Back to:
Mixed Numbers WORKSHEET
Suitable for Grades: 3rd Grade, 4th Grade
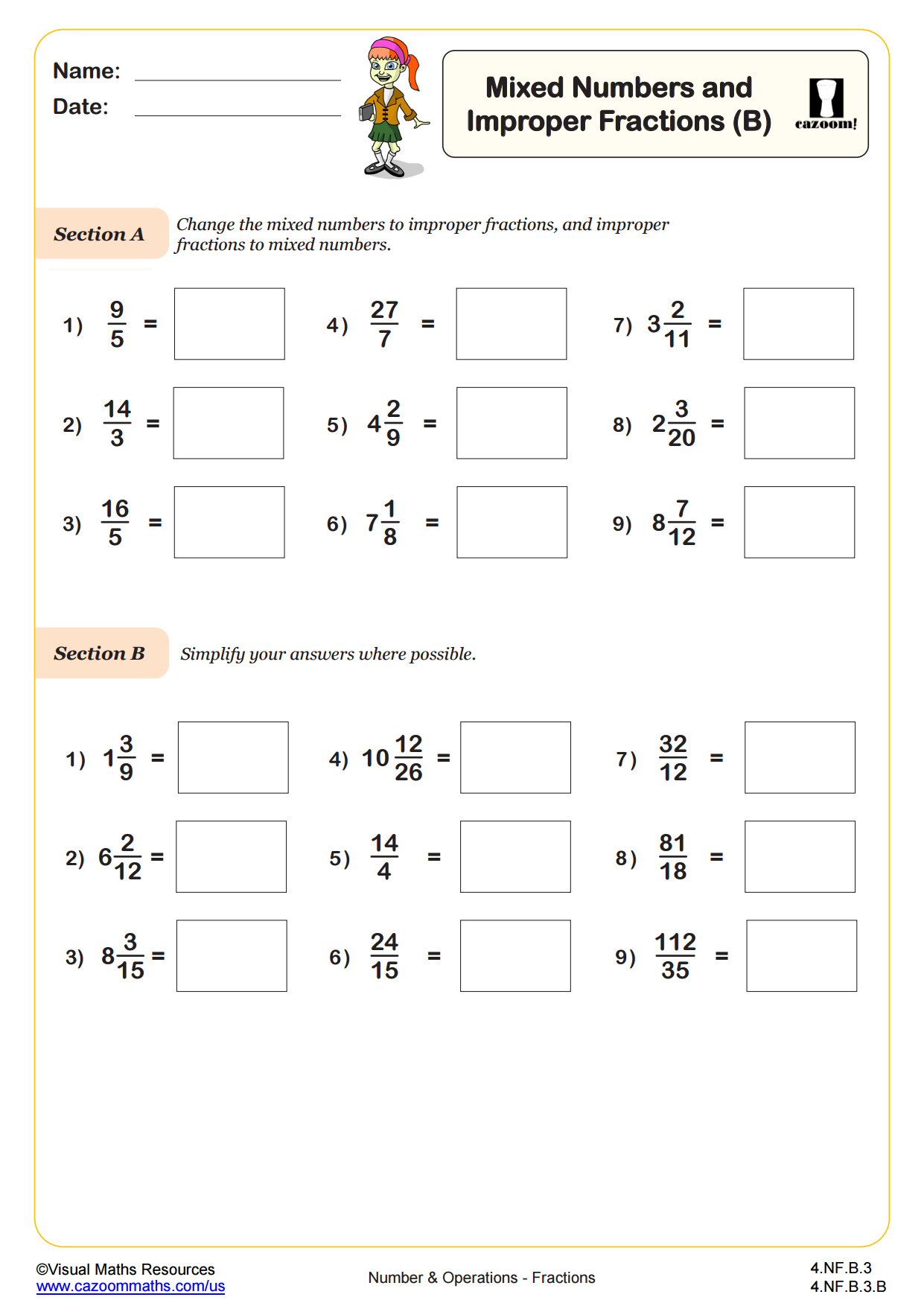
CCSS: 3.NF.A.3.C, 4.NF.B.3.B
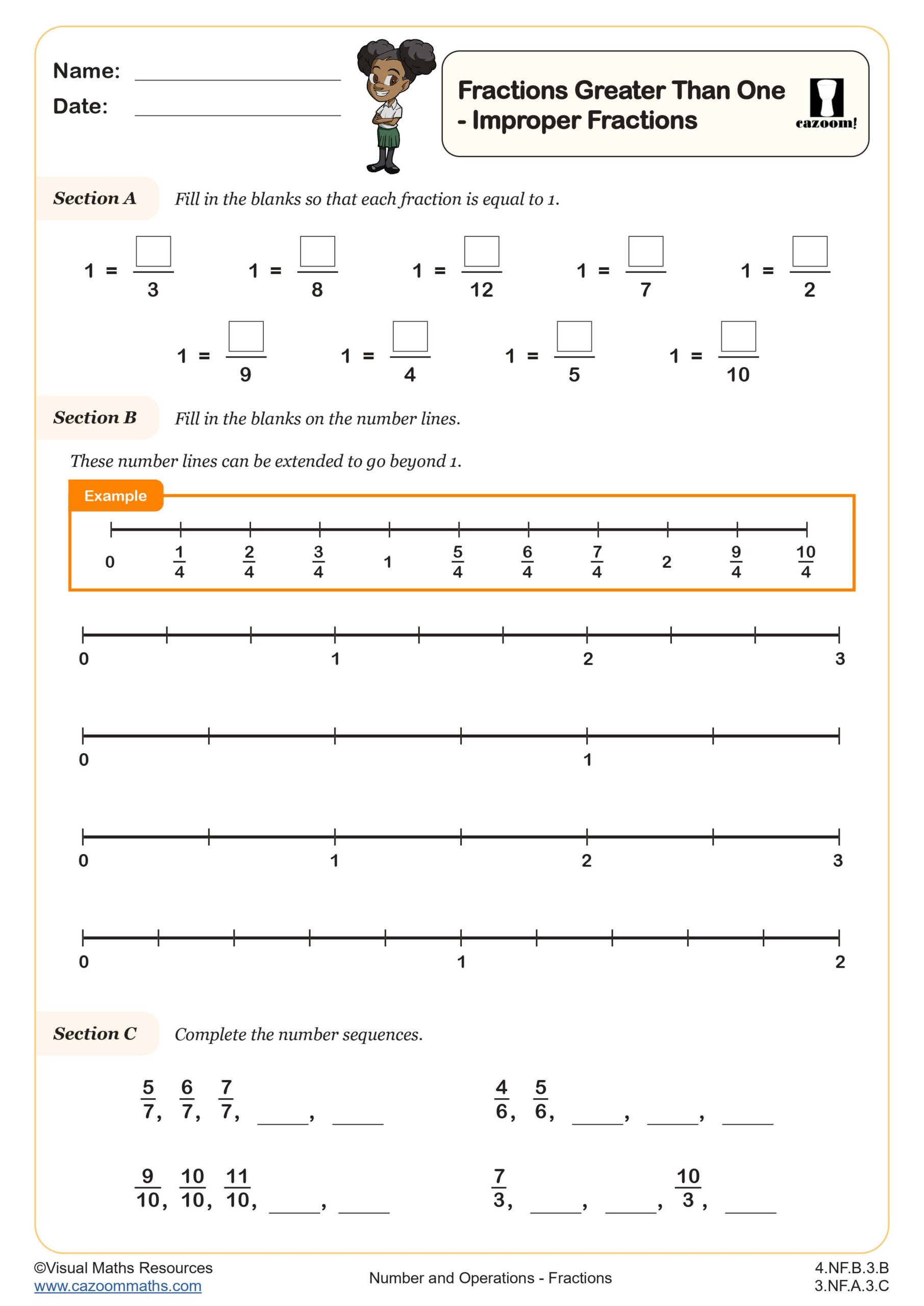
CCSS Description: Explain equivalence of fractions in special cases, and compare fractions by reasoning about their size. c. Express whole numbers as fractions, and recognize fractions that are equivalent to whole numbers. Examples: Express 3 in the form 3 = 3/1; recognize that 6/1 = 6; locate 4/4 and 1 at the same point of a number line diagram.
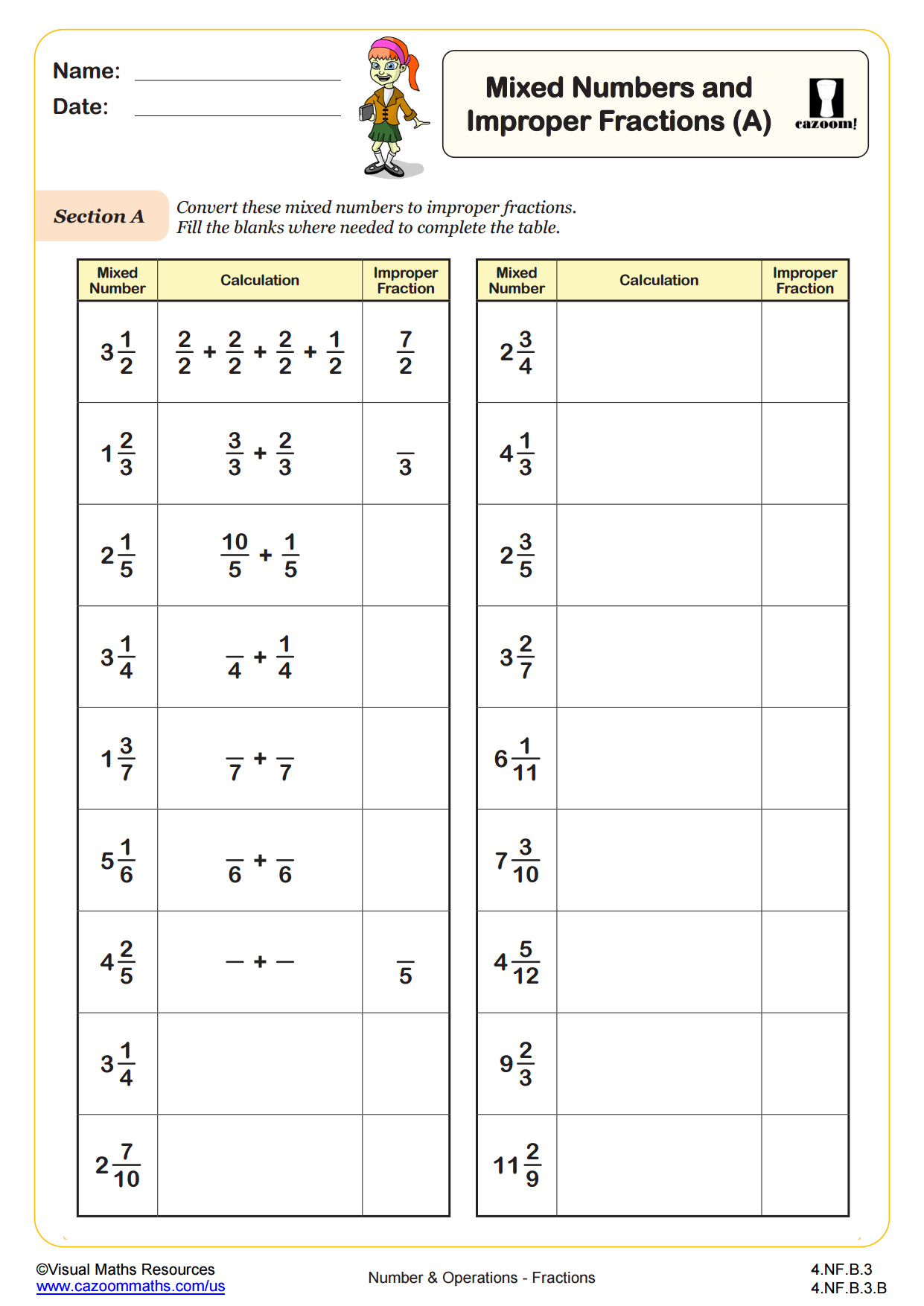
Decompose a fraction into a sum of fractions with the same denominator in more than one way, recording each decomposition by an equation. Justify decompositions, e.g., by using a visual fraction model. Examples: 3/8 = 1/8 + 1/8 + 1/8 ; 3/8 = 1/8 + 2/8 ; 2 1/8 = 1 + 1 + 1/8 = 8/8 + 8/8 + 1/8.
Decompose a fraction into a sum of fractions with the same denominator in more than one way, recording each decomposition by an equation. Justify decompositions, e.g., by using a visual fraction model. Examples: 3/8 = 1/8 + 1/8 + 1/8 ; 3/8 = 1/8 + 2/8 ; 2 1/8 = 1 + 1 + 1/8 = 8/8 + 8/8 + 1/8.
Mixed Numbers WORKSHEET DESCRIPTION
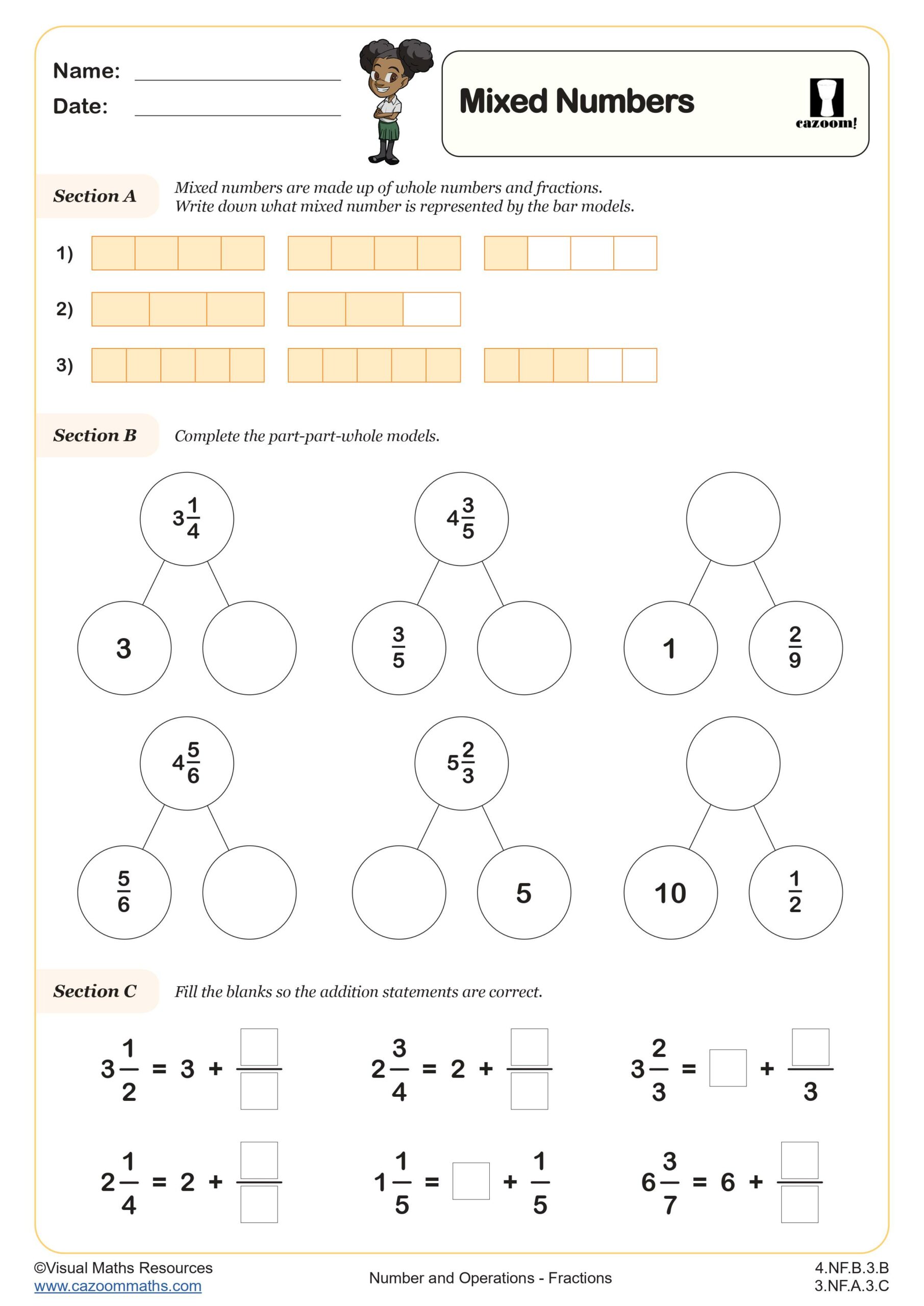
Partitioning mixed numbers is a vital tool when it comes to the conversion of mixed numbers to improper fractions (and vice versa), as well as using the four operations with mixed numbers. This worksheet helps to ensure your pupils can separate the fractional and whole parts of mixed numbers as well as partition with flexibility. We have used bar model and part part whole model representations throughout. Pupils will; identify mixed numbers from bar models, complete part part whole models, fill the gaps in addition statements and match bar models to part part whole models when completing this worksheet.
RELATED TO Mixed Numbers WORKSHEET
Frequently Asked Questions
This mixed numbers worksheet is designed for students in 3rd Grade and 4th Grade and aligns with Common Core State Standards.