Angles in Polygons Worksheets
What are the rules for angles in polygons?
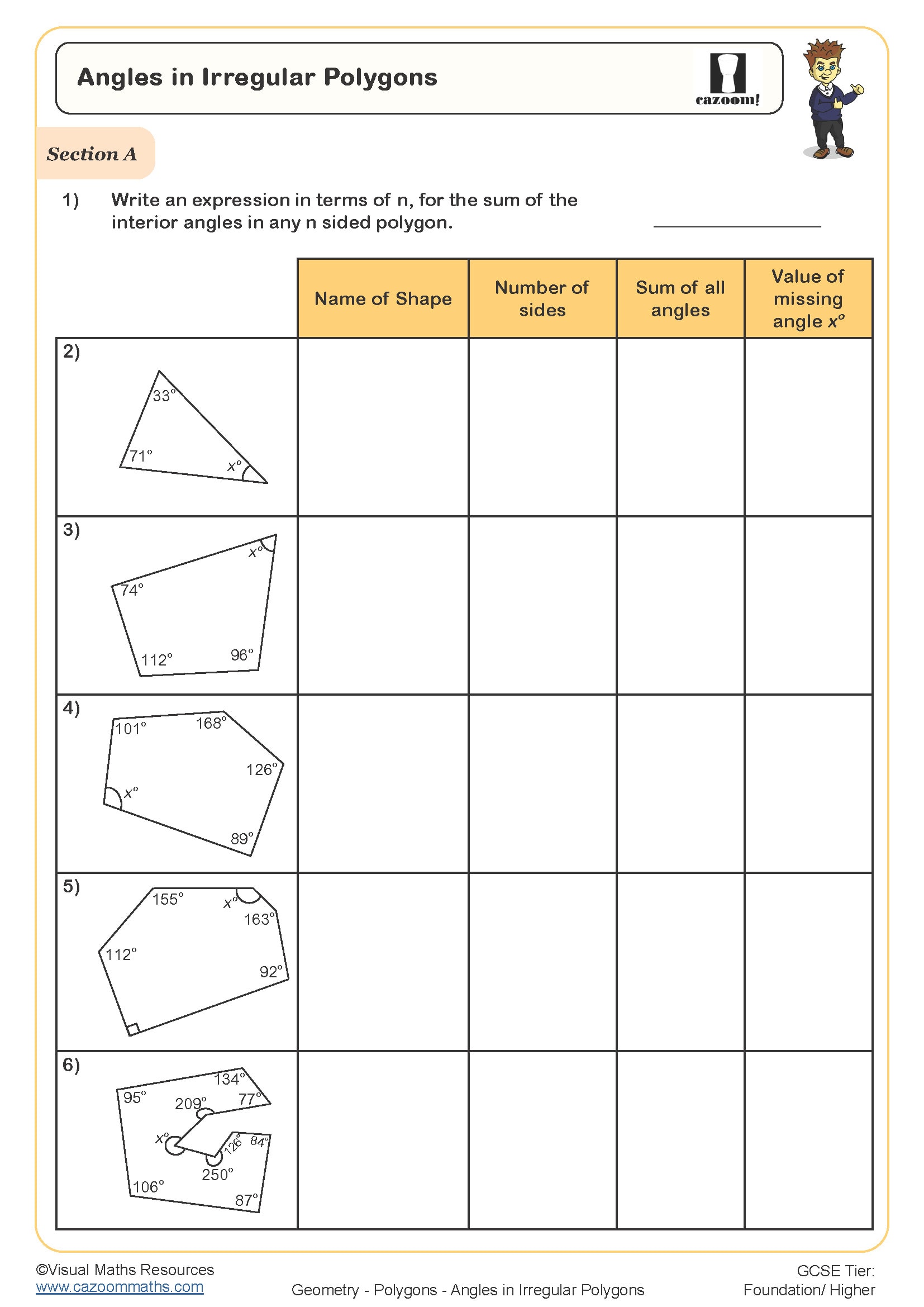
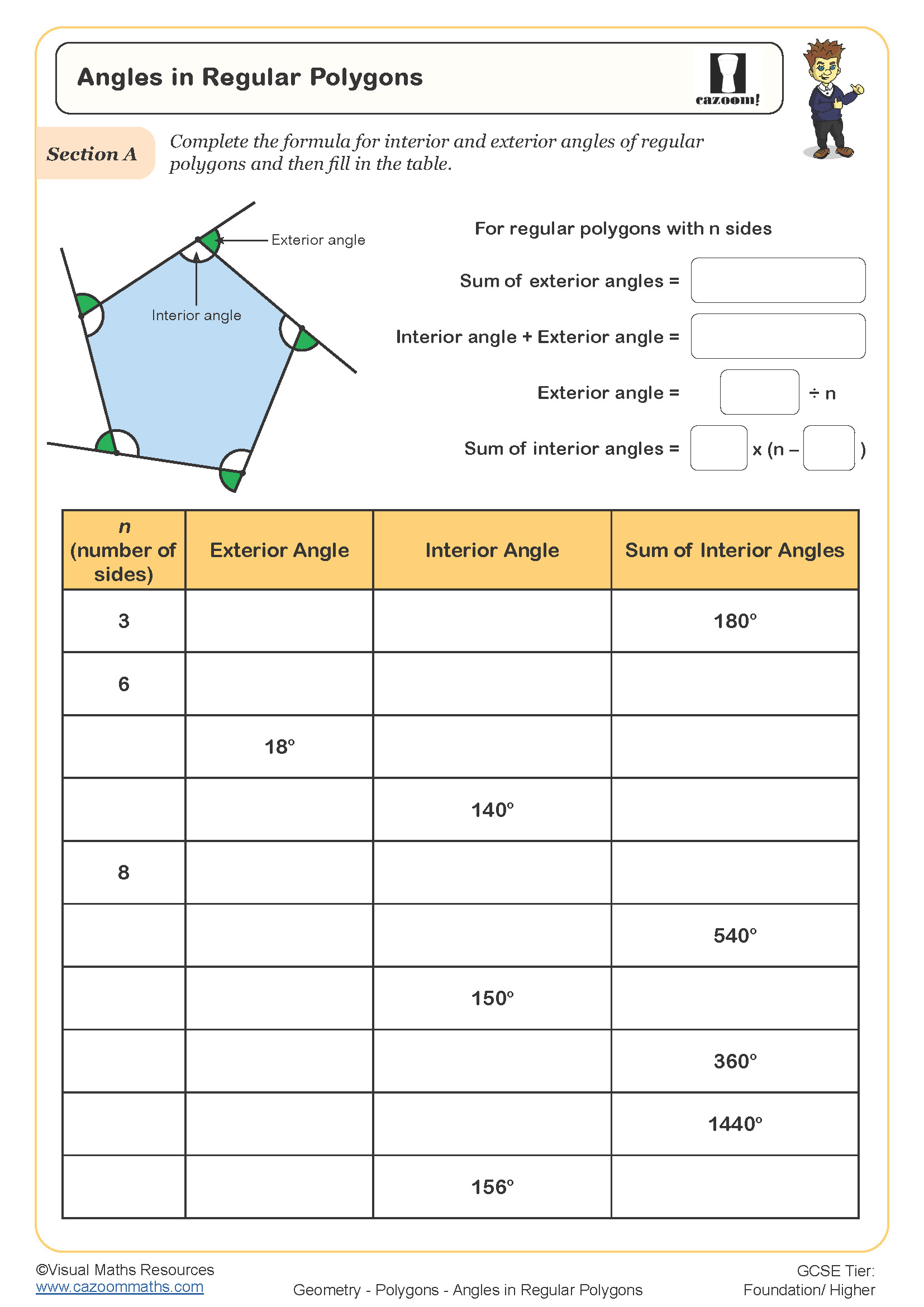
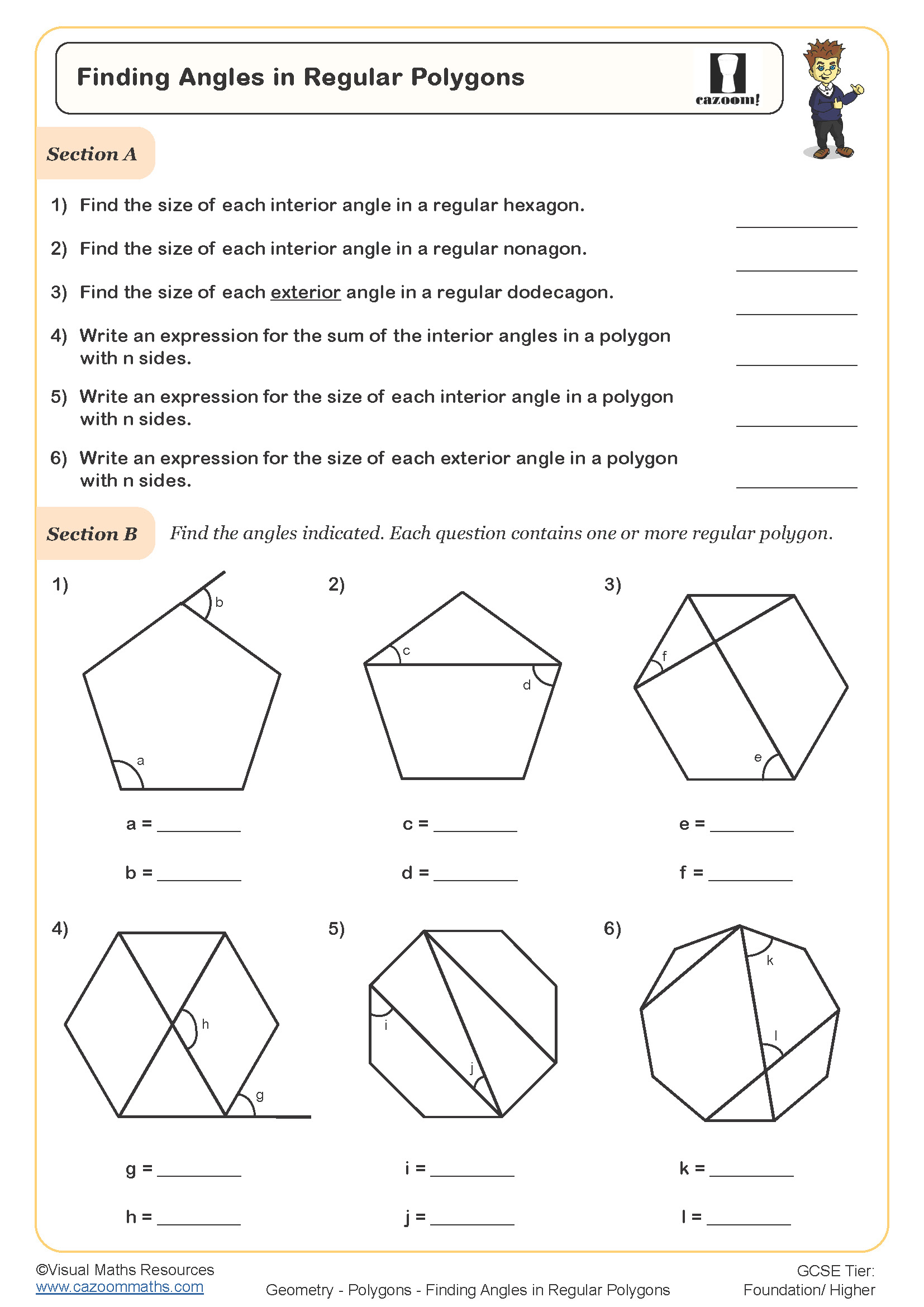
The sum of interior angles in any polygon follows the formula (n - 2) × 180°, where n represents the number of sides. Exterior angles of any polygon always sum to 360°, regardless of how many sides it has. For regular polygons, each interior angle can be found by dividing the total by the number of sides, and each exterior angle equals 360° ÷ n. These rules form part of the KS3 geometry curriculum and build directly on angle work from Year 7.
Students often confuse interior and exterior angle formulas, particularly when questions involve finding the number of sides from a given angle. A common error occurs when students try to use 360° ÷ angle for interior angles rather than exterior angles. Teachers notice that explicitly labelling which type of angle the question asks for helps students select the correct approach before starting calculations.
Which year groups study angles in polygons?
Angles in polygons appears in the KS3 National Curriculum, with these worksheets targeting Year 8 and Year 9 students. The topic builds on basic angle facts from Year 7, such as angles on a straight line and around a point, and extends understanding to more complex geometric figures. Students need confidence with forming and solving linear equations, as many polygon problems require algebraic methods rather than direct calculation.
The progression across Year 8 and Year 9 involves increasing algebraic complexity and problem-solving demands. Year 8 students typically work with finding missing angles when the number of sides is known, whilst Year 9 content includes finding the number of sides from angle information and tackling multi-step problems where interior and exterior angles must be considered together. Questions may also incorporate angle notation and proof-style explanations.
How do you find exterior angles of a polygon?
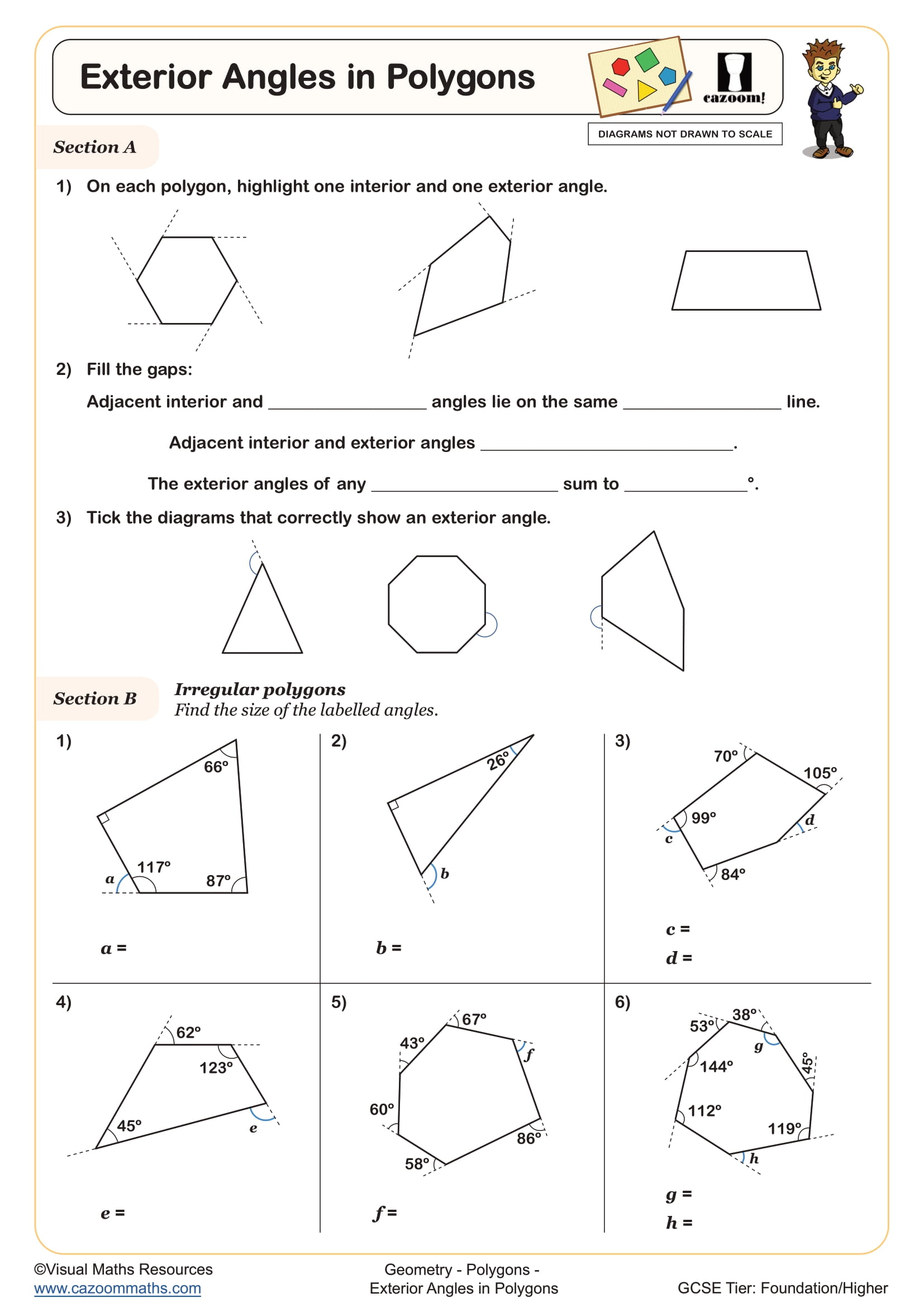
Each exterior angle of a regular polygon equals 360° divided by the number of sides. For irregular polygons, exterior angles still sum to 360°, but individual angles differ. Students form an exterior angle at each vertex by extending one side of the polygon, creating an angle between the extension and the adjacent side. This approach connects to the idea that as you walk around any polygon, turning through each exterior angle, you complete one full turn of 360°.
This concept has practical applications in navigation and robotics. Programmers use exterior angles to calculate how much a robot must turn at each corner when following a polygonal path. Architects and designers apply these principles when planning walkways or tiling patterns with regular shapes. Understanding that the exterior angle sum remains constant regardless of polygon size or shape demonstrates an invariant property that appears throughout mathematics and engineering contexts.
How can teachers use these angles in polygons worksheets?
The worksheets provide structured practice that moves from straightforward calculations to problems requiring equation-solving and strategic thinking. Questions include diagrams where students must identify which angles are interior or exterior, calculate missing values using appropriate formulas, and work backwards from angle information to determine properties of the polygon. Answer sheets allow students to check their working independently or support teachers with quick marking during lessons.
Many teachers use these resources for intervention with students who can apply formulas mechanically but struggle with problem-solving. The worksheets work well for homework after introducing the topic, as revision before assessments, or for paired work where students explain their reasoning to each other. Teachers often find that asking students to justify which formula they're using before calculating helps address the common confusion between interior and exterior angle rules.