Mean, Mode, Median and Range RESOURCE (FREE DOWNLOAD)
Mean, Mode, Median and Range RESOURCE DESCRIPTION
Mean, Median, Mode, and Range in Maths
What is Mean, Median, and Mode?
Mean, median, and mode are fundamental concepts in descriptive statistics. These measures help us summarise and interpret data, making them essential for analysing information effectively. This resource simplifies these concepts for Year 7, 8, and 9.
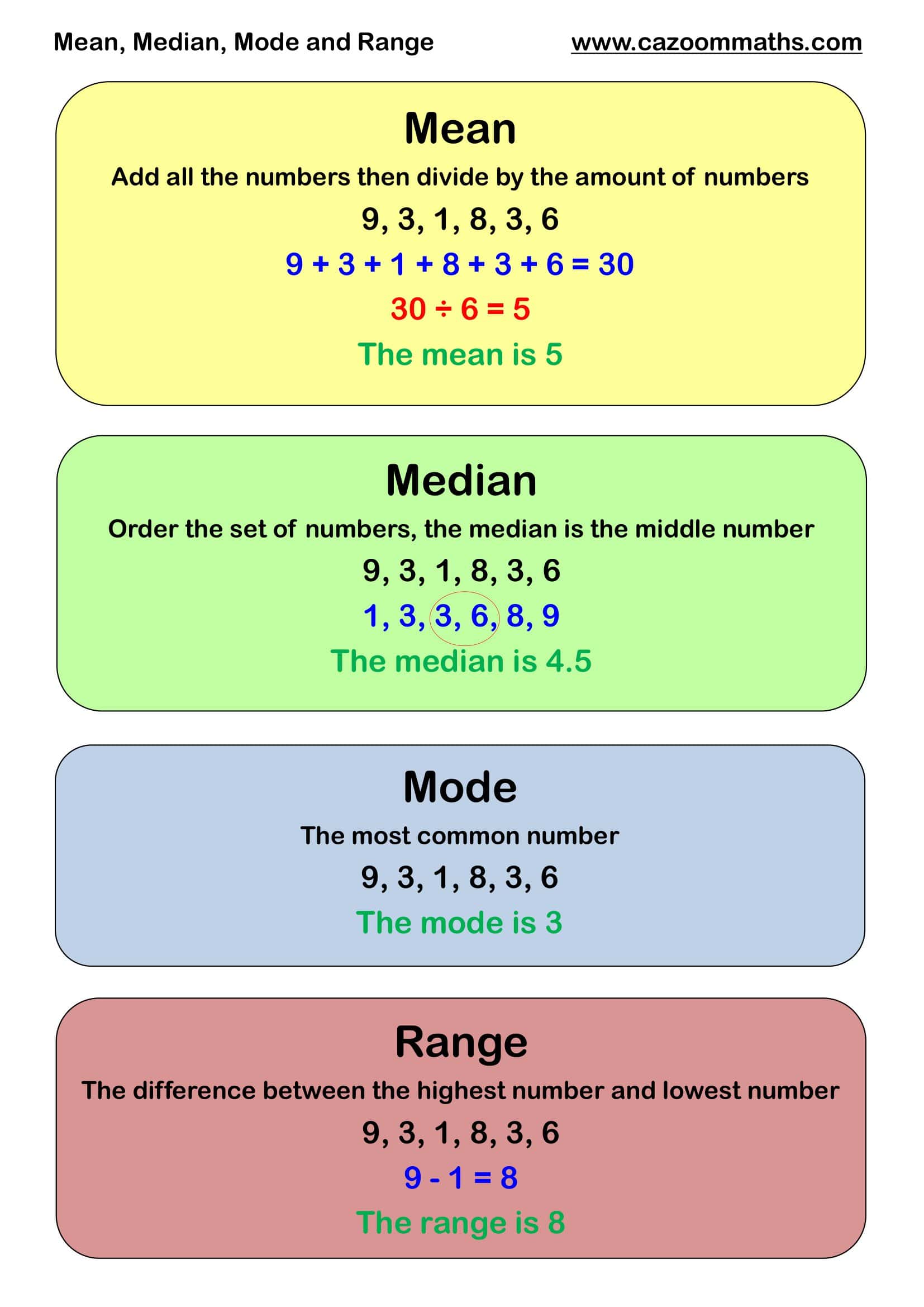
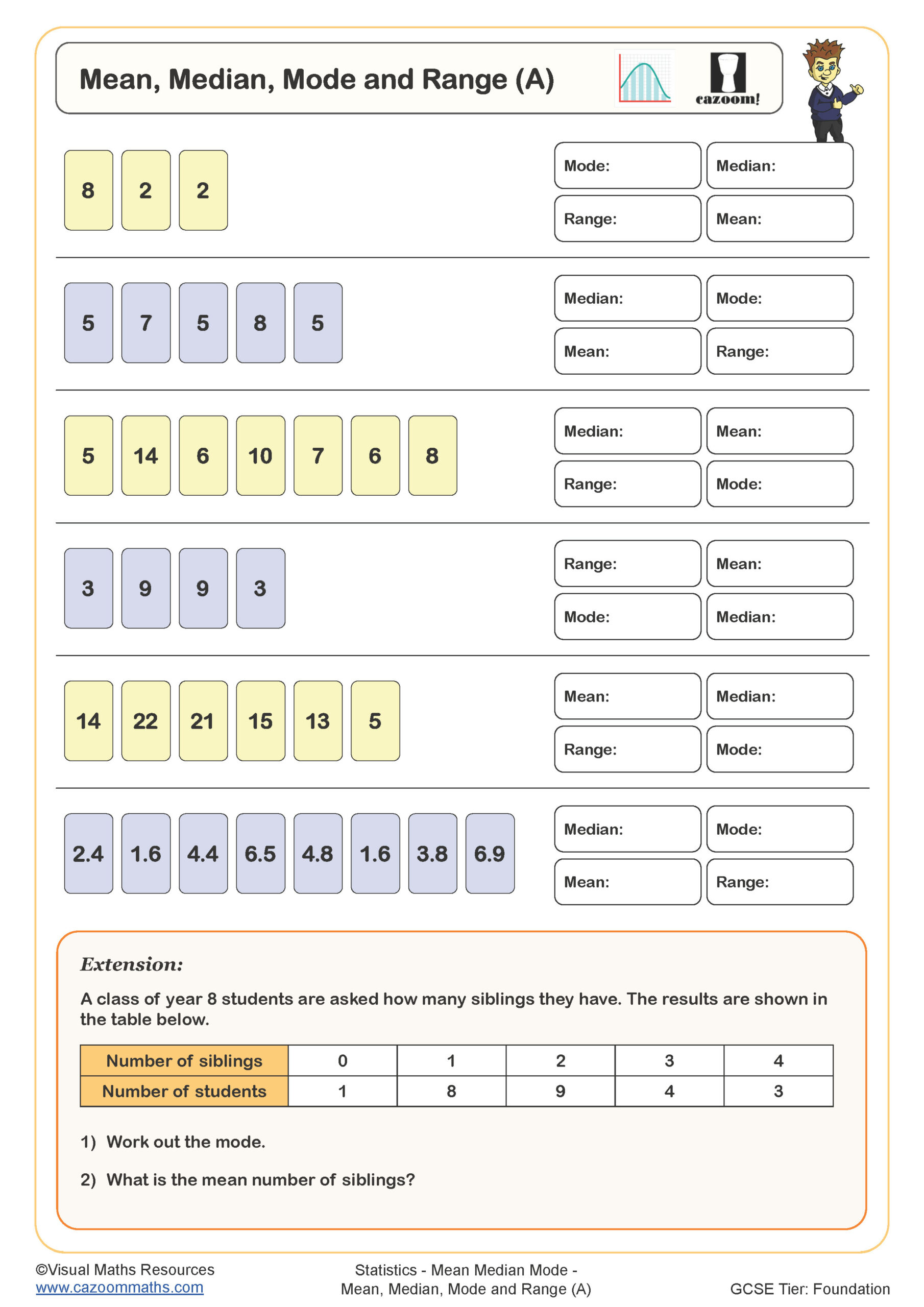
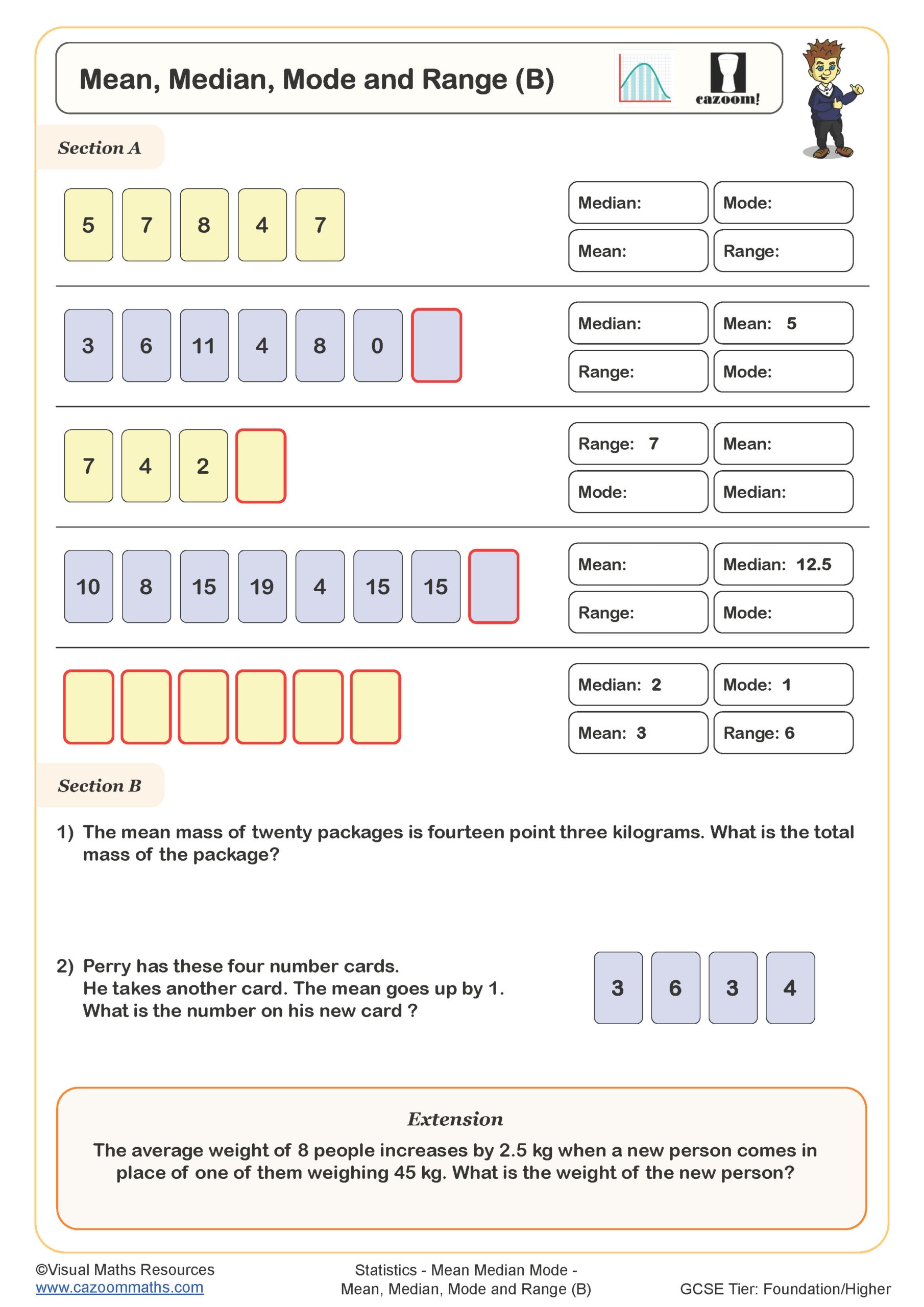
Understanding Mean in Maths
The mean is the average of a set of numbers. To calculate it, add all the numbers together and divide by the total count. For example:
Numbers: 3, 7, 5, 9, 6
Calculation: (3 + 7 + 5 + 9 + 6) / 5 = 30 / 5 = 6
The mean of this dataset is 6.
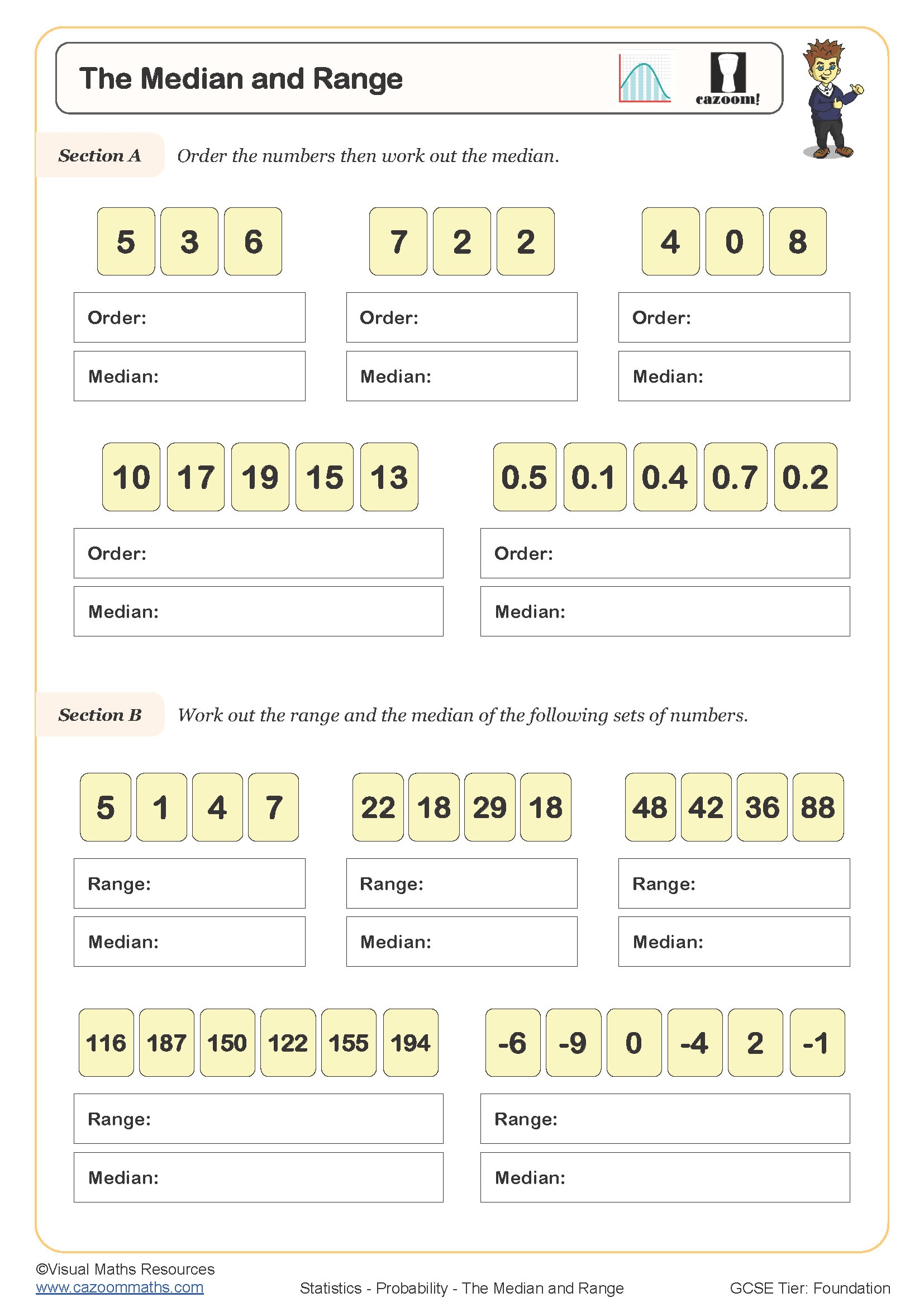
Exploring Median in Maths
The median represents the middle value in an ordered dataset. If the dataset has an odd number of values, the middle value is the median. For even numbers, it’s the average of the two middle values.
Example: For the dataset 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, the median is 7.
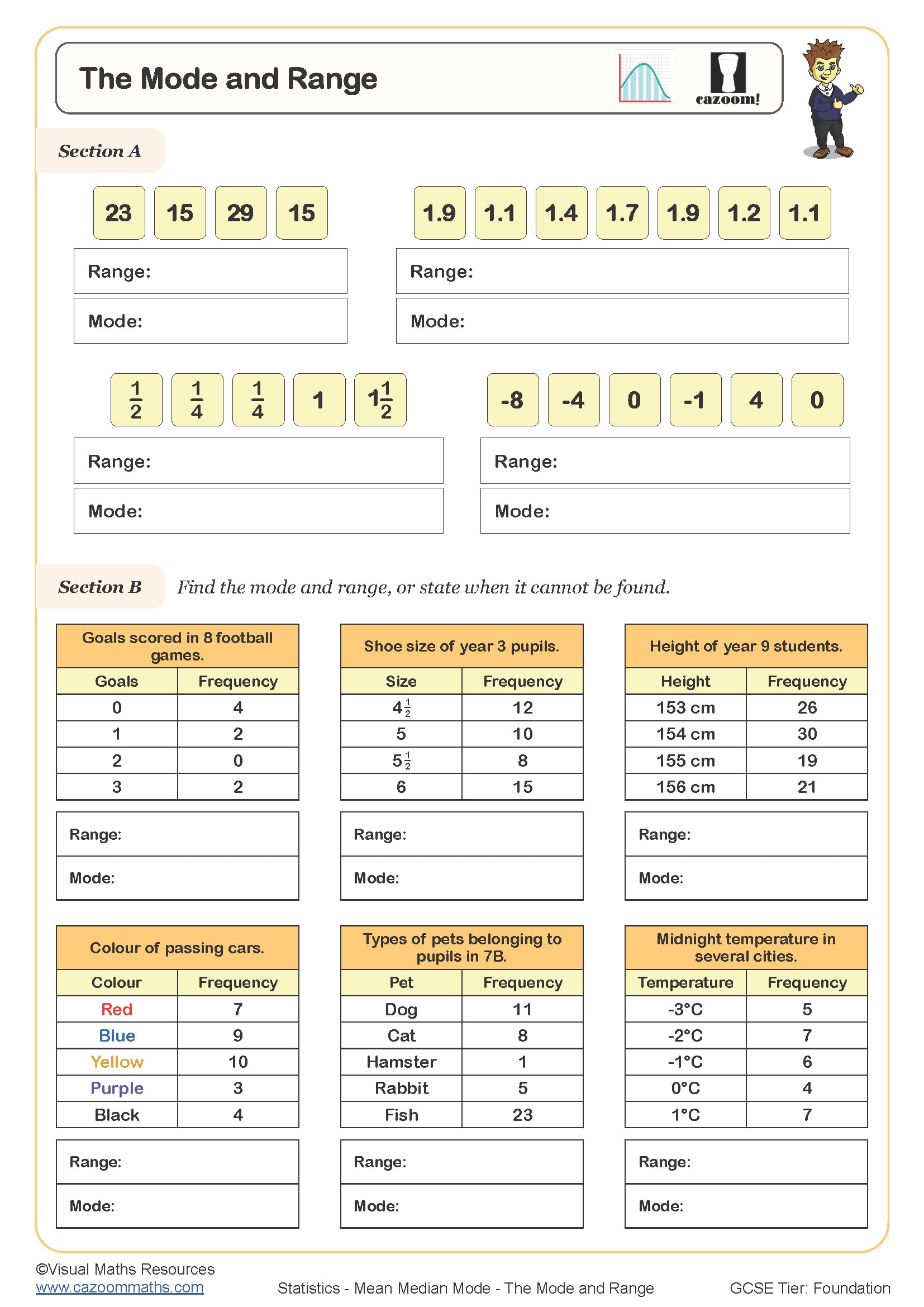
What is Mode in Maths?
The mode is the most frequently occurring number in a dataset. A dataset may have one mode, more than one mode, or no mode at all.
Example: In the dataset 3, 5, 5, 7, 9, the mode is 5 because it appears twice.
Calculating Range in Maths
The range is the difference between the highest and lowest values in a dataset. It gives an idea of the spread of the data.
Example: For the dataset 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, the range is 11 - 3 = 8.
Why Are These Measures Important?
- Summarising Data: Quickly understand the central tendency and spread of a dataset.
- Comparing Datasets: Identify patterns, differences, or similarities between groups of data.
- Making Decisions: Use statistical insights to draw conclusions and make informed choices.
How This Resource Helps
- Clear Explanations: Definitions and examples simplify mean, median, mode, and range.
- Step-by-Step Calculations: Guided examples make learning easier.
- Real-Life Applications: Demonstrates practical uses of these concepts.
Benefits for Learners
- Builds confidence in working with descriptive statistics.
- Enhances analytical and problem-solving skills.
- Provides a strong foundation for interpreting data.
Who Is This For?
- Teachers: A helpful tool for introducing and revising these topics.
- Students: Ideal for extra practice or revision support.
- Parents: A great resource for assisting with homework.
Discover More!
Browse our extensive collection of worksheets, tailored to help students master mean, median, mode, and range concepts. All worksheets are downloadable in PDF format, ensuring easy access for classroom and home use.
Download your free Mean, Median, Mode, and Range resource today!