Rotation Worksheets
What is rotation in maths?
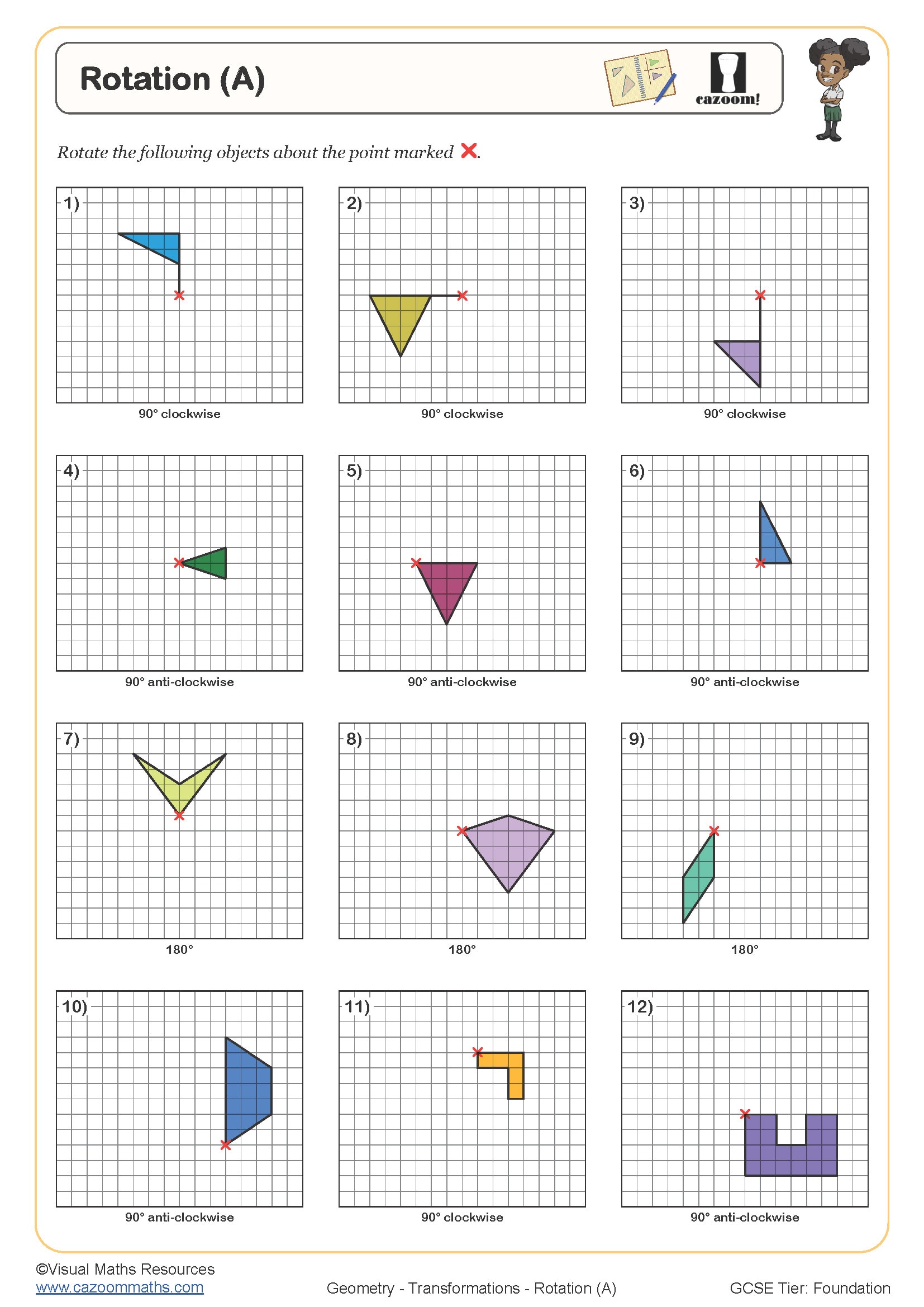
Rotation is a transformation that turns a shape around a fixed point called the centre of rotation. The shape moves through a specified angle (typically 90°, 180° or 270°) in either a clockwise or anticlockwise direction. At Key Stage 3, students begin by rotating simple shapes on squared paper, whilst GCSE expects them to describe rotations fully using three pieces of information: the angle, direction, and centre of rotation.
Students lose marks in exams when they forget to specify all three properties of a rotation. A common error occurs when rotating around centres other than the origin, where students count incorrectly from the centre point rather than using tracing paper or systematic coordinate tracking. Many teachers find that demonstrating rotations physically with cut-out shapes helps students visualise the movement before tackling coordinate problems.
Which year groups study rotation?
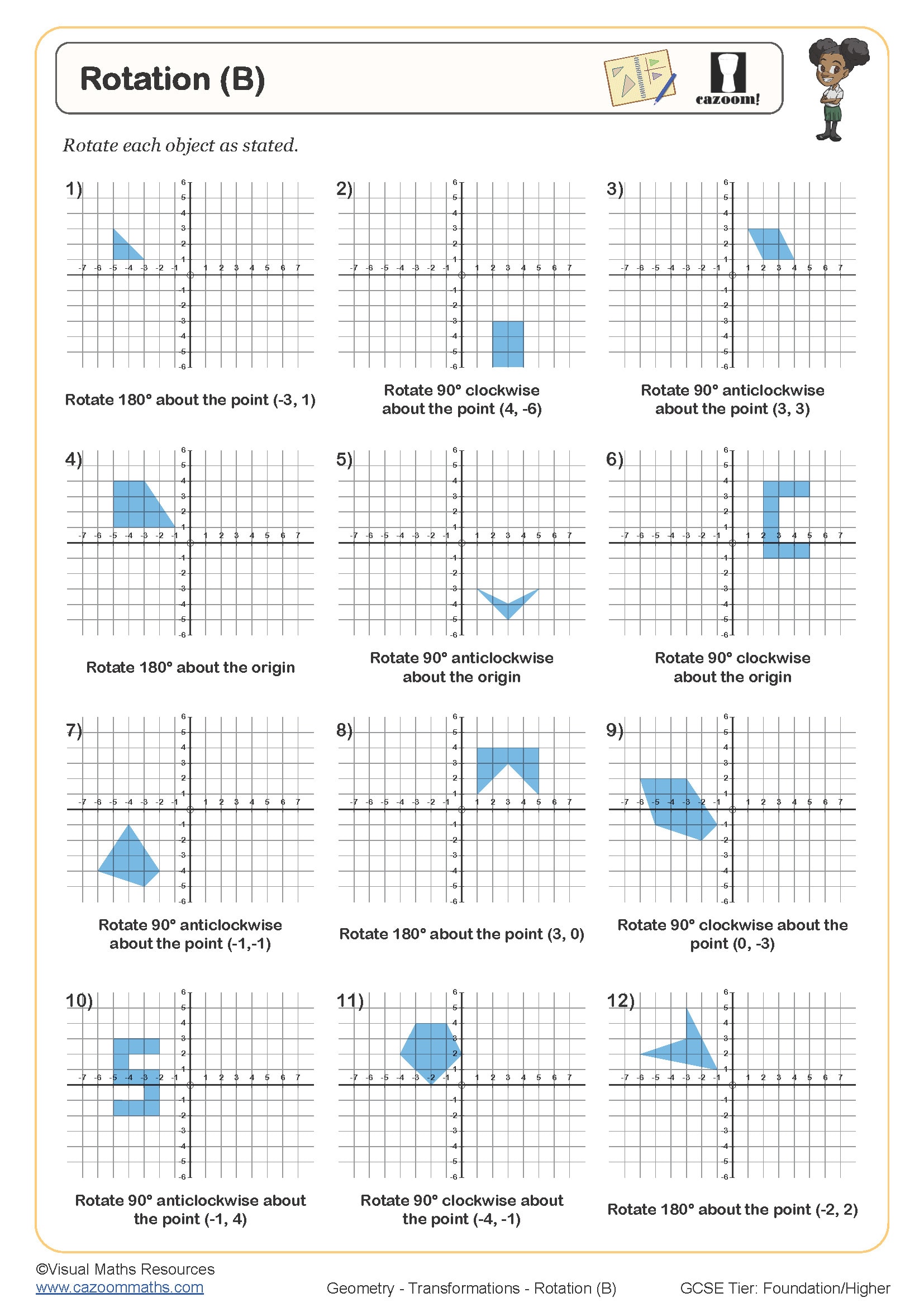
These worksheets cover rotation from Year 7 through to Year 11, spanning both Key Stage 3 and Key Stage 4. Rotation first appears in the National Curriculum during Key Stage 3, where students learn to rotate shapes on grids and describe the transformation using mathematical language. By GCSE, students must handle rotations in all four quadrants, work with fractional centres of rotation, and combine rotations with other transformations.
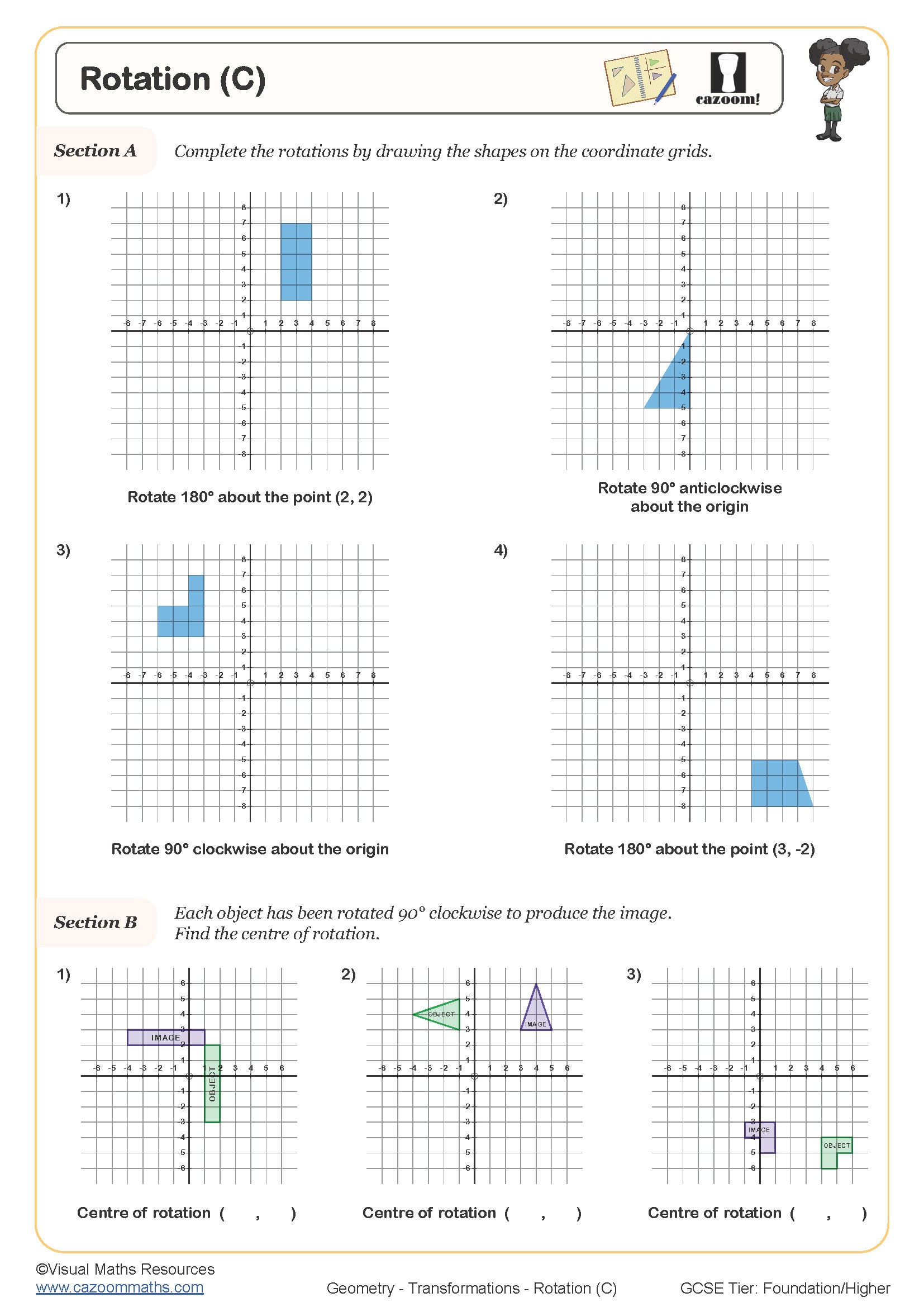
The progression builds systematically across year groups. Year 7 and 8 students typically rotate shapes 90° and 180° around the origin or simple grid points. Year 9 introduces 270° rotations and centres away from the origin. At Key Stage 4, rotation questions become more algebraic, requiring students to identify the centre and angle of rotation by comparing object and image positions, or to solve problems involving multiple transformations in sequence.
How does rotation differ from reflection?
Rotation turns a shape around a point, maintaining the shape's orientation relative to its centre, whilst reflection flips a shape across a mirror line to create a reversed image. Although these worksheets focus on rotation, understanding reflective symmetry helps students recognise that rotations preserve the 'handedness' of shapes whereas reflections reverse it. Teachers often notice confusion between 180° rotations and reflections, as both can position a shape 'upside down', but a 180° rotation maintains left-right orientation whilst a horizontal reflection reverses it.
This distinction matters in engineering and design contexts. Computer graphics and animation rely heavily on rotation matrices to turn objects smoothly in 3D space without distorting them. Similarly, architects use rotational transformations when designing structures with rotational symmetry, such as wind turbines or cooling towers, where identical components must be positioned at precise angles around a central axis for structural balance and aesthetic appeal.
How do these worksheets help students practise rotation?
The worksheets scaffold rotation skills through carefully sequenced questions that begin with rotations on squared grids before progressing to coordinate geometry problems. Questions include visual prompts and centres of rotation marked clearly in early exercises, gradually removing support as students build confidence. The answer sheets show worked solutions with rotated shapes drawn accurately, allowing students to self-check their work and identify where errors occurred in their counting or directional understanding.
These resources work well for differentiated classroom teaching, where students can access the year group matching their current understanding rather than their chronological age. Many teachers use them during intervention sessions to rebuild foundational transformation skills before tackling combined transformation problems. The worksheets also suit homework assignments where answer sheets enable parents to support their children, or for revision booklets where students need focused practice on rotation ahead of assessments without mixing in other transformation types.