Back to:
Estimating Area WORKSHEET
Suitable for Grades: 3rd Grade, 6th Grade
CCSS: 3.MD.C.7, 6.G.A.1
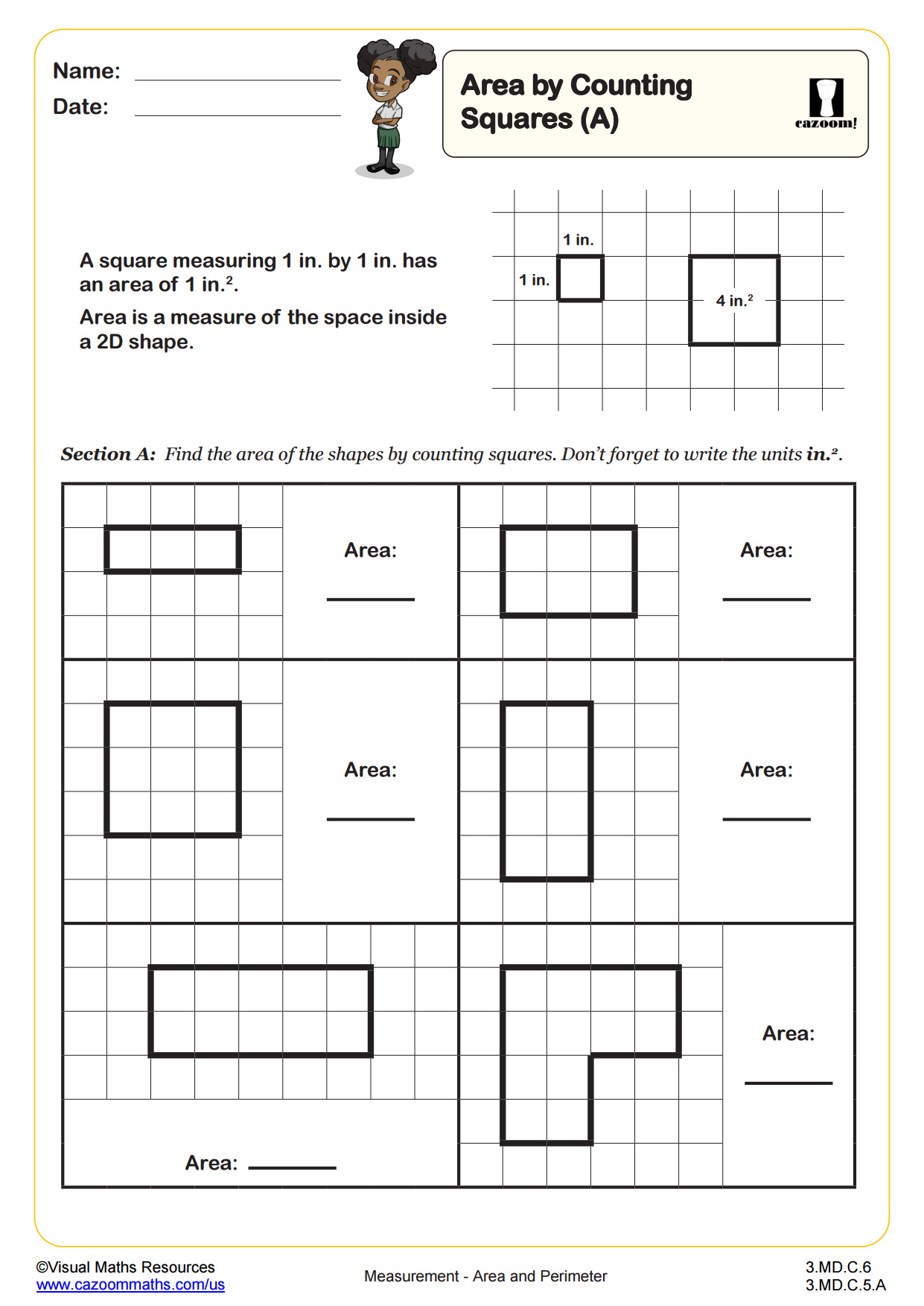
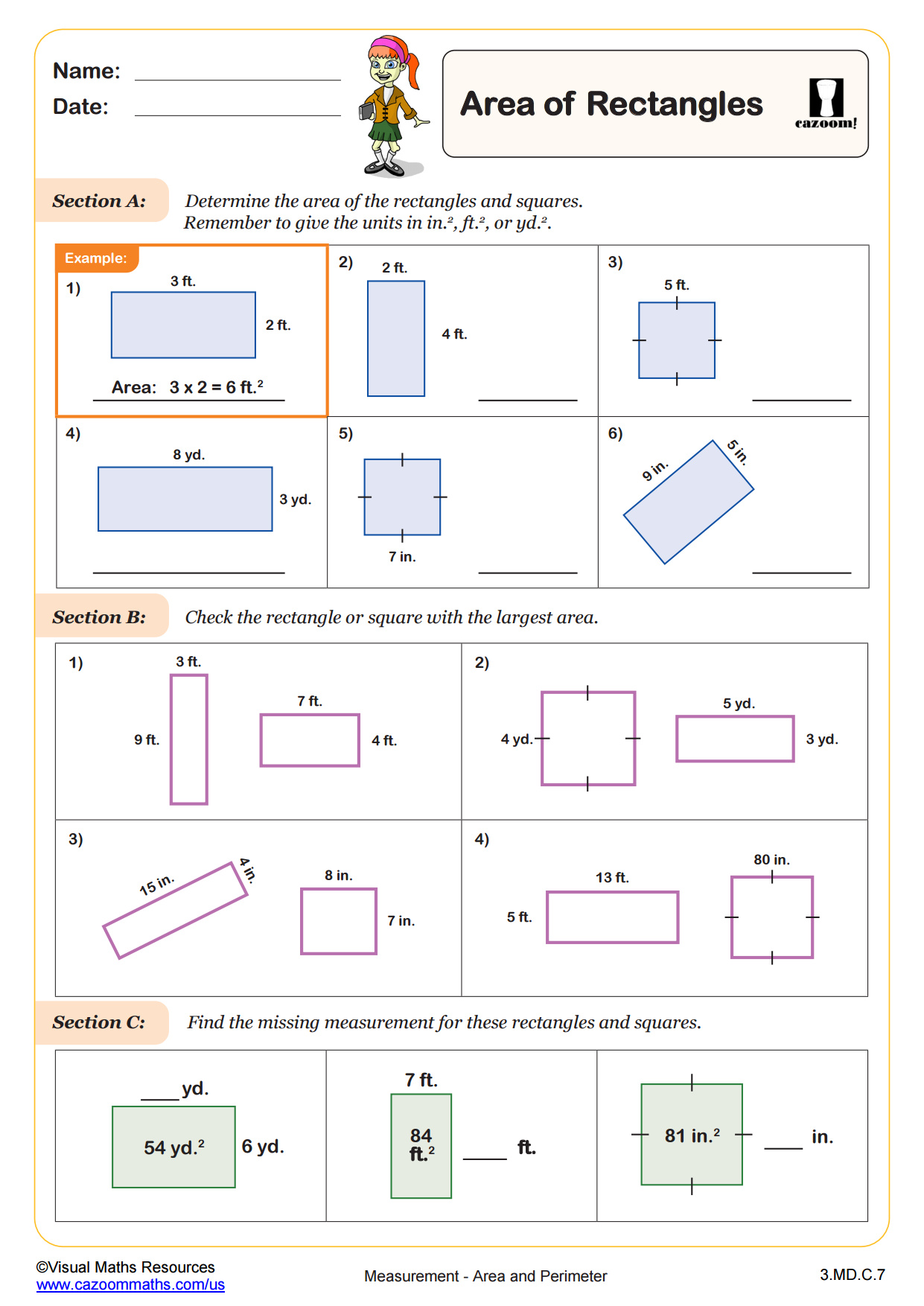
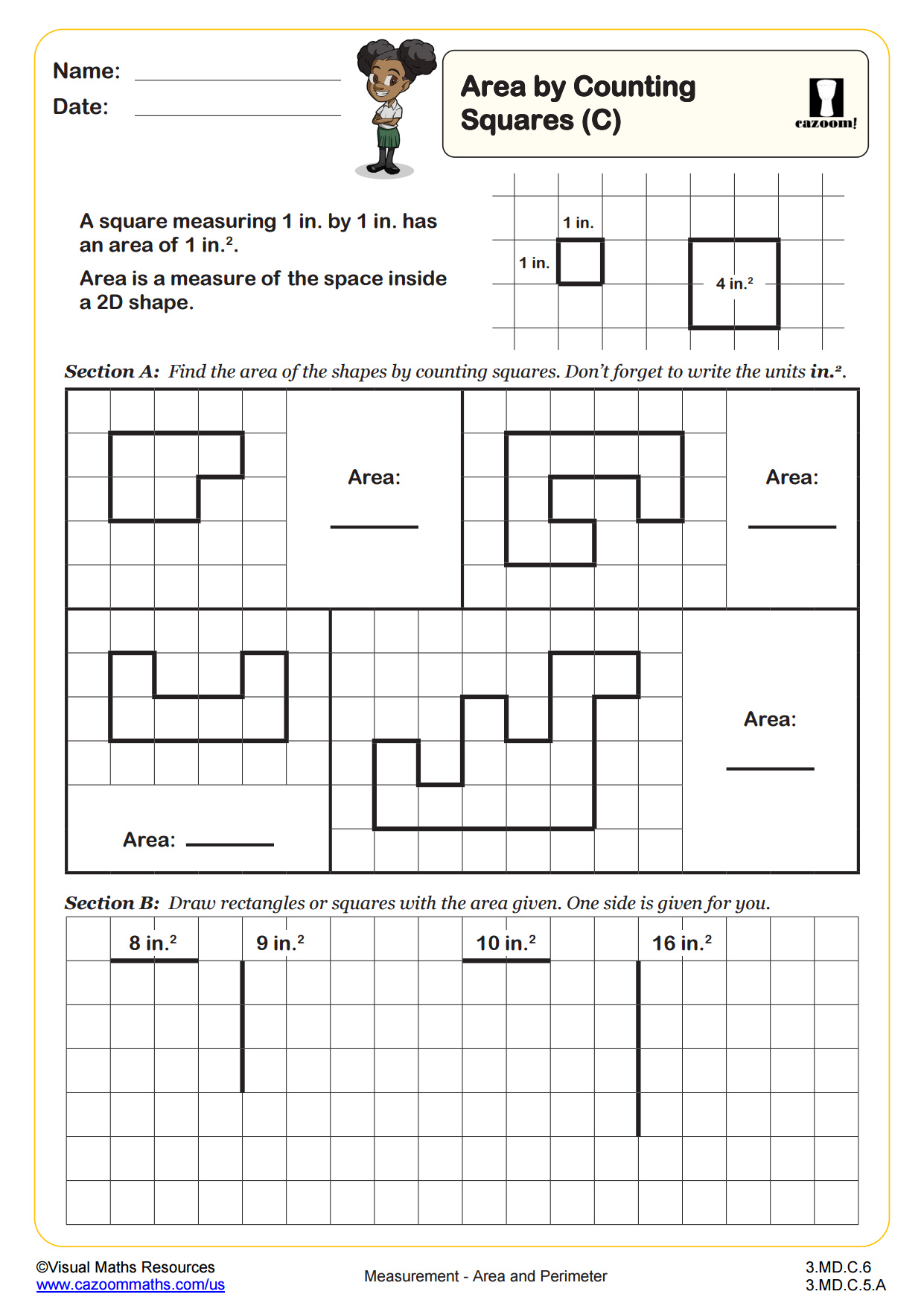
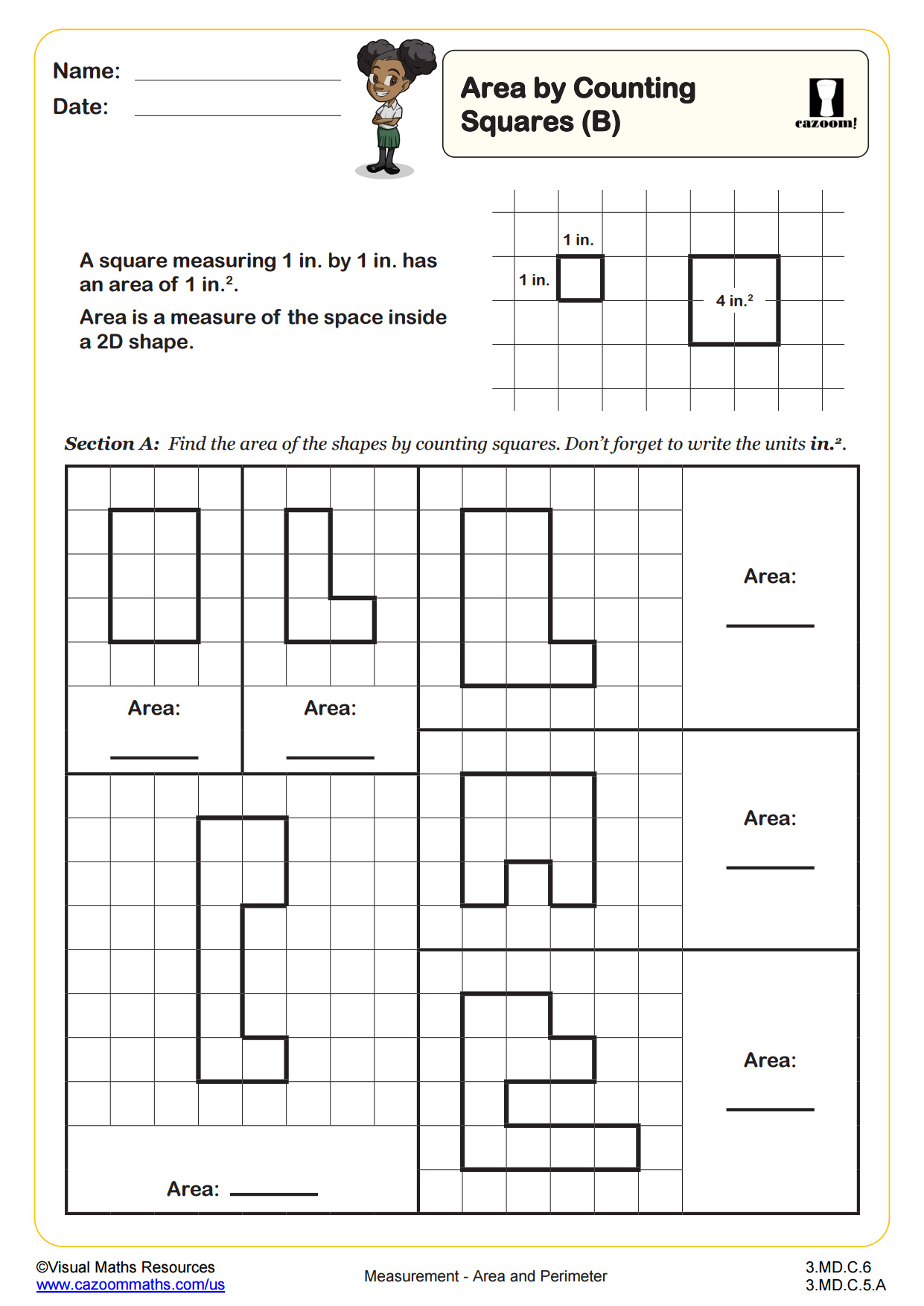
CCSS Description: Relate area to the operations of multiplication and addition. a. Find the area of a rectangle with whole-number side lengths by tiling it, and show that the area is the same as would be found by multiplying the side lengths. b. Multiply side lengths to find areas of rectangles with whole-number side lengths in the context of solving real world and mathematical problems, and represent whole-number products as rectangular areas in mathematical reasoning. c. Use tiling to show in a concrete case that the area of a rectangle with wholenumber side lengths a and b + c is the sum of a × b and a × c. Use area models to represent the distributive property in mathematical reasoning. d. Recognize area as additive. Find areas of rectilinear figures by decomposing them into non-overlapping rectangles and adding the areas of the nonoverlapping parts, applying this technique to solve real world problems.
Find the area of right triangles, other triangles, special quadrilaterals, and polygons by composing into rectangles or decomposing into triangles and other shapes; apply these techniques in the context of solving real-world and mathematical problems.
Find the area of right triangles, other triangles, special quadrilaterals, and polygons by composing into rectangles or decomposing into triangles and other shapes; apply these techniques in the context of solving real-world and mathematical problems.
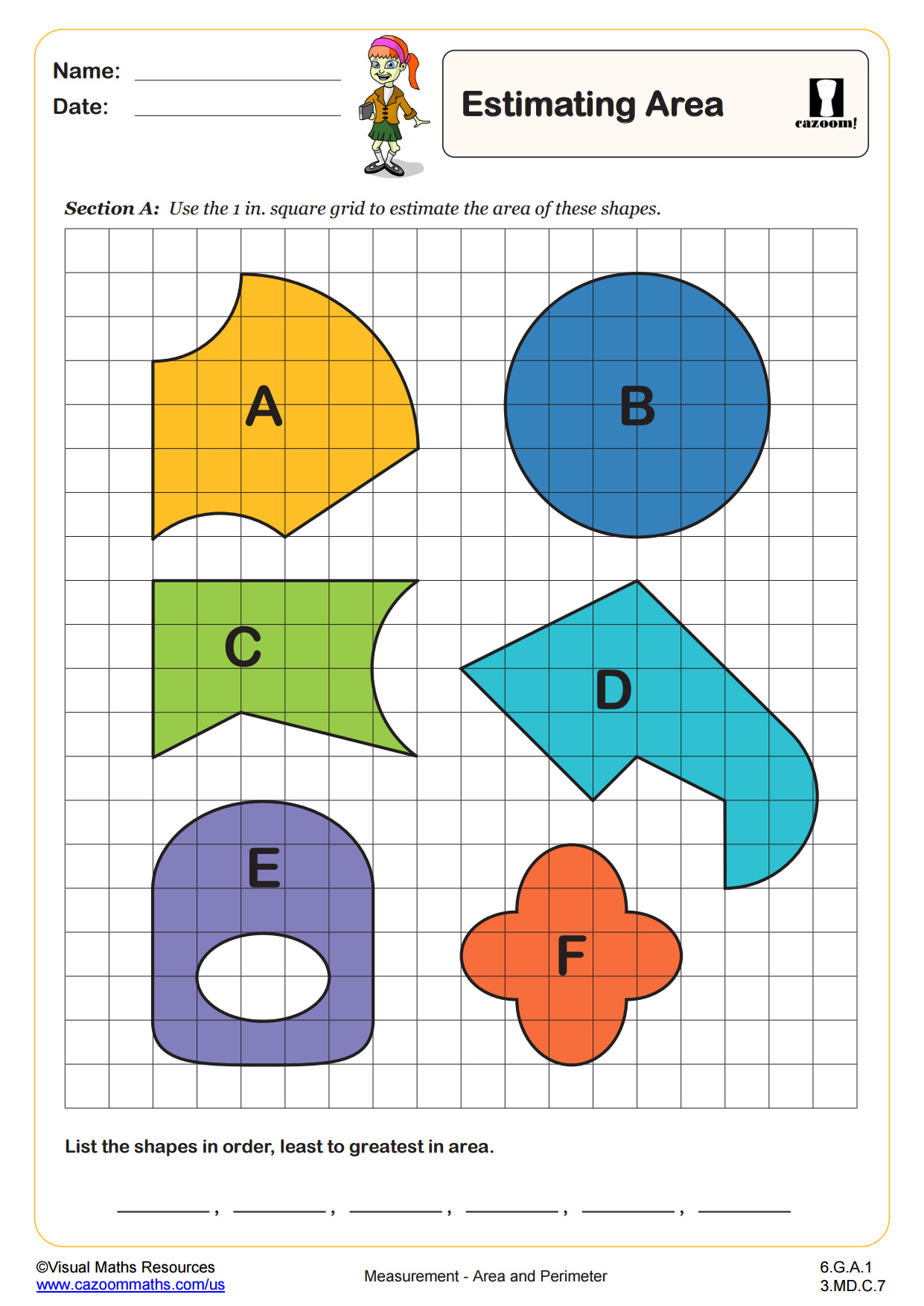
Estimating Area WORKSHEET DESCRIPTION
Once students have found the area of rectilinear shapes by counting squares they can start to estimate the area of irregular shapes using the same method. In section A, will estimate the areas of six different shapes constructed using straight, diagonal and curved edges drawn on a cm square grid and then write these areas in ascending order. Section B is a similar task but here the shapes contain no curved edges and students are encouraged to use parts of squares to help them.
RELATED TO Estimating Area WORKSHEET
Frequently Asked Questions
This estimating area worksheet is designed for students in 3rd Grade and 6th Grade and aligns with Common Core State Standards.