Exact Trigonometric Values Worksheets
What are the exact trigonometric values students need to know?
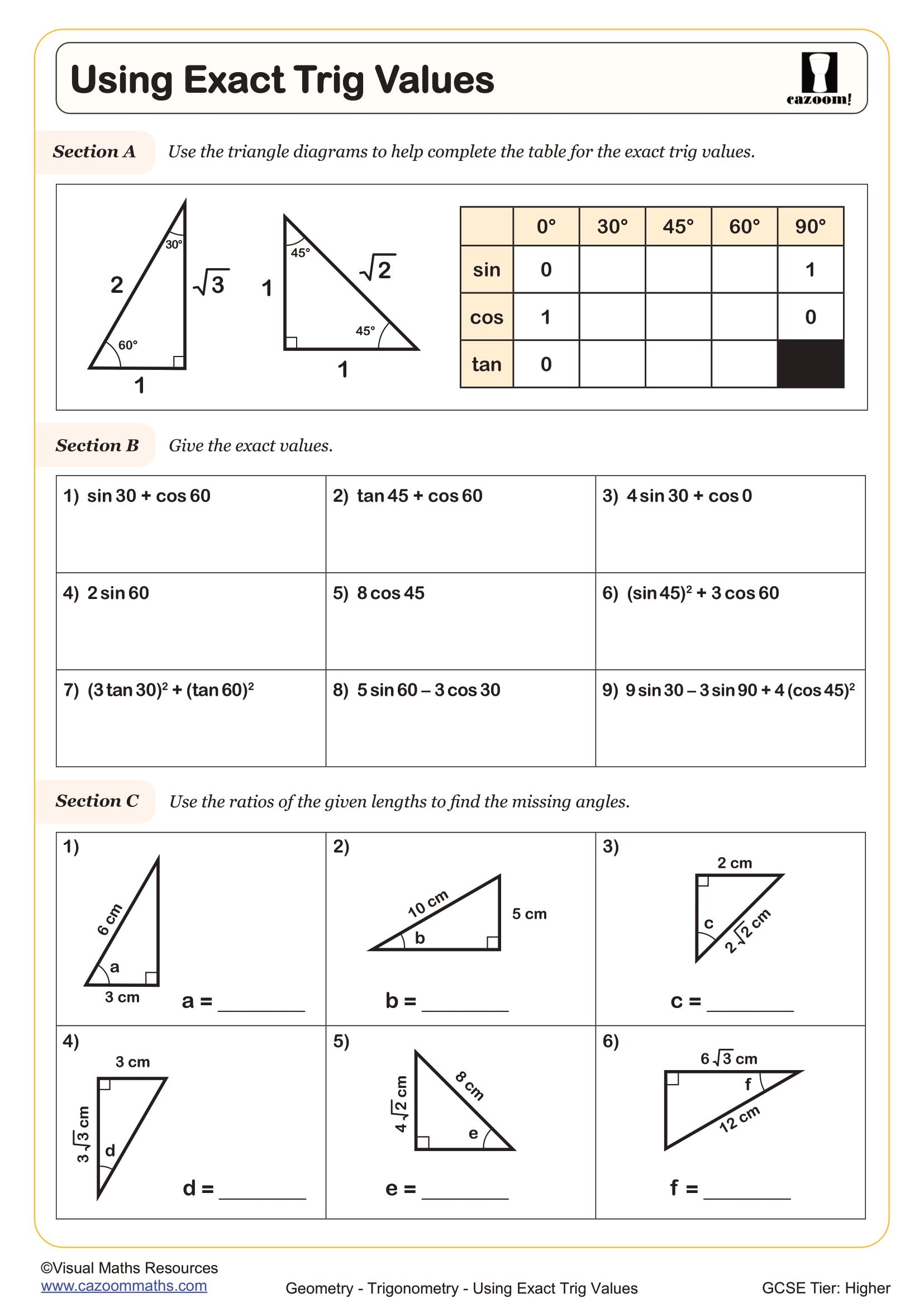
Students must memorise the exact values for sine, cosine and tangent at five key angles: 0°, 30°, 45°, 60° and 90°. These values include fractions like ½, surds such as √3/2 and √2/2, and zero or undefined values depending on the function. The National Curriculum expects Higher Tier GCSE students to recall these instantly without calculators, as they underpin problem-solving in trigonometry, vectors and advanced geometry questions.
A common error occurs when students confuse complementary angles—many remember that sin 30° = ½ but then incorrectly write sin 60° = ½ as well, forgetting that sin 60° = √3/2. Exam mark schemes penalise decimal approximations like 0.866 when exact surd form is required, so students must practise expressing answers precisely with radicals rather than reaching for the calculator.
Which year groups study exact trigonometric values?
Exact trigonometric values appear in Year 9, Year 10 and Year 11, spanning both KS3 and KS4. Students typically encounter these special angles when they've built confidence with basic trigonometry in right-angled triangles and are ready to work beyond calculator-dependent methods. At GCSE Higher Tier, exact values become essential knowledge tested explicitly in non-calculator papers and embedded within multi-step problem-solving questions.
Progression across these year groups moves from recognition and recall towards application in increasingly complex contexts. Year 9 students focus on memorising the values and identifying them in straightforward triangles, whilst Year 10 and 11 students apply exact values within algebraic trigonometry, solving equations like 2sin x = √3, and handling them confidently alongside surds and exact fractional answers in coordinate geometry and trigonometric proofs.
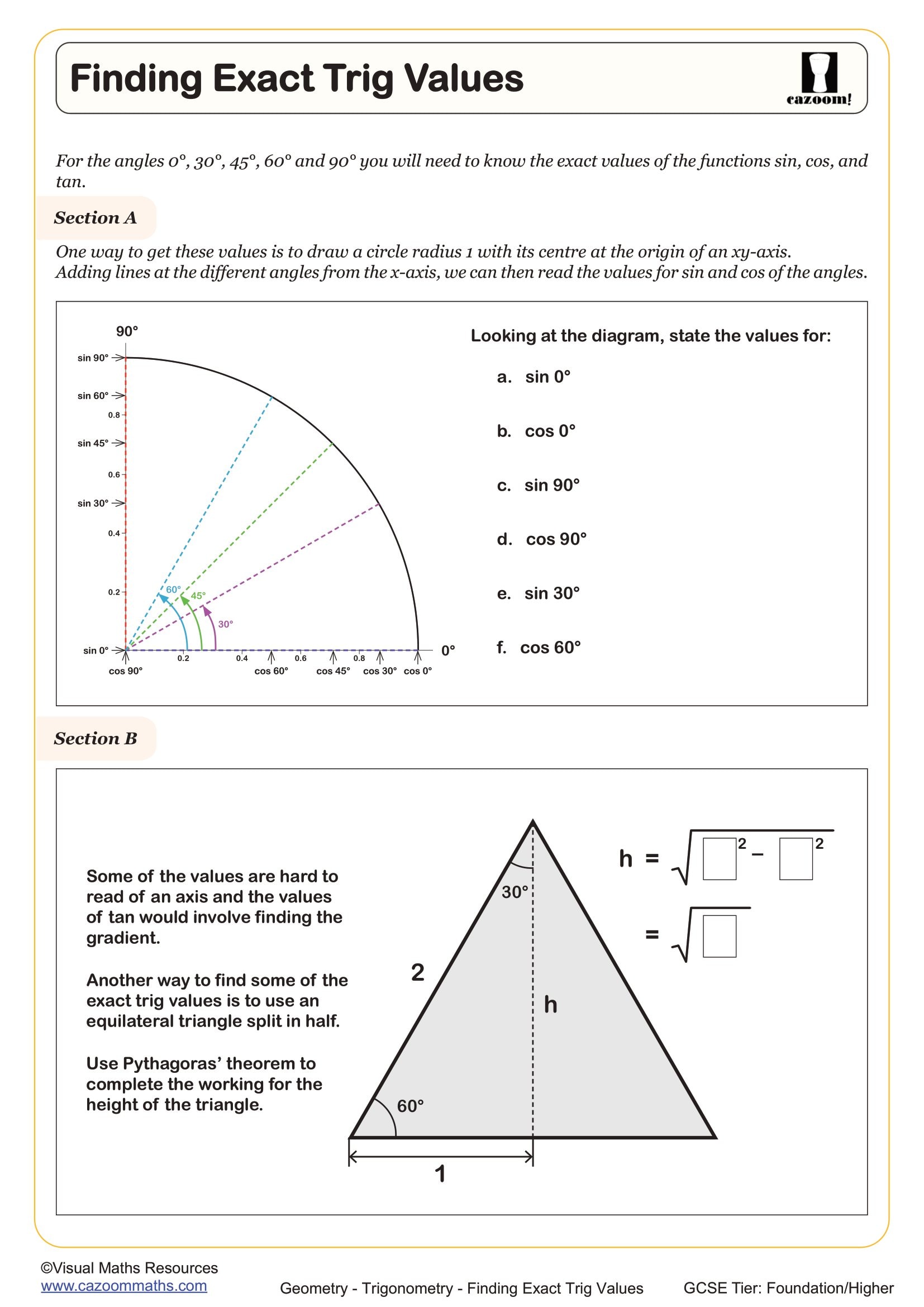
How do students derive exact values using special triangles?
Students derive exact trigonometric values by constructing two special triangles: an equilateral triangle split in half for 30° and 60° angles, and an isosceles right-angled triangle for 45°. For the 30-60-90 triangle, starting with side length 2 and using Pythagoras gives sides of 1, √3 and 2, allowing students to work out sin 30° = 1/2, cos 30° = √3/2 and tan 30° = 1/√3. The 45-45-90 triangle with sides 1, 1 and √2 yields sin 45° = cos 45° = √2/2 = 1/√2.
These special triangles connect directly to engineering and architecture, where standard angles appear in roof trusses, structural supports and mechanical linkages. Engineers rely on exact values when calculating forces in frameworks at 30°, 45° or 60° angles, as decimal approximations accumulate error in iterative calculations. Understanding the geometric origin of these values helps students remember them and reinforces why precision matters in technical applications where safety margins depend on accurate trigonometric calculations.
How do these worksheets help students remember exact values?
The worksheets build fluency through varied practice that moves between recognising exact values, applying them in equations and working with them alongside surds and fractions. Rather than relying on rote memorisation alone, questions encourage students to reconstruct values from special triangles and check their recalled values against geometric reasoning. The answer sheets allow students to self-assess immediately, identifying which specific angles cause confusion and targeting those gaps before moving to more complex applications.
Teachers use these resources flexibly across different classroom scenarios. Short starter activities work well for regular retrieval practice, embedding exact values into long-term memory through spaced repetition. They're equally effective as focused intervention for students approaching GCSE non-calculator papers who need concentrated practice, or as homework tasks that parents can support using the provided answers. Paired work where students quiz each other on random angles often proves more engaging than individual drills whilst building the instant recall that exam conditions demand.