Perimeter Worksheets
What is perimeter in maths?
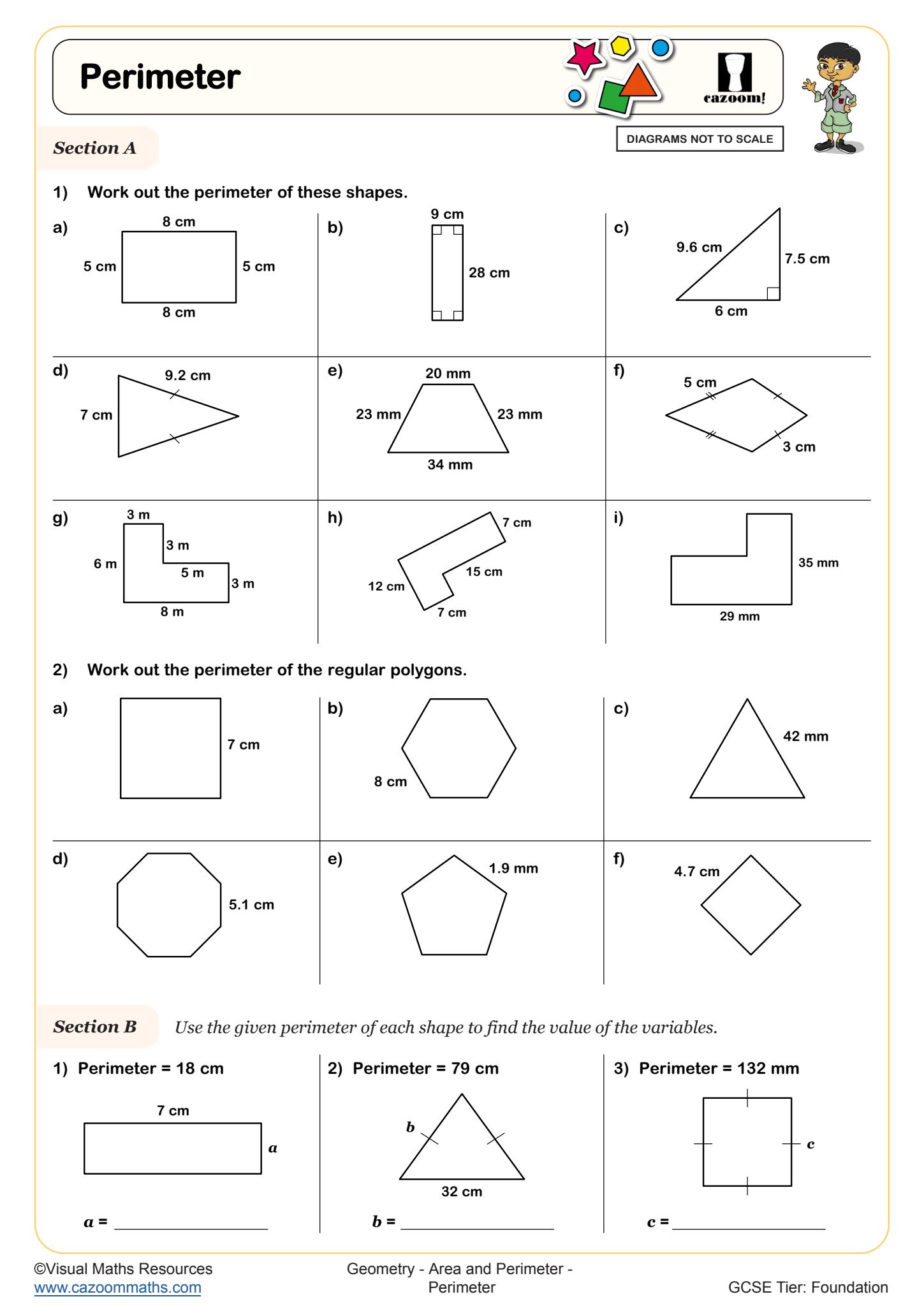
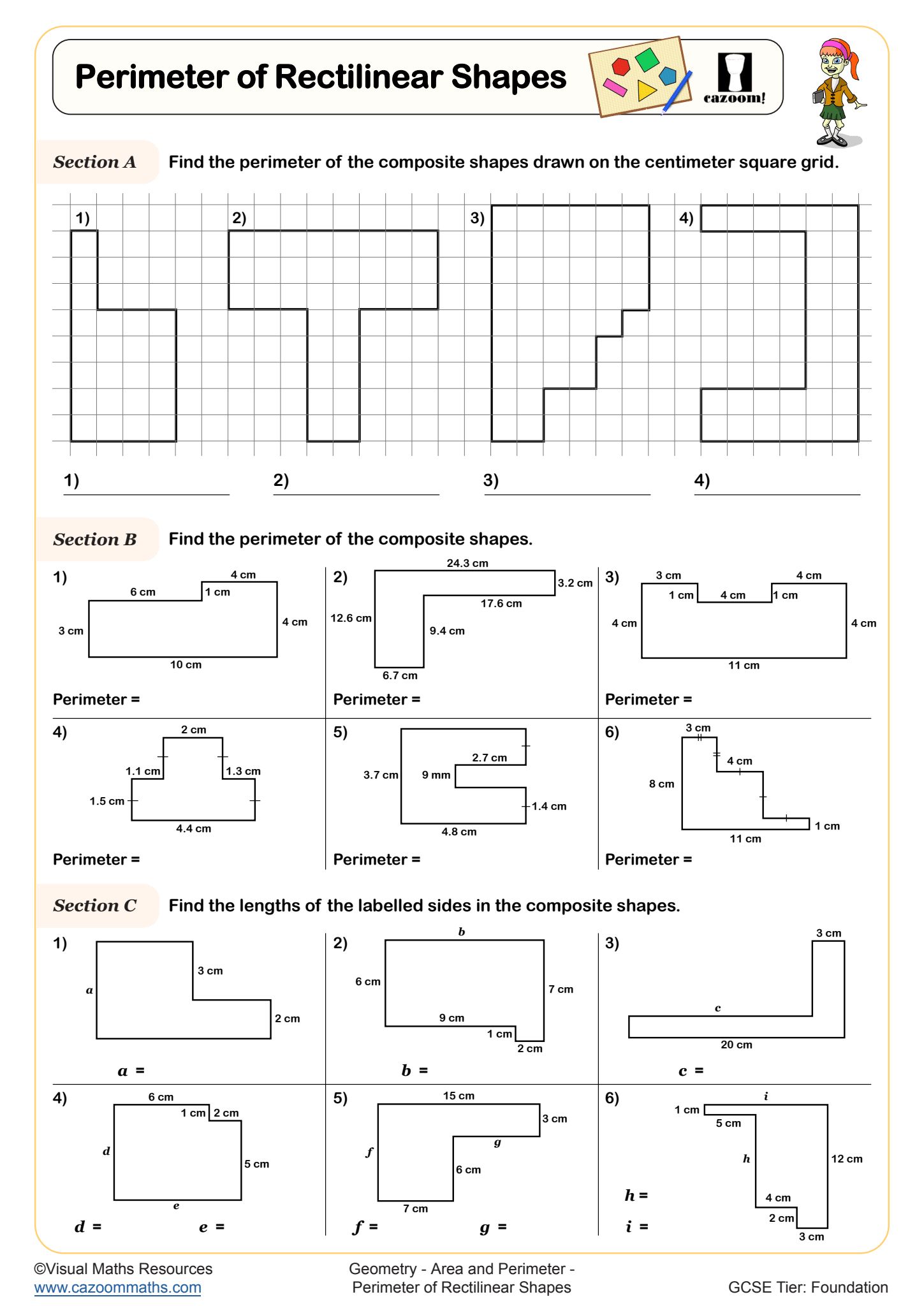
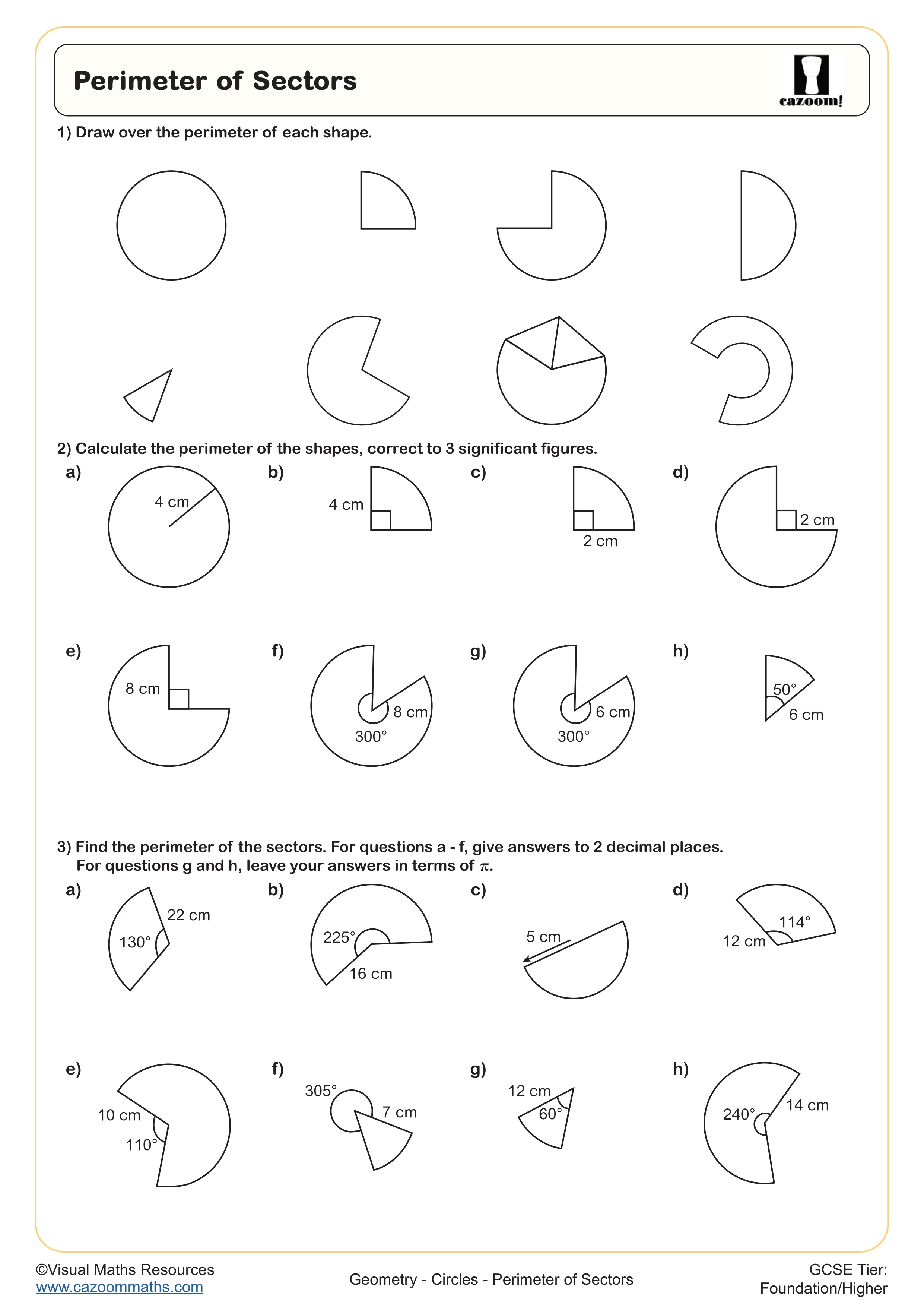
Perimeter is the total distance around the outside edge of a two-dimensional shape, measured by adding together the lengths of all its sides. In the National Curriculum, students begin calculating perimeters of regular polygons in Key Stage 2 before progressing to more complex shapes, including those with missing side lengths and algebraic expressions at Key Stage 3.
Students often lose marks when they forget to include all sides in their calculation, particularly with composite shapes made from rectangles where some edges aren't explicitly labelled. Exam mark schemes expect students to show their working by listing each side length before adding, especially in multi-step questions where perimeter forms part of a larger problem involving area or algebra.
Which year groups study perimeter?
These worksheets cover perimeter for Year 7, Year 8, Year 10, and Year 11, addressing both Key Stage 3 foundations and GCSE applications. At Key Stage 3, the focus sits on calculating perimeters of polygons, compound shapes, and introducing algebraic perimeters where side lengths are given as expressions rather than numbers.
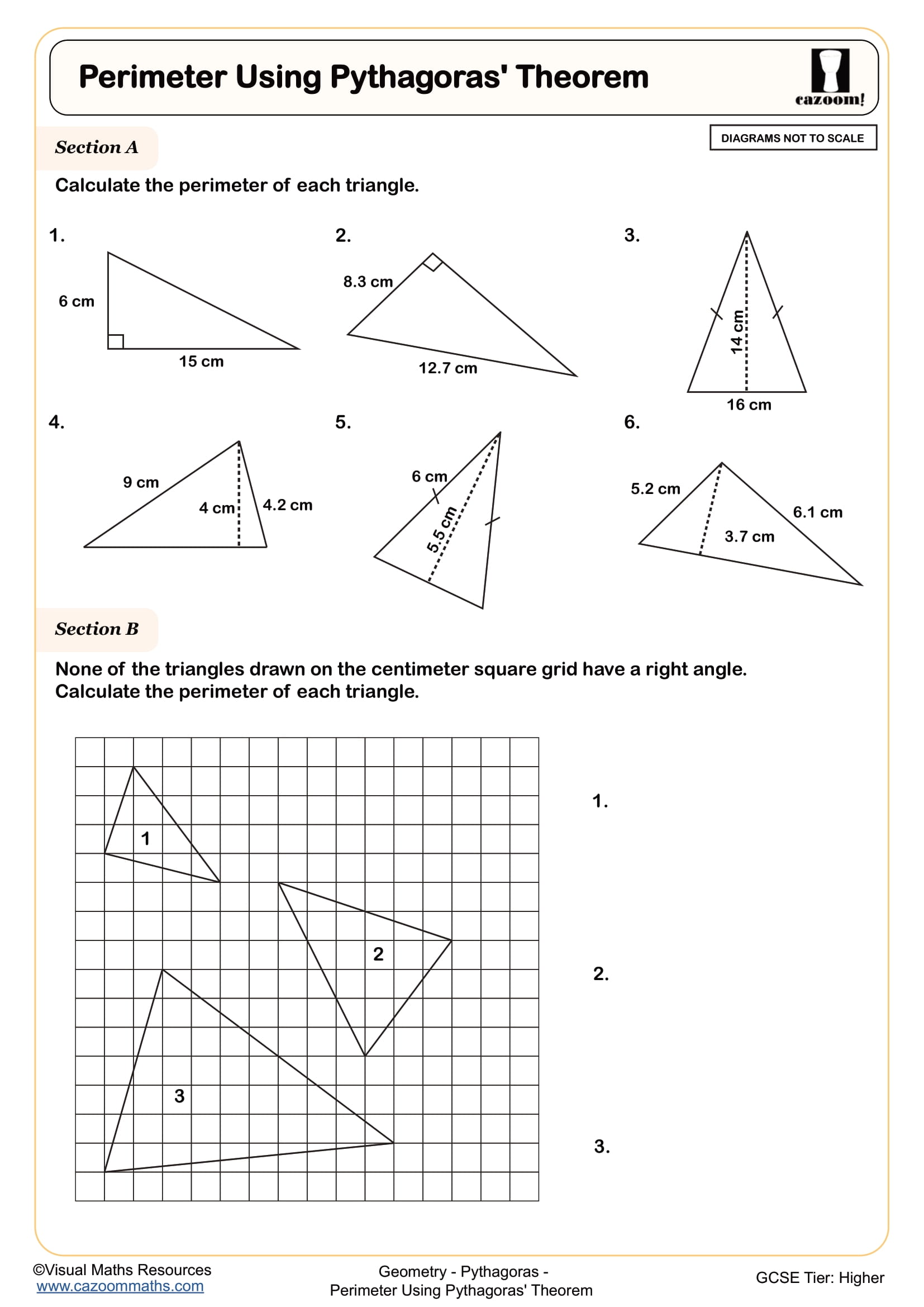
The difficulty increases as students progress from straightforward addition of given measurements in Year 7 to working backwards from a known perimeter to find missing dimensions in Year 8. By Years 10 and 11, perimeter questions often appear within problem-solving contexts at GCSE, requiring students to form and solve equations or apply perimeter alongside area and volume in multi-step questions.
How do you calculate perimeter with algebraic expressions?
Algebraic perimeters involve writing expressions for side lengths using letters, then forming an expression for the total perimeter by adding all sides and simplifying through collecting like terms. Students must recognise that a rectangle with sides of length 2x and x + 3 has a perimeter of 2(2x) + 2(x + 3), which simplifies to 6x + 6 by expanding brackets and combining x terms.
This skill connects directly to engineering and construction, where professionals calculate fencing requirements or material quantities when exact dimensions aren't yet determined. Architects use algebraic perimeter when designing scalable floor plans, whilst landscape gardeners estimate border edging costs for variable-sized plots, demonstrating how algebra models real situations before specific measurements are finalised.
How do these perimeter worksheets support learning?
The worksheets build confidence through structured practice that begins with straightforward shapes before progressing to problems requiring multiple steps or algebraic reasoning. Answer sheets allow students to identify errors in their method immediately, particularly helpful when practising the collection of like terms in algebraic perimeter questions where mistakes compound quickly.
Many teachers use these resources for targeted intervention with students who consistently confuse perimeter and area, setting focused practice on perimeter only before reintroducing both concepts together. The worksheets work effectively as homework after introducing composite shapes, as starters to recap measurement skills before area lessons, or during revision sessions where students need to rebuild accuracy with fundamental geometry calculations ahead of GCSE assessments.