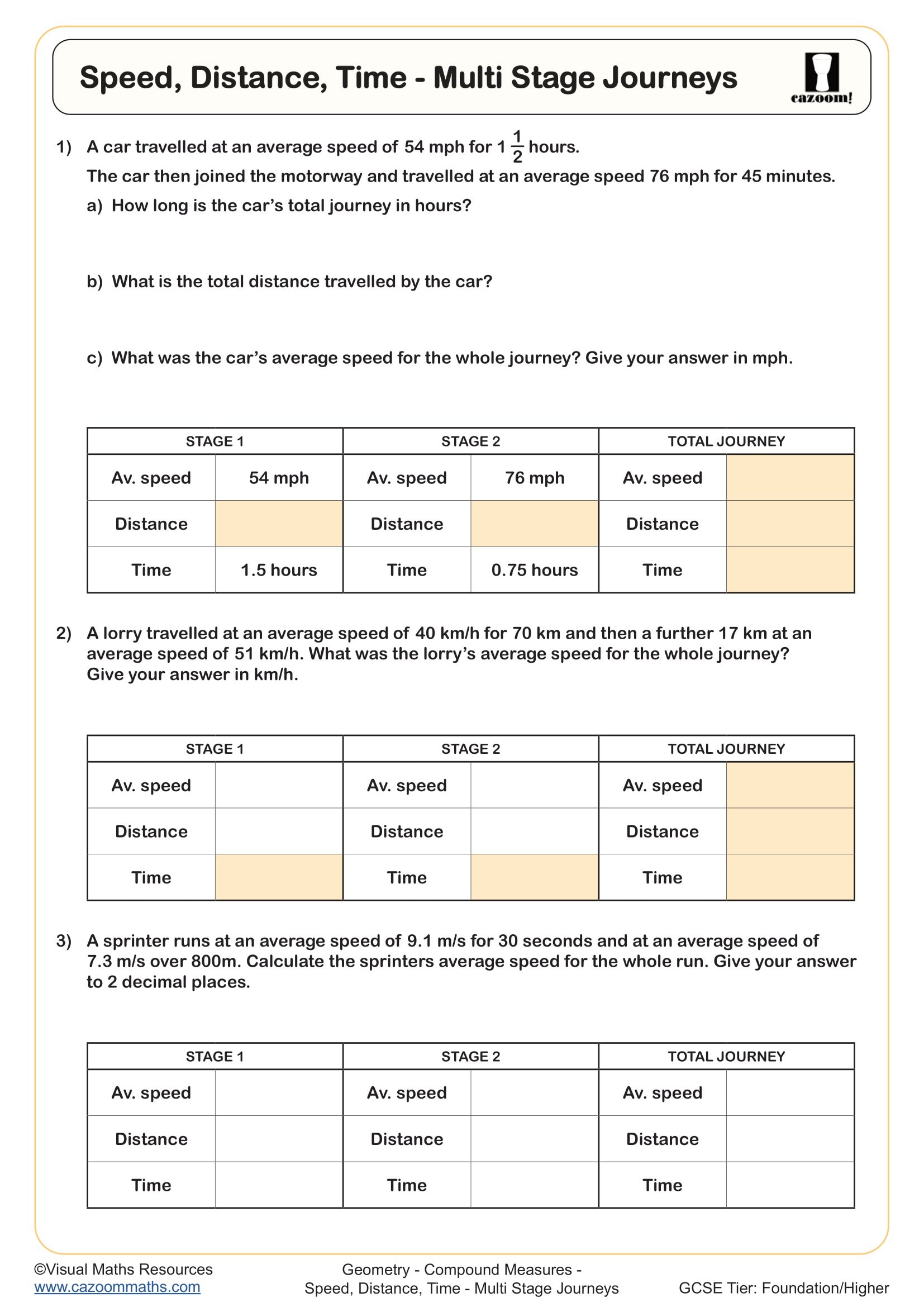
Density, Mass and Volume (C) - Mixtures
Year groups: 10, 11
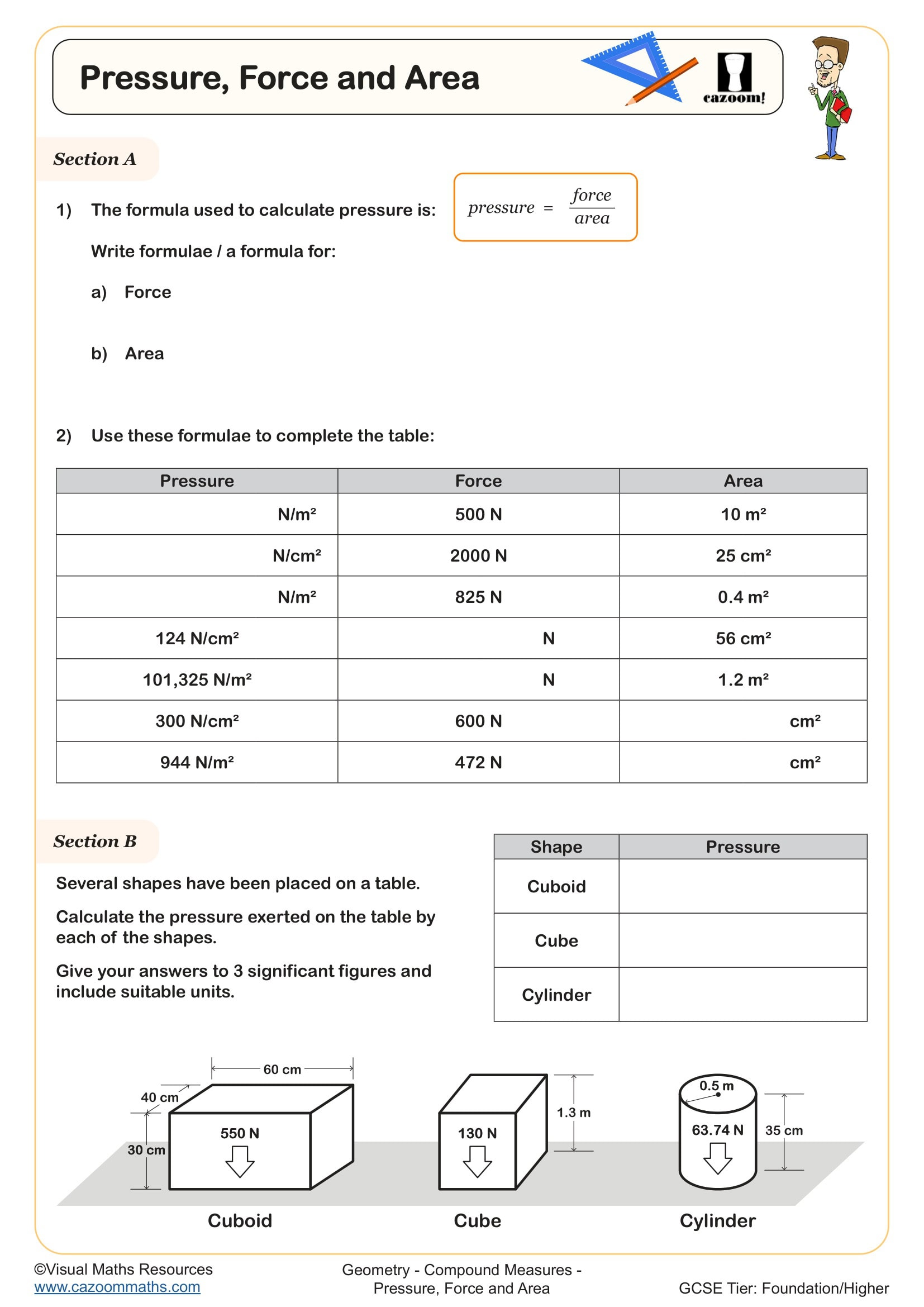
Pressure, Force and Area
Year groups: 10, 11
Printable PDF GCSE Compound Worksheets with Answers
Compound measures are used in various different mathematical and scientific careers therefore it is important for your student or child to learn. Cazoom Maths have provided a number of different problem worksheets along with the answers and formulas suitable for all abilities.
What Are Compound Measures?
Compound measures are measurements that use two or more quantities. Students can identify a few common types of compounds in modern mathematics, including measurements of speed, density and rates of pay.Let’s take density as an example. It is calculated using the equation mass/volume and written as mass per volume. Common measurement units include kg/m³ (also written as kg m⁻³) and g/cm³. The fact that density is used to measure the quantities mass and volume in two different measurement units is what makes this system of measurement compound.
What Is a Compound Unit?
A compound unit is another term for a compound measurement. In addition to speed, density and rate of pay, pressure and acceleration are measured in compound units.The key concept behind compound measurements is that they are comprised of two different units. It is important to note the system of measurements being used, as it differs between different areas of the world. The metric system is the most commonly used system of measurement in the UK, but in the United States and elsewhere, the Imperial system is also common. Students should make sure to convert differing units within the compound measurement so they are comparing apples to apples. It doesn’t make sense to use the metric system for one set of measurements and the Imperial system for another. Converting to the metric system if it’s necessary should be the student’s first step.
How Can Students Work Out Compound Units?
Students can work out compound units by substituting known values within a formula.To determine density, use the formula density = mass/volume. To determine speed, use the formula speed = distance/time. To determine acceleration, use the formula acceleration = change in velocity/time. To determine pressure, use the formula pressure = force/area.
Worked Example of Compound Measurement
Once students have gotten a grasp on the basic concept of compound units, they can begin to use them to solve problems.Let’s take a look at one worked example. If a car is traveling for two-and-a-half hours and makes it 160 miles, how fast is the car traveling in kilometers per hour (kph)? In order to solve this problem, students should substitute the values for time and distance into the formula, speed = distance/time. This would leave them with the equation speed = 160/2.5. Solving this equation produces the answer: 64 kph.
Where Are Compounds Used?
Compounds are used extensively in chemistry, physics and statistics. Students should complete stats worksheets until they feel comfortable solving simple equations using compound measures. Parents, tutors, and teachers can find statistics worksheets on this website that will help students understand measures and gain experience solving basic maths equations that use compounds.