Fraction, Decimal and Percentage Equivalence and Converting Worksheets
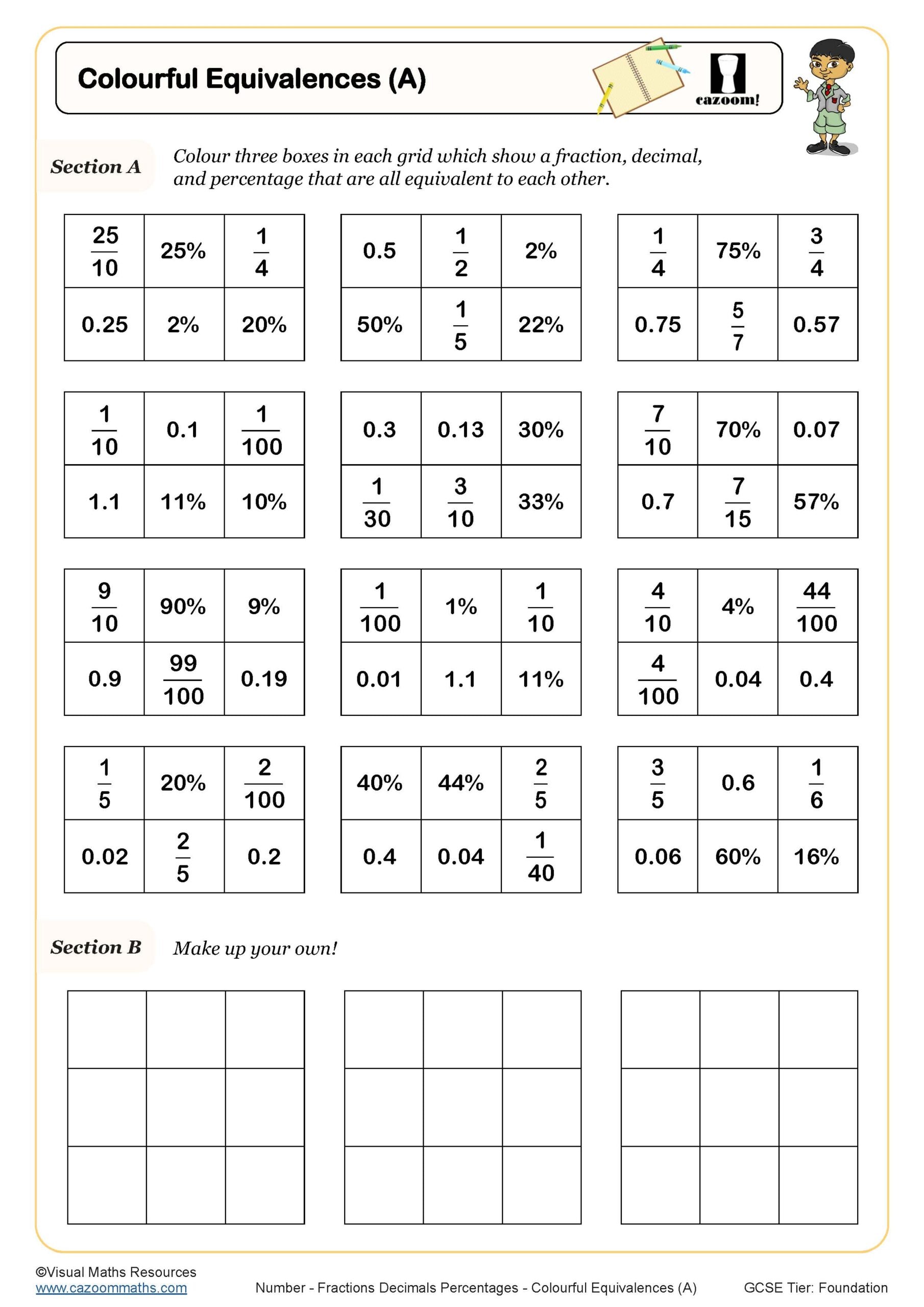
Colourful Equivalences (A)
Year groups: 7, 8
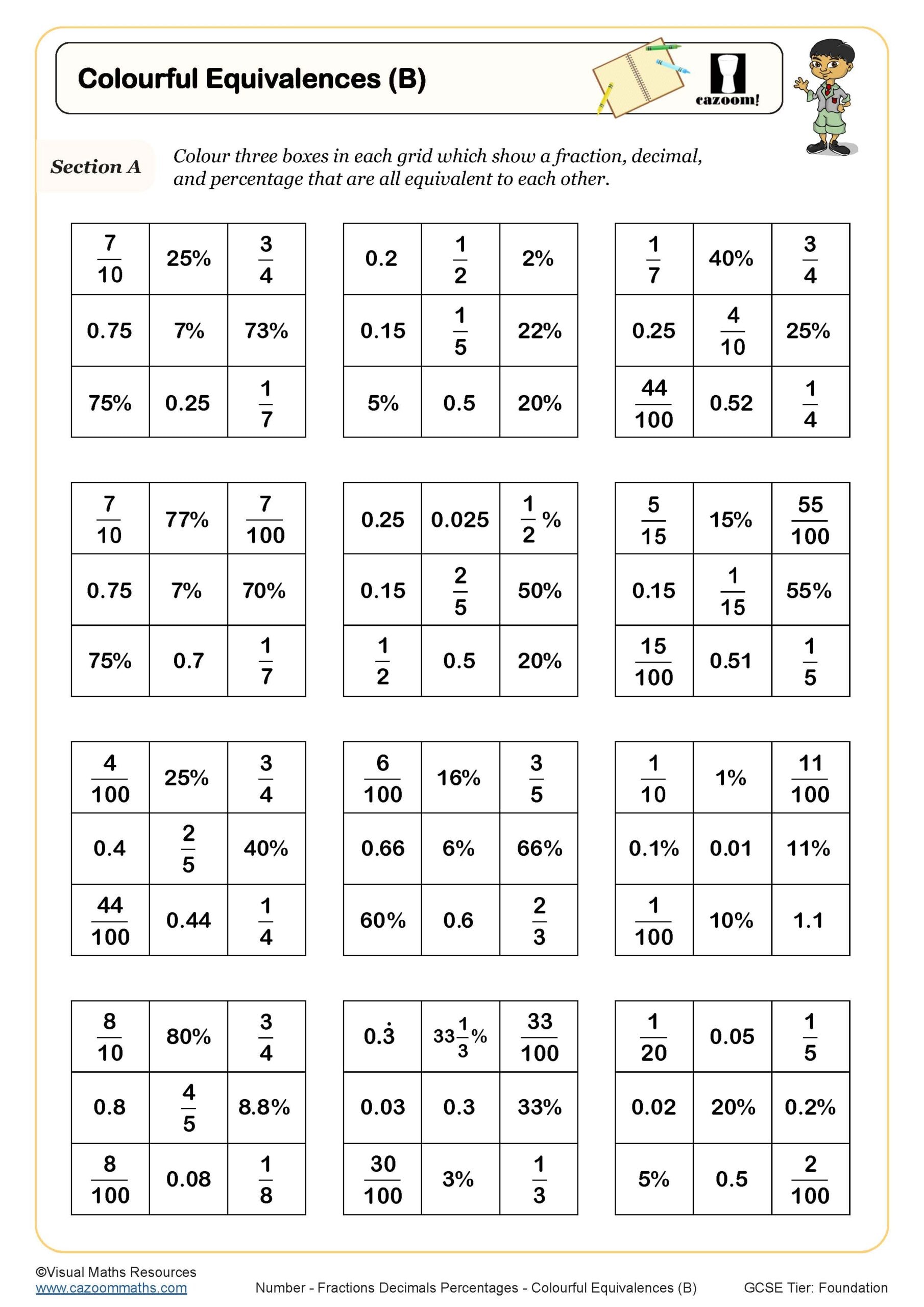
Colourful Equivalences (B)
Year groups: 7, 8, 9
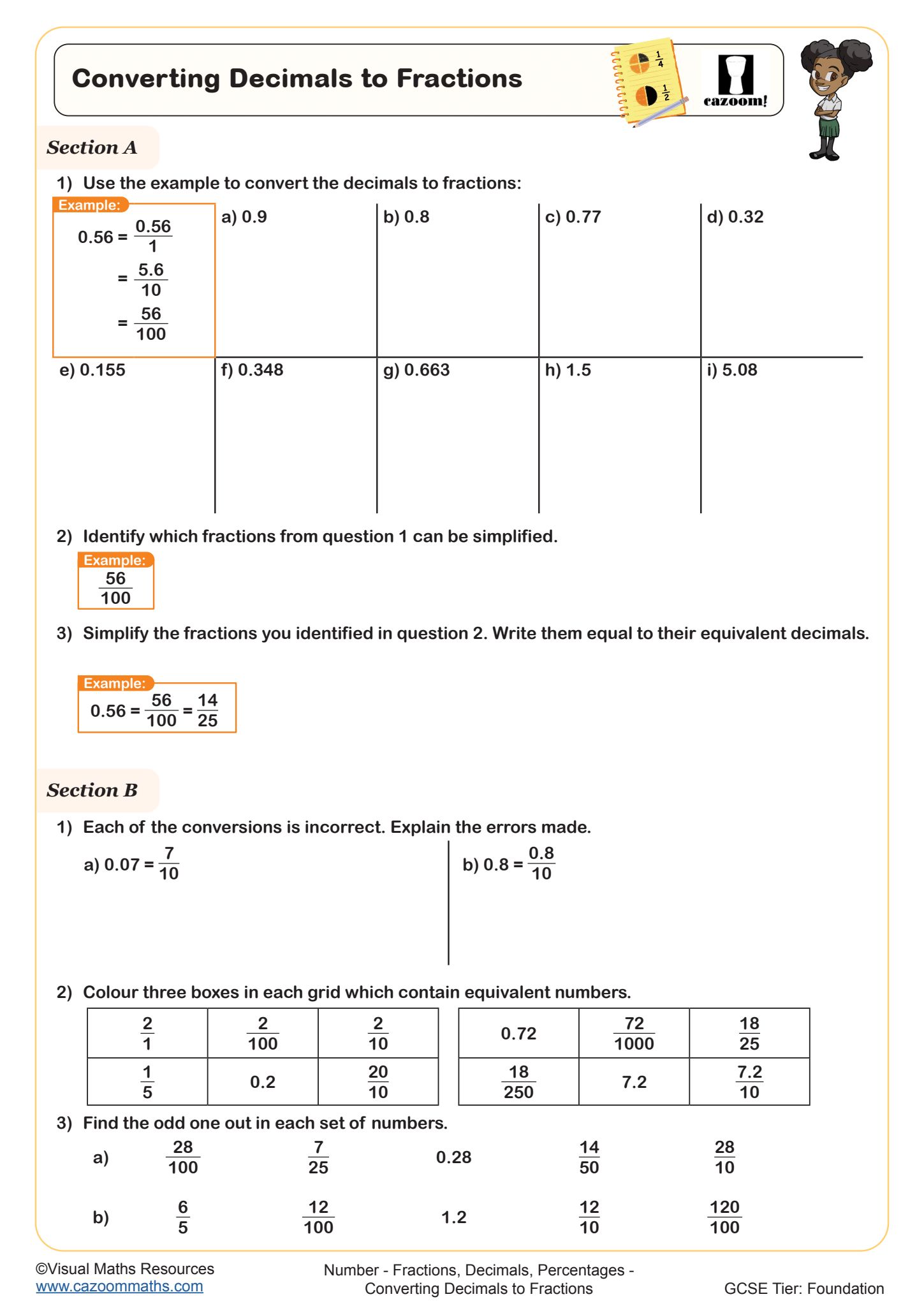
Converting Decimals to Fractions
Year groups: 7, 8
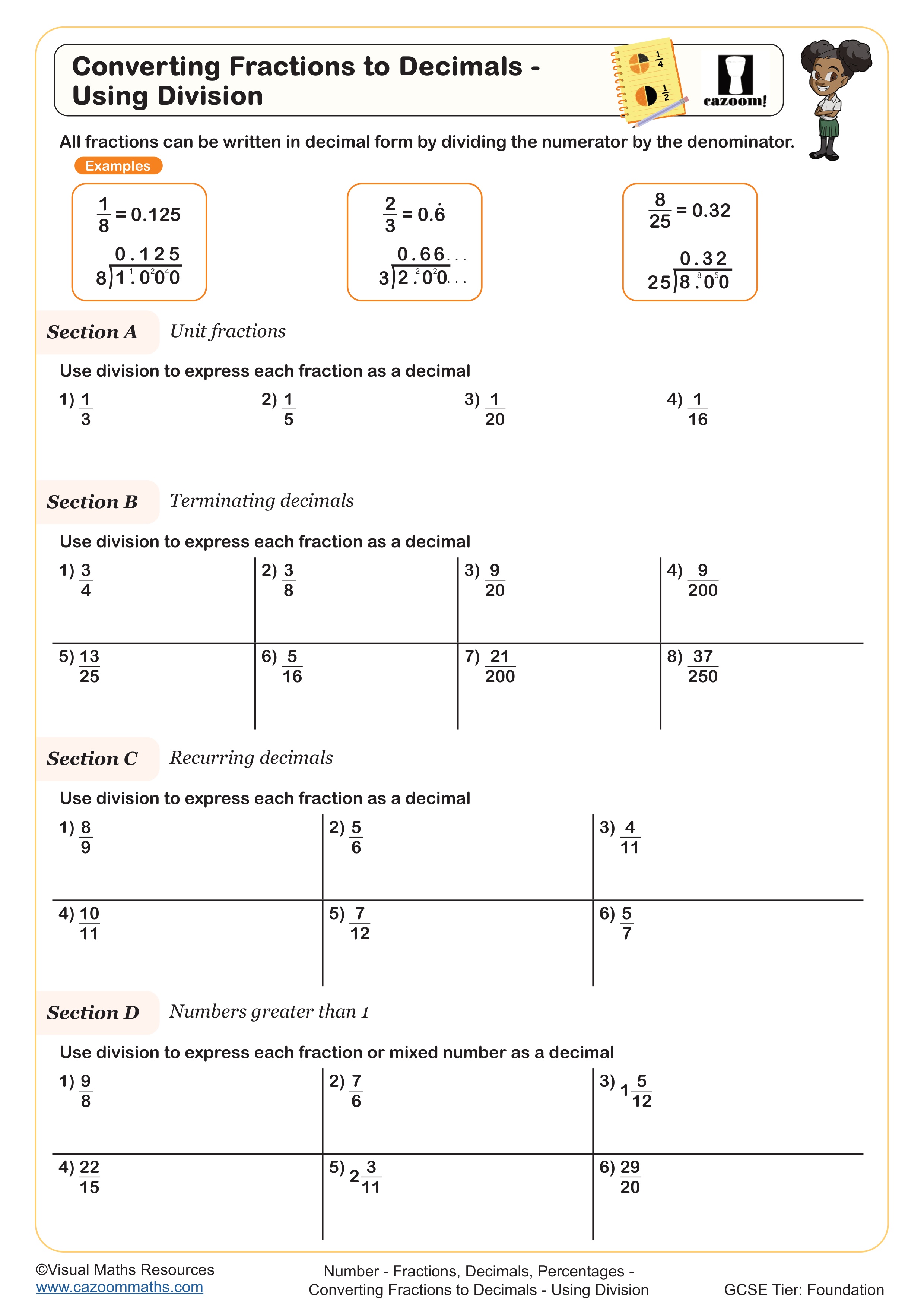
Converting Fractions to Decimals - Using Division
Year groups: 7, 8
Converting Fractions to Decimals - Using Equivalent Fractions
Year groups: 7, 8
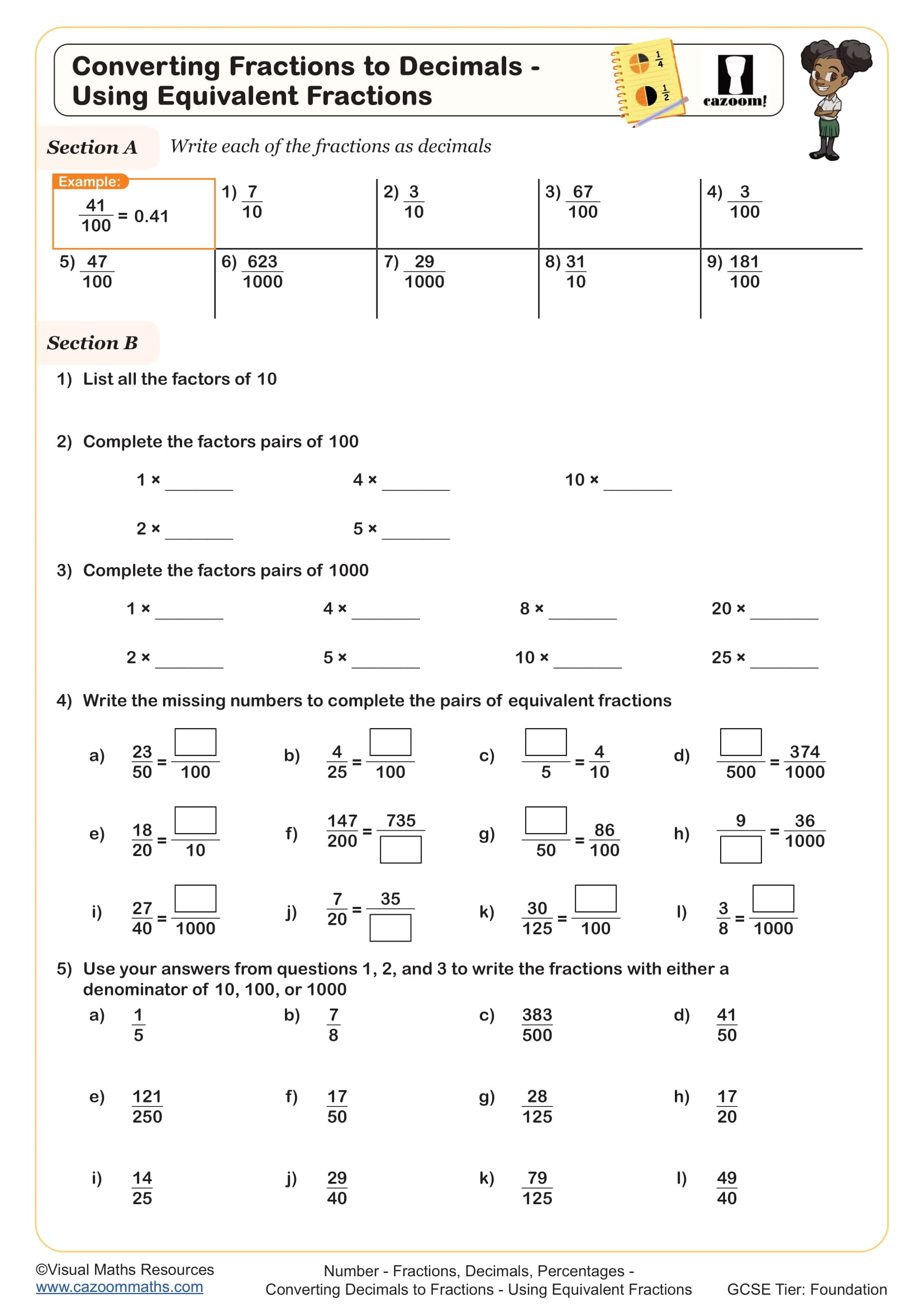
Decimal and Percentage Equivalence
Year groups: 7, 8
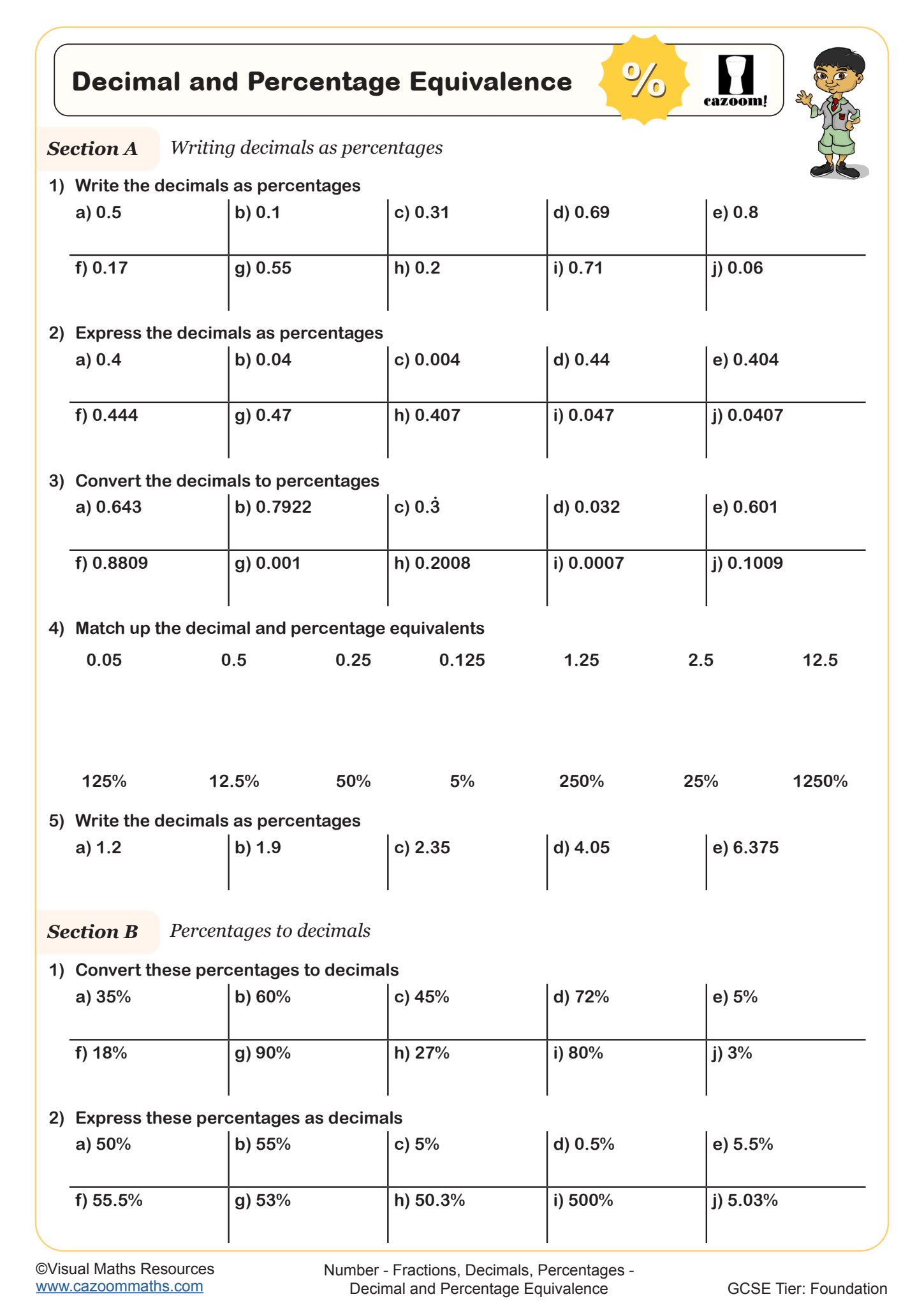
Equivalence Search (A)
Year groups: 7, 8
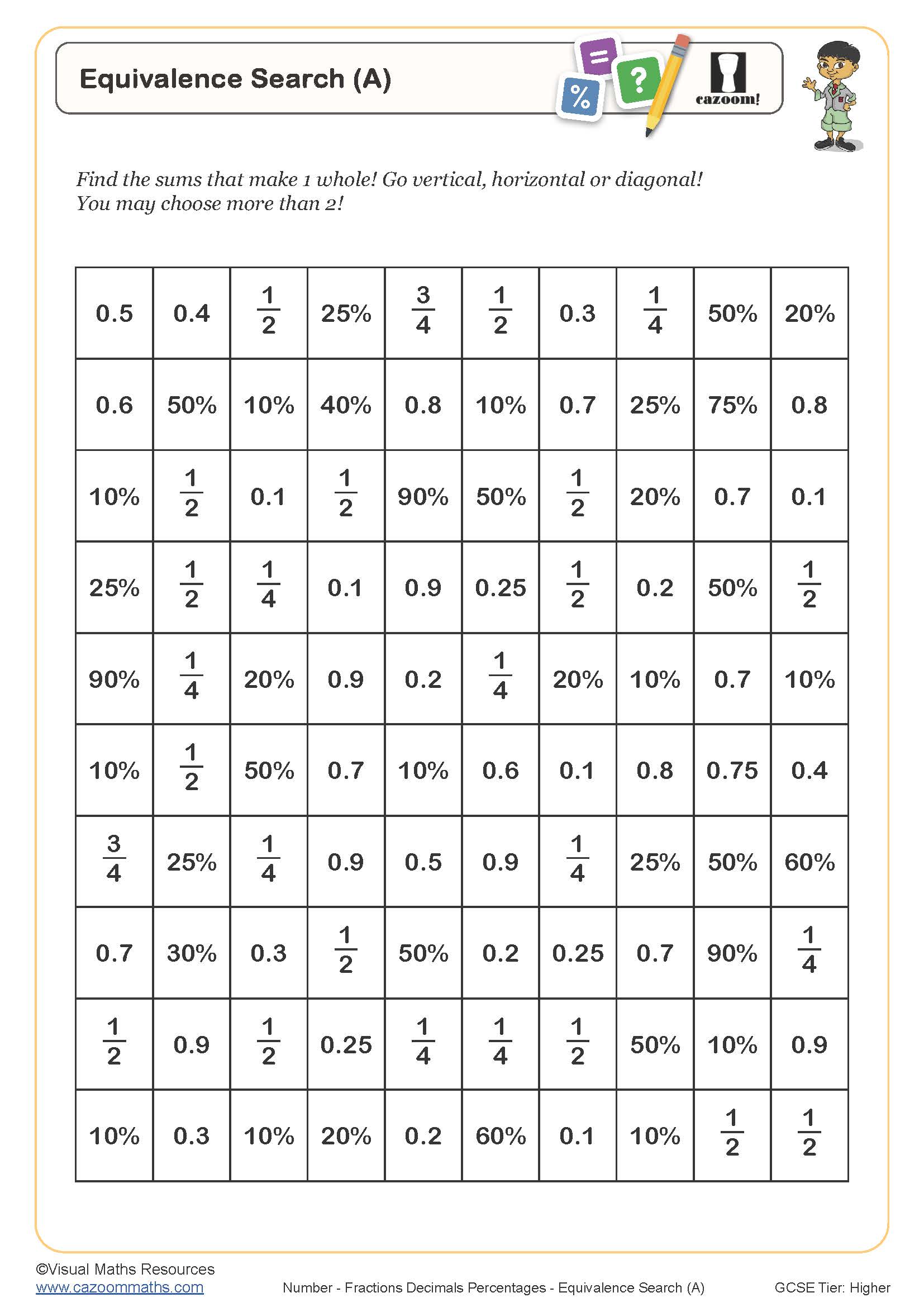
Equivalence Search (B)
Year groups: 7, 8, 9
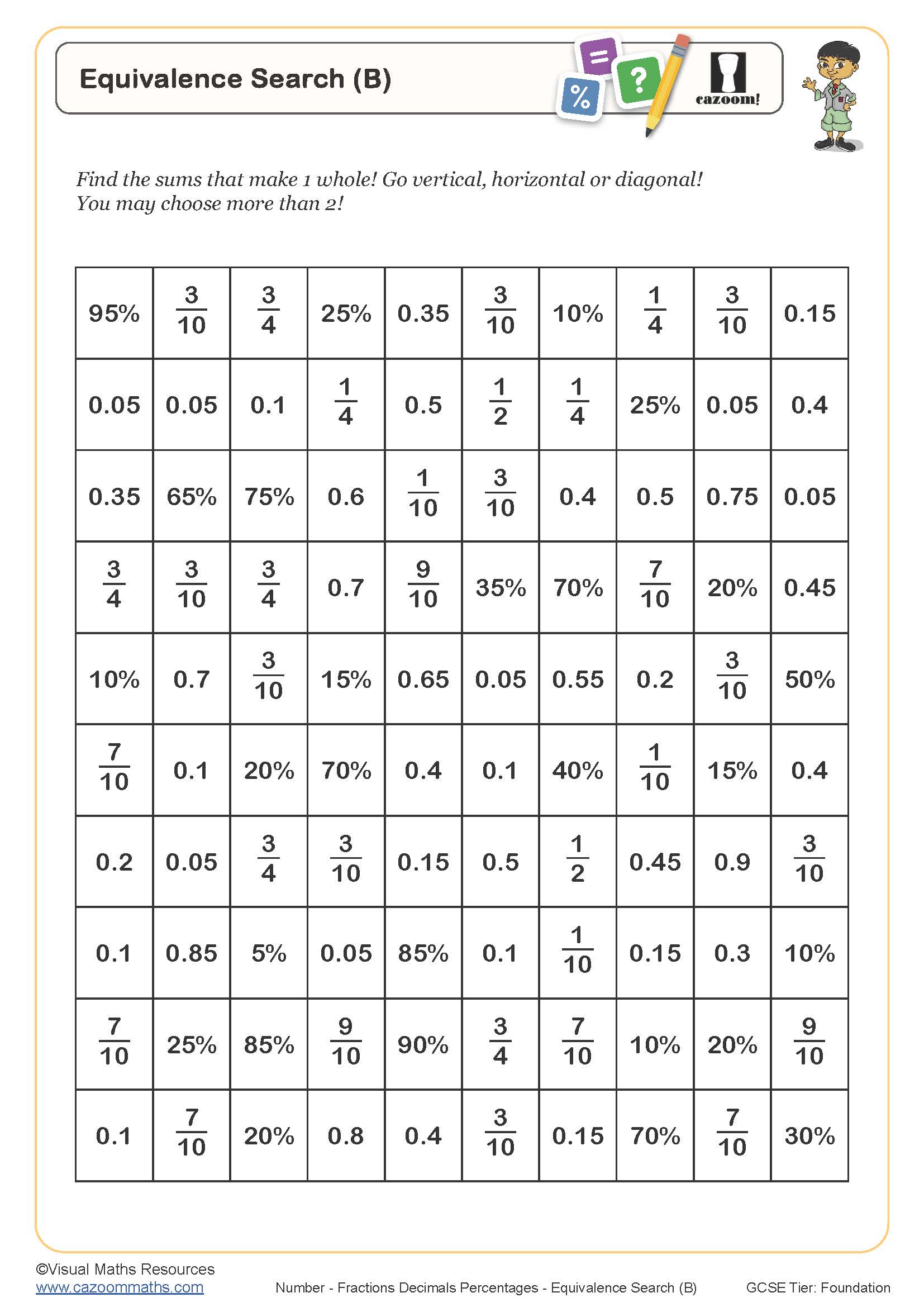
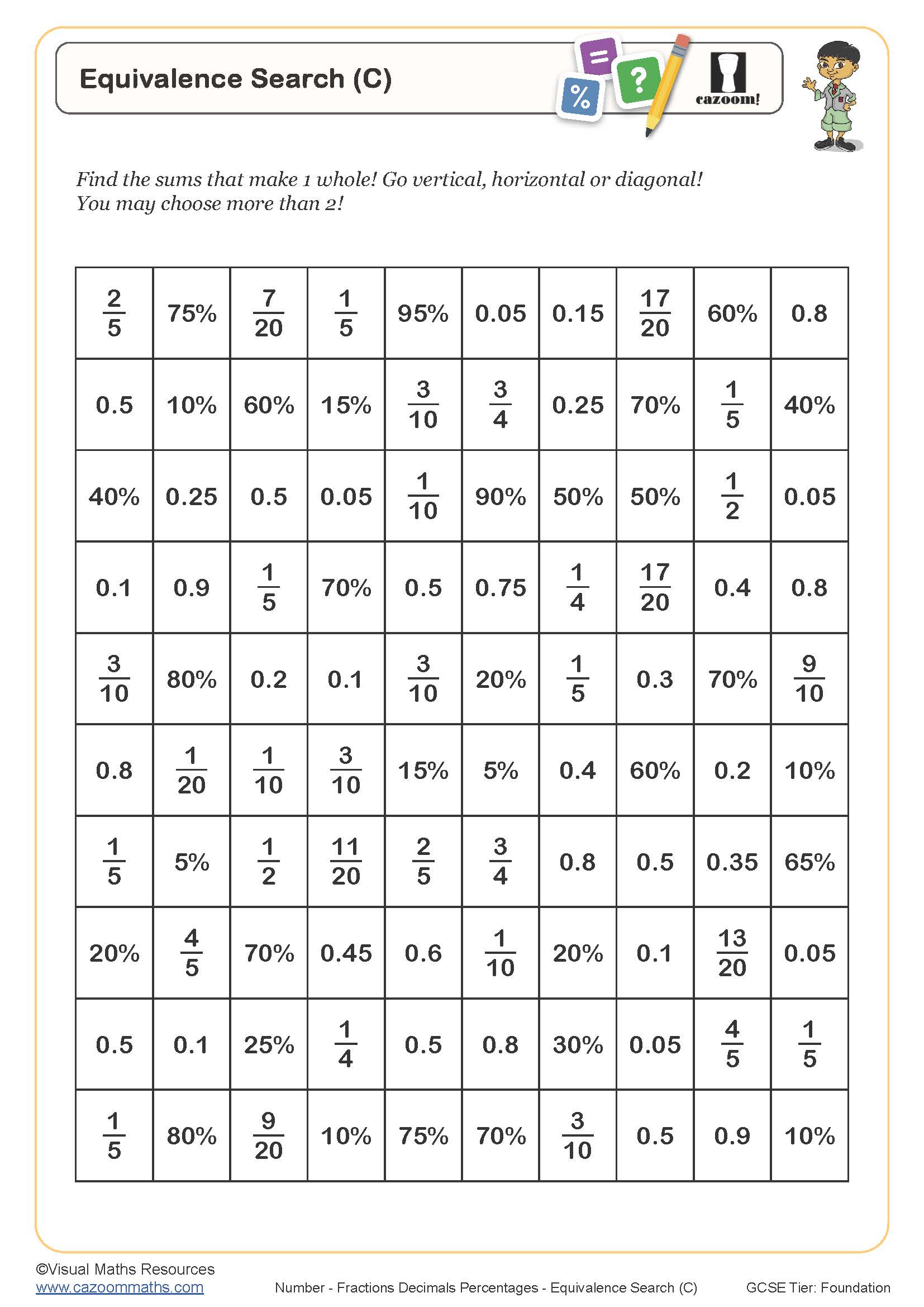
Equivalence Search (C)
Year groups: 7, 8, 9
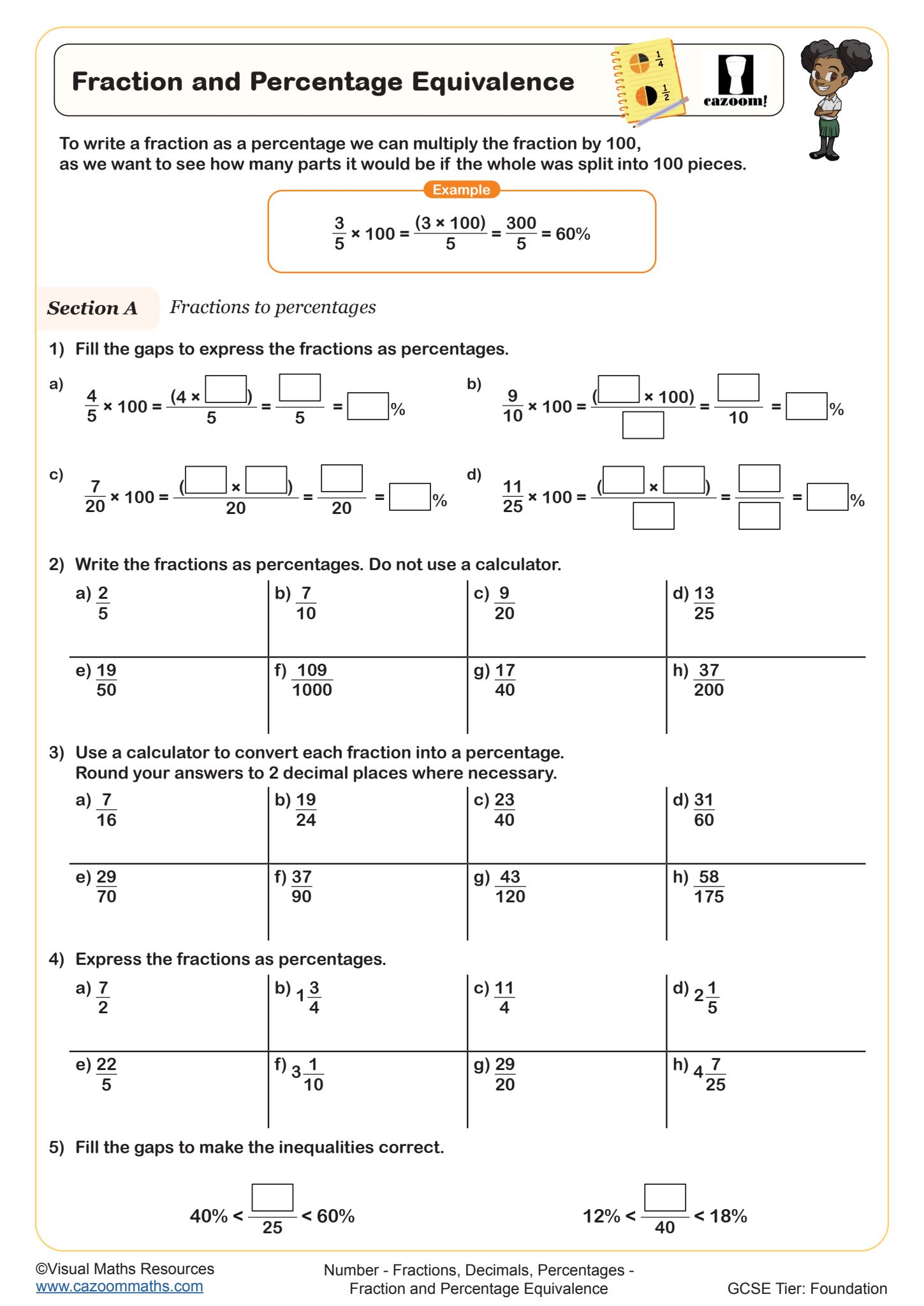
Fraction and Percentage Equivalence
Year groups: 7, 8
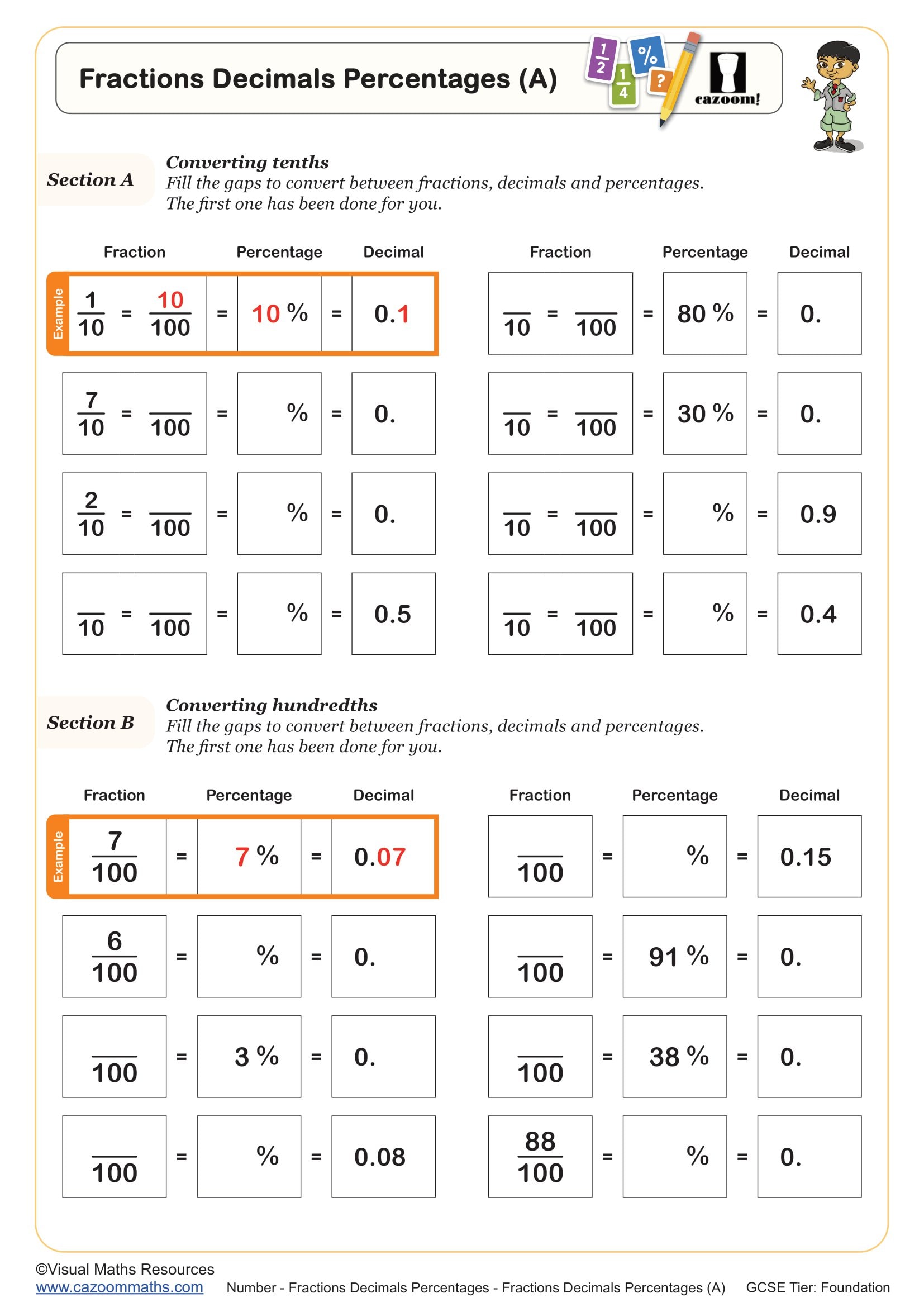
Fractions Decimals Percentages (A)
Year groups: 7, 8
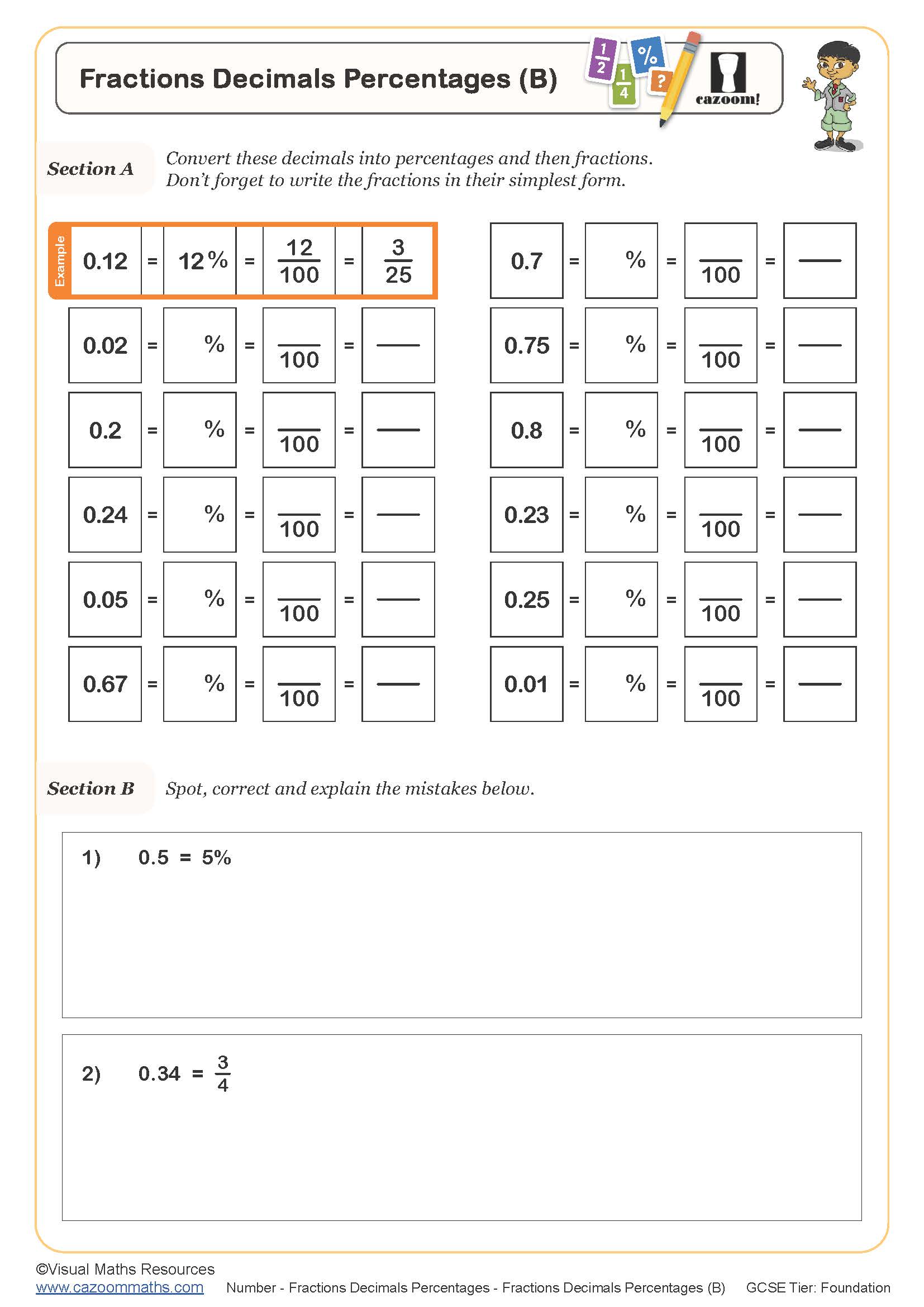
Fractions Decimals Percentages (B)
Year groups: 7, 8, 9
Quick Conversions (A)
Year groups: 7, 8
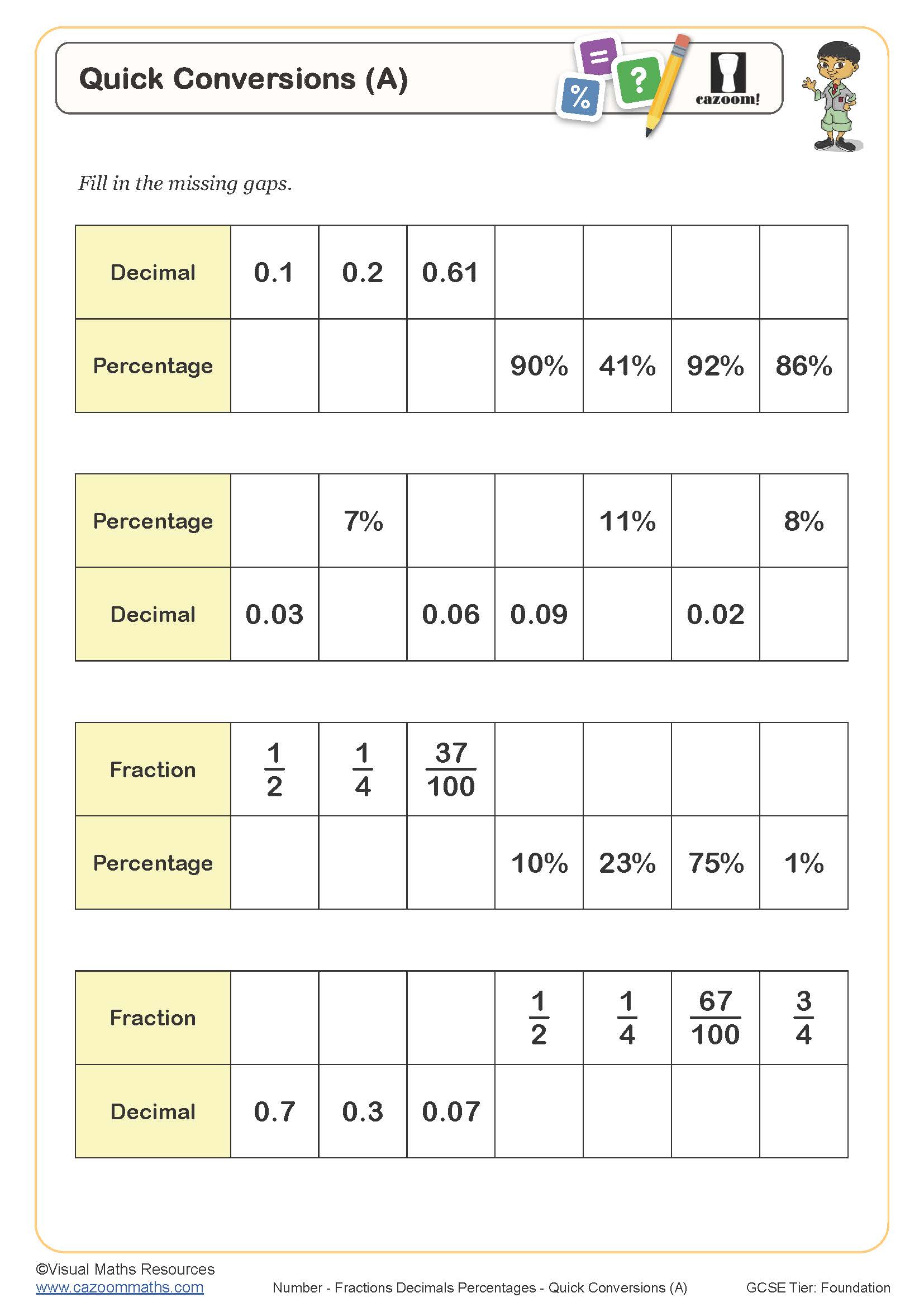
Fractions Decimals Percentages (C)
Year groups: 8, 9
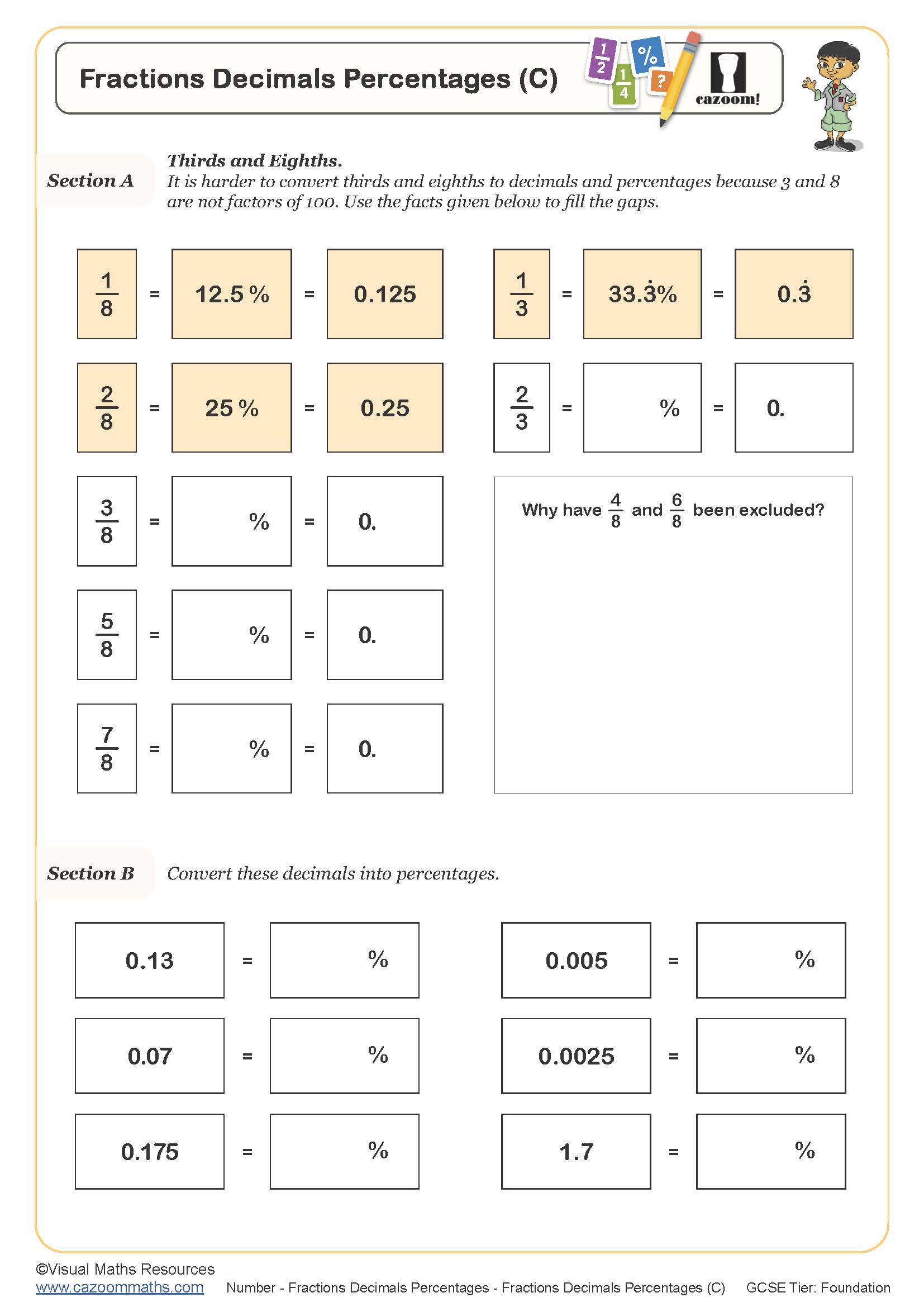
Quick Conversions (B)
Year groups: 8, 9
Writing Rational Numbers as Decimals
Year groups: 9, 10

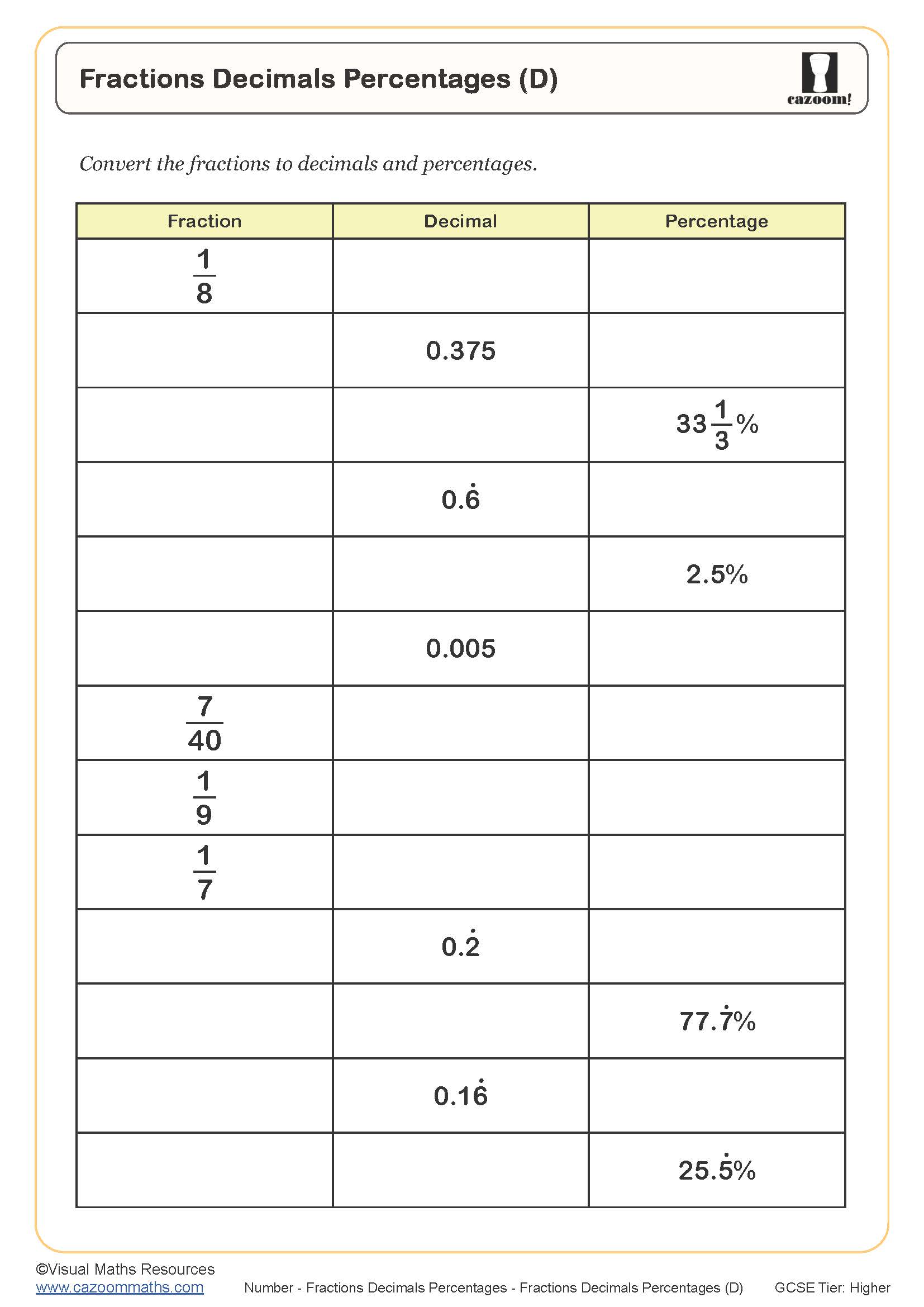
Fractions Decimals Percentages (D)
Year groups: 10, 11
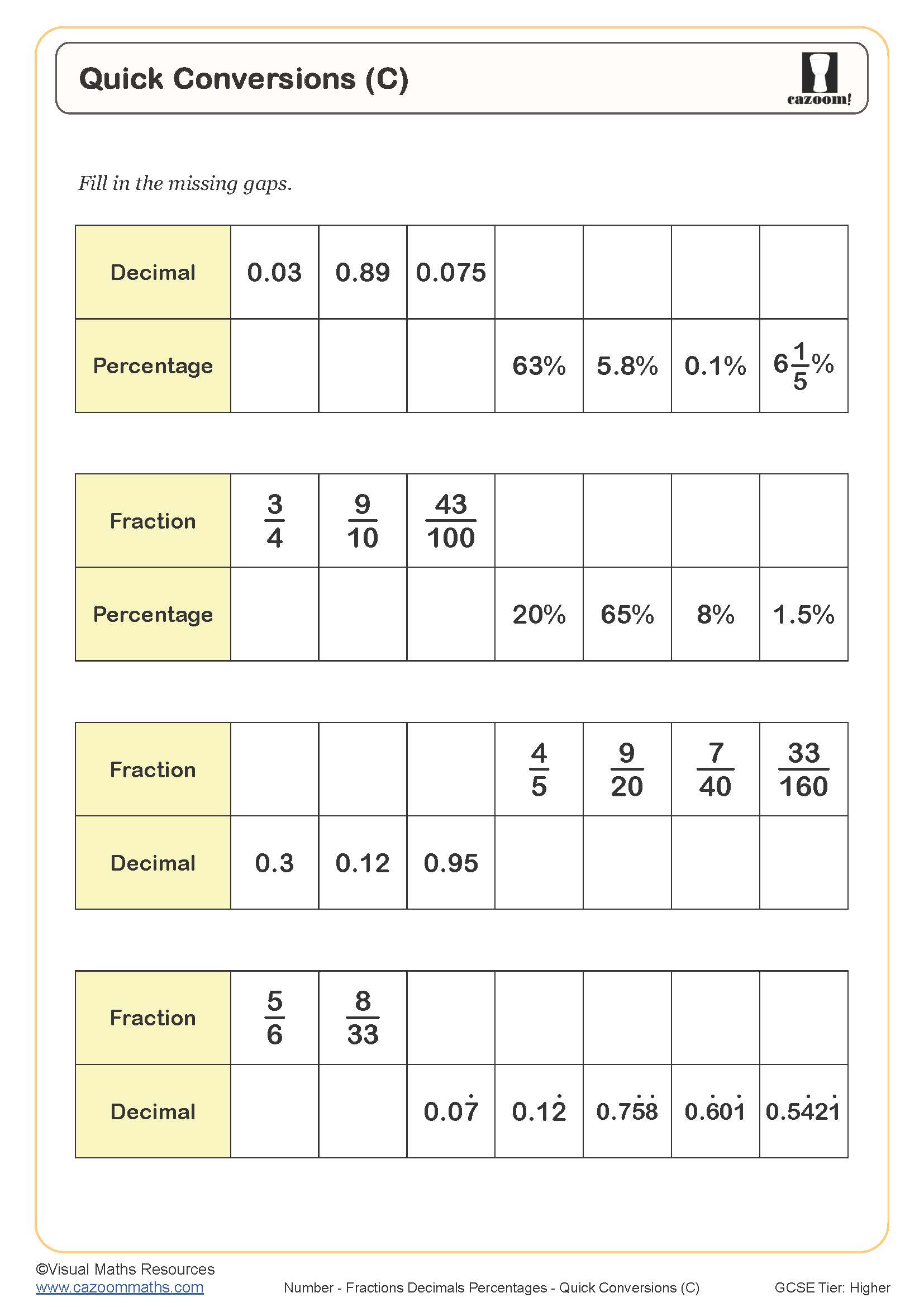
Quick Conversions (C)
Year groups: 10, 11
What are the easiest fractions, decimals and percentages to convert?
The most straightforward conversions involve halves, quarters, fifths and tenths because these fractions have simple decimal and percentage equivalents: ½ = 0.5 = 50%, ¼ = 0.25 = 25%, and ⅕ = 0.2 = 20%. Students who memorise these common equivalents can tackle conversion questions more efficiently and spot them in problem-solving contexts. The National Curriculum expects Year 6 students to begin recognising these relationships, with increasing fluency developed throughout Key Stage 3.
A common error occurs when students try to calculate every conversion from scratch rather than using these known values as building blocks. For instance, many students don't recognise that finding ¾ becomes straightforward once they know ¼ = 0.25, or that 15% can be found by halving 10% and adding it to the original. Exam mark schemes reward efficient methods, and students who rely solely on calculator algorithms often lose time under exam conditions.
Which year groups study fraction, decimal and percentage conversions?
These worksheets cover Years 7 through 11, reflecting how conversion skills develop from basic equivalence in Key Stage 3 to GCSE-level problems involving recurring decimals, complex fractions and reverse percentage calculations. Year 7 students typically focus on converting simple fractions to decimals and percentages using known equivalents, whilst Year 8 introduces division methods for less familiar fractions and begins work with decimal to fraction conversions.
By Year 9, students work with all conversion types including harder fractions like sevenths and ninths that produce recurring decimals. Years 10 and 11 consolidate these skills within GCSE problem-solving contexts, where students must choose the most efficient form for calculations, convert values embedded in worded questions, and work with percentage multipliers that require fluent conversion between all three representations. The progression builds from recognition to calculation to application across increasingly challenging scenarios.
How do you convert recurring decimals to fractions?
Converting recurring decimals to fractions requires an algebraic method where students set the recurring decimal equal to x, multiply by an appropriate power of 10 to shift the decimal point, then subtract the original equation to eliminate the recurring part. For example, to convert 0.7̇ to a fraction, let x = 0.777..., then 10x = 7.777..., and subtracting gives 9x = 7, so x = 7/9. This technique appears in the higher GCSE tier and many students find it counterintuitive because it uses algebra to solve a number problem.
This skill has practical applications in engineering and computer science, where recurring decimals appear in calculations involving ratios and proportions. Engineers working with metric conversions or gear ratios often encounter recurring decimal values that need expressing as exact fractions for precision manufacturing. Understanding that 0.3̇ = 1/3 exactly, rather than approximately 0.333, matters when tolerances are measured in thousandths of a millimetre, connecting this abstract skill to real-world accuracy requirements in STEM fields.
How do these worksheets help students master conversions?
The worksheets build conversion skills through carefully sequenced questions that start with recognition of common equivalents before progressing to calculations requiring division or the fraction-to-percentage algorithm. Each worksheet typically includes visual representations alongside numerical practise, helping students see why 0.75 and 75% represent the same portion as ¾. The answer sheets allow students to identify exactly where their method breaks down, particularly useful for spotting whether errors occur in the division process or in understanding place value when writing decimals.
Teachers use these worksheets for targeted intervention when assessment data reveals gaps in conversion fluency, particularly before teaching topics like ratio or percentage change that assume secure conversion skills. They work well as homework to reinforce classroom teaching or as starter activities to maintain fluency. Many teachers set paired work where one student converts fractions to decimals whilst another converts the same values to percentages, then partners check their answers represent equivalent values, building both accuracy and conceptual understanding of the relationships between all three forms.