Cubic Functions: Identifying, Graphing, and Interpreting WORKSHEET
Distinguish between situations that can be modeled with linear functions and with exponential functions. a. Prove that linear functions grow by equal differences over equal intervals, and that exponential functions grow by equal factors over equal intervals. b. Recognize situations in which one quantity changes at a constant rate per unit interval relative to another. c. Recognize situations in which a quantity grows or decays by a constant percent rate per unit interval relative to another.
Construct linear and exponential functions, including arithmetic and geometric sequences, given a graph, a description of a relationship, or two input‑output pairs (include reading these from a table).
Cubic Functions: Identifying, Graphing, and Interpreting WORKSHEET DESCRIPTION
Deepen students' knowledge of graphs of cubic functions with this worksheet.
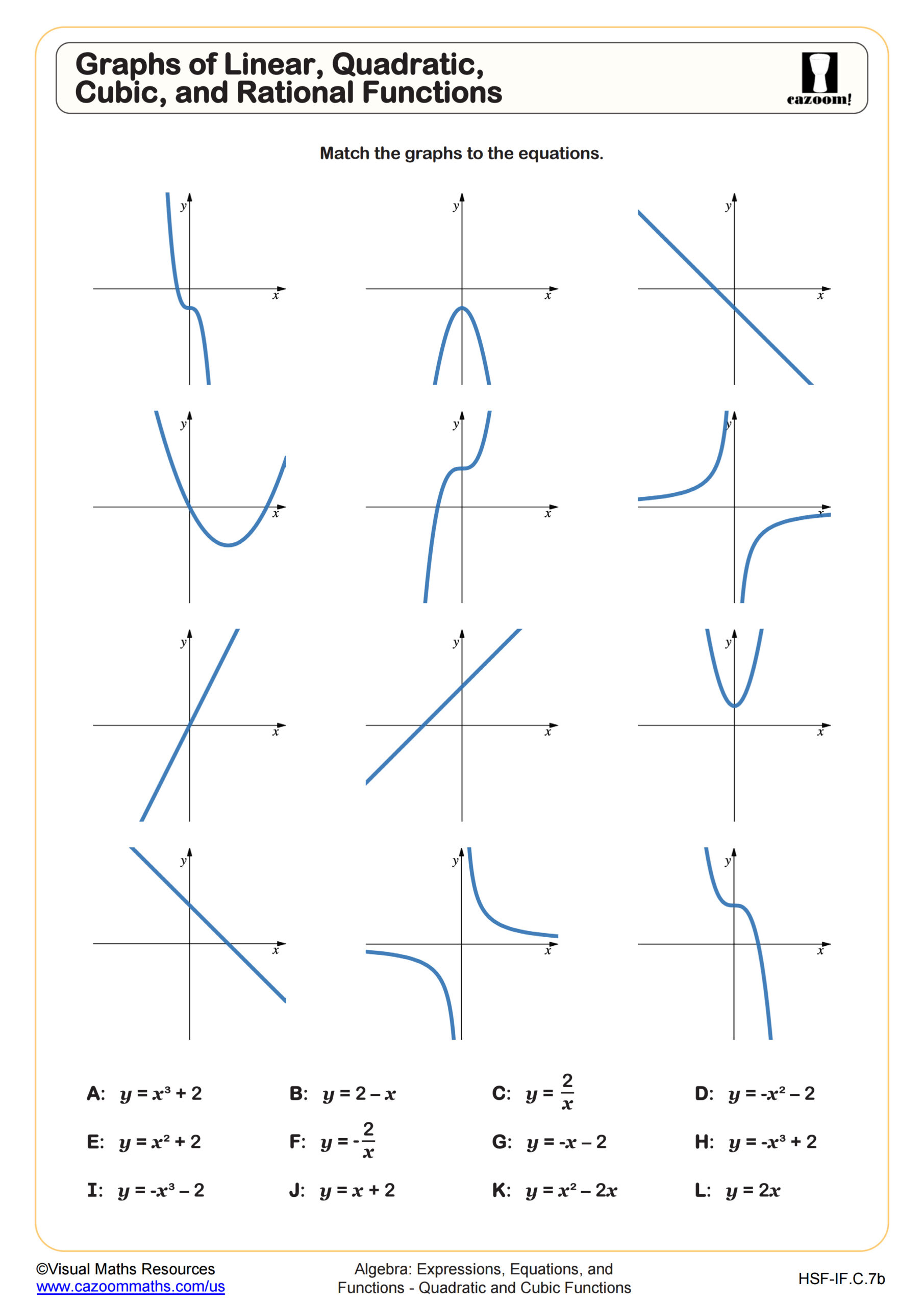
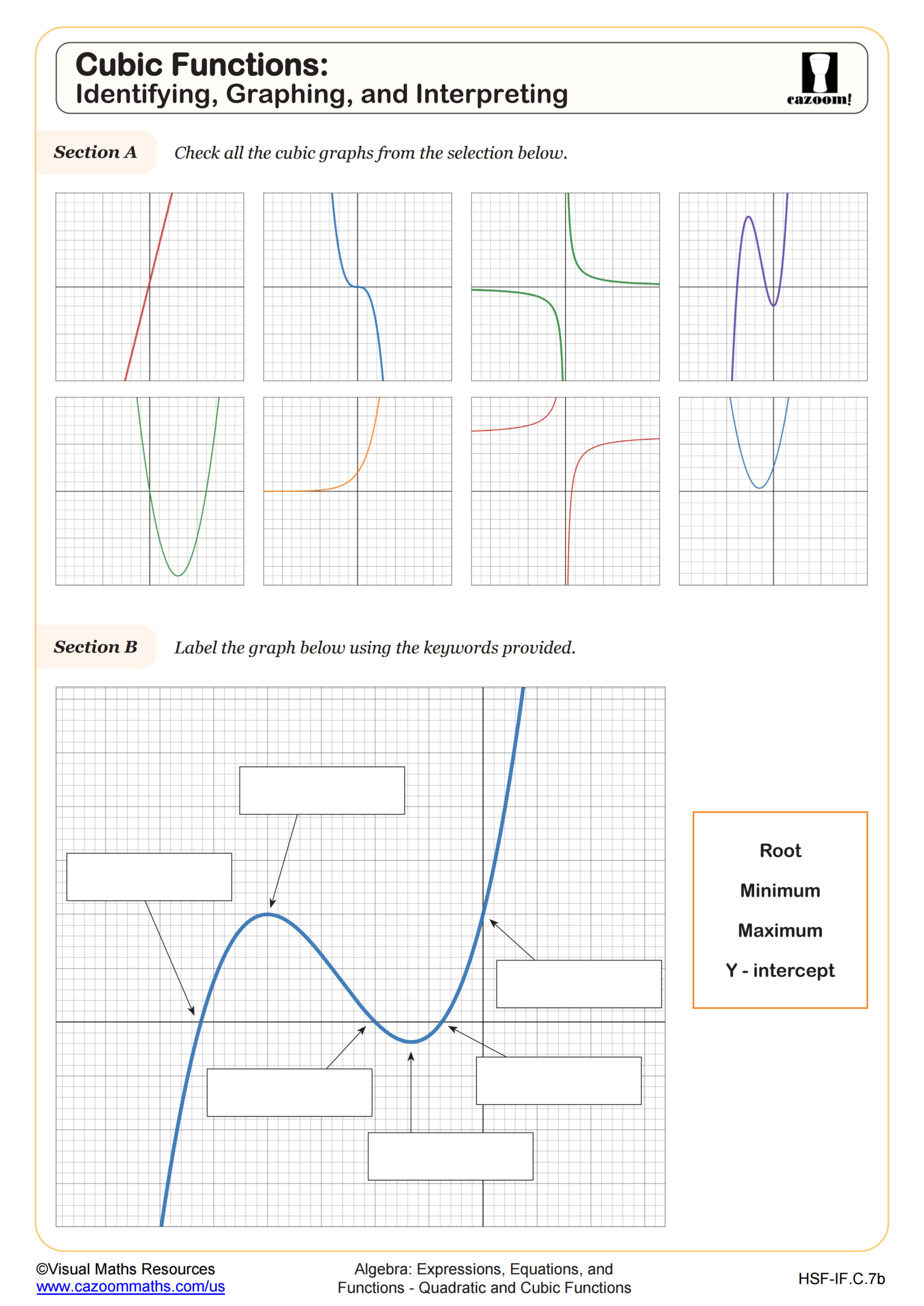
Section A asks learners to recognize cubic graphs, as they have to select cubic graphs from a selection of eight different graphs. The other functions are linear, quadratic, rational, and exponential.
In section B, learners label features of a cubic graph with given keywords such as root and y intercept.
Then, students will read values from a given graph of a cubic function such as the roots and interpret these as solutions.
Section D uses y intercepts to match three graphs to three equations.
The worksheet closes with an extension, where students will use their knowledge to sketch the graph of a cubic function by using its solutions, roots, and y intercept.
RELATED TO Cubic Functions: Identifying, Graphing, and Interpreting WORKSHEET
Frequently Asked Questions
This cubic functions: identifying, graphing, and interpreting worksheet is designed for students in Algebra II and IM 3 and aligns with Common Core State Standards.