Back to:
Multiplication and Division Fact Families WORKSHEET
Suitable for Grades: 3rd Grade
CCSS: 3.OA.B.5, 3.OA.B.6
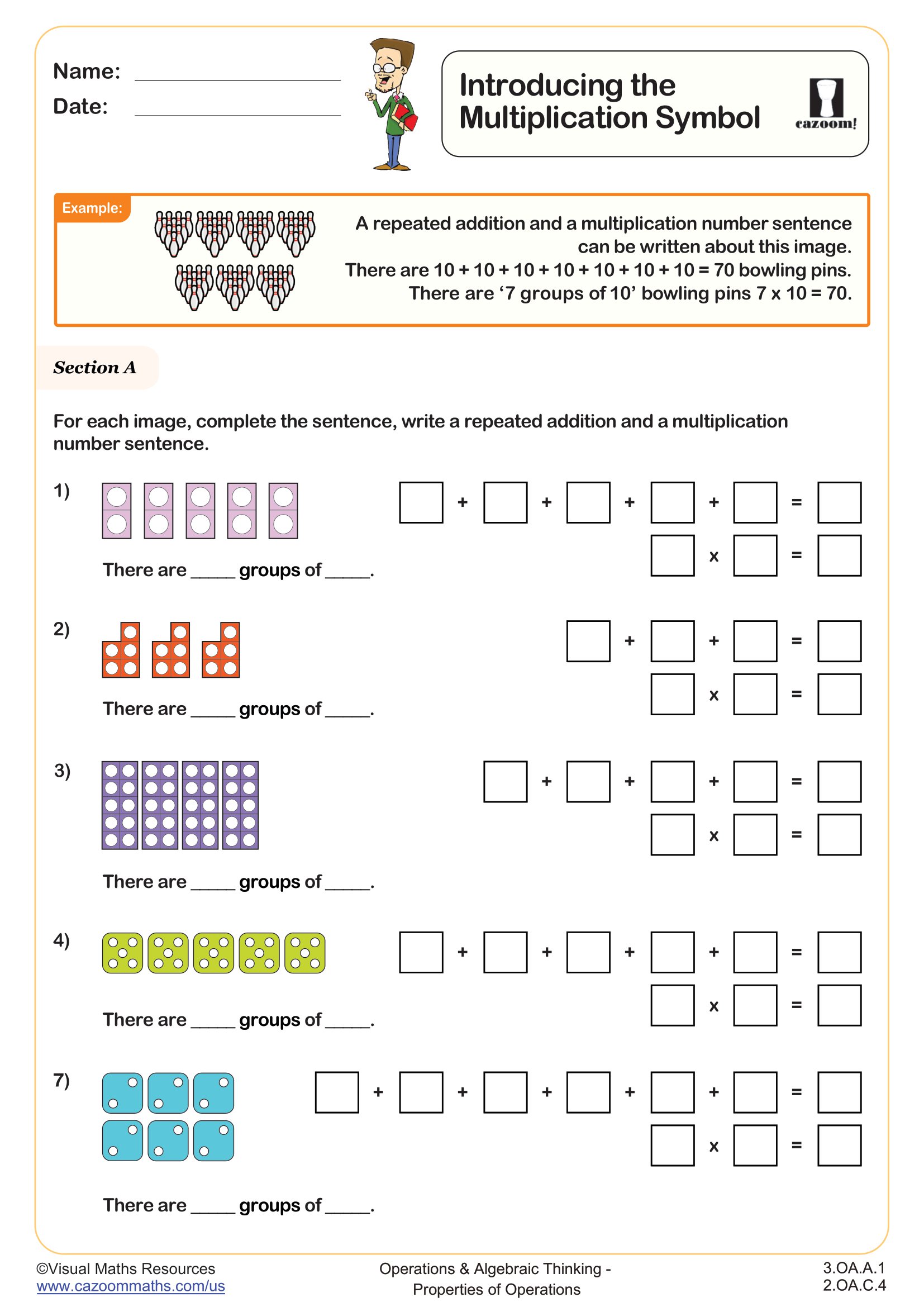
CCSS Description: Apply properties of operations as strategies to multiply and divide.2 Examples: If 6 × 4 = 24 is known, then 4 × 6 = 24 is also known. (Commutative property of multiplication.) 3 × 5 × 2 can be found by 3 × 5 = 15, then 15 × 2 = 30, or by 5 × 2 = 10, then 3 × 10 = 30. (Associative property of multiplication.) Knowing that 8 × 5 = 40 and 8 × 2 = 16, one can find 8 × 7 as 8 × (5 + 2) = (8 × 5) + (8 × 2) = 40 + 16 = 56. (Distributive property.)
Understand division as an unknown‑factor problem, for example, find 32 ÷ 8 by finding the number that makes 32 when multiplied by 8.
Understand division as an unknown‑factor problem, for example, find 32 ÷ 8 by finding the number that makes 32 when multiplied by 8.
Multiplication and Division Fact Families WORKSHEET DESCRIPTION
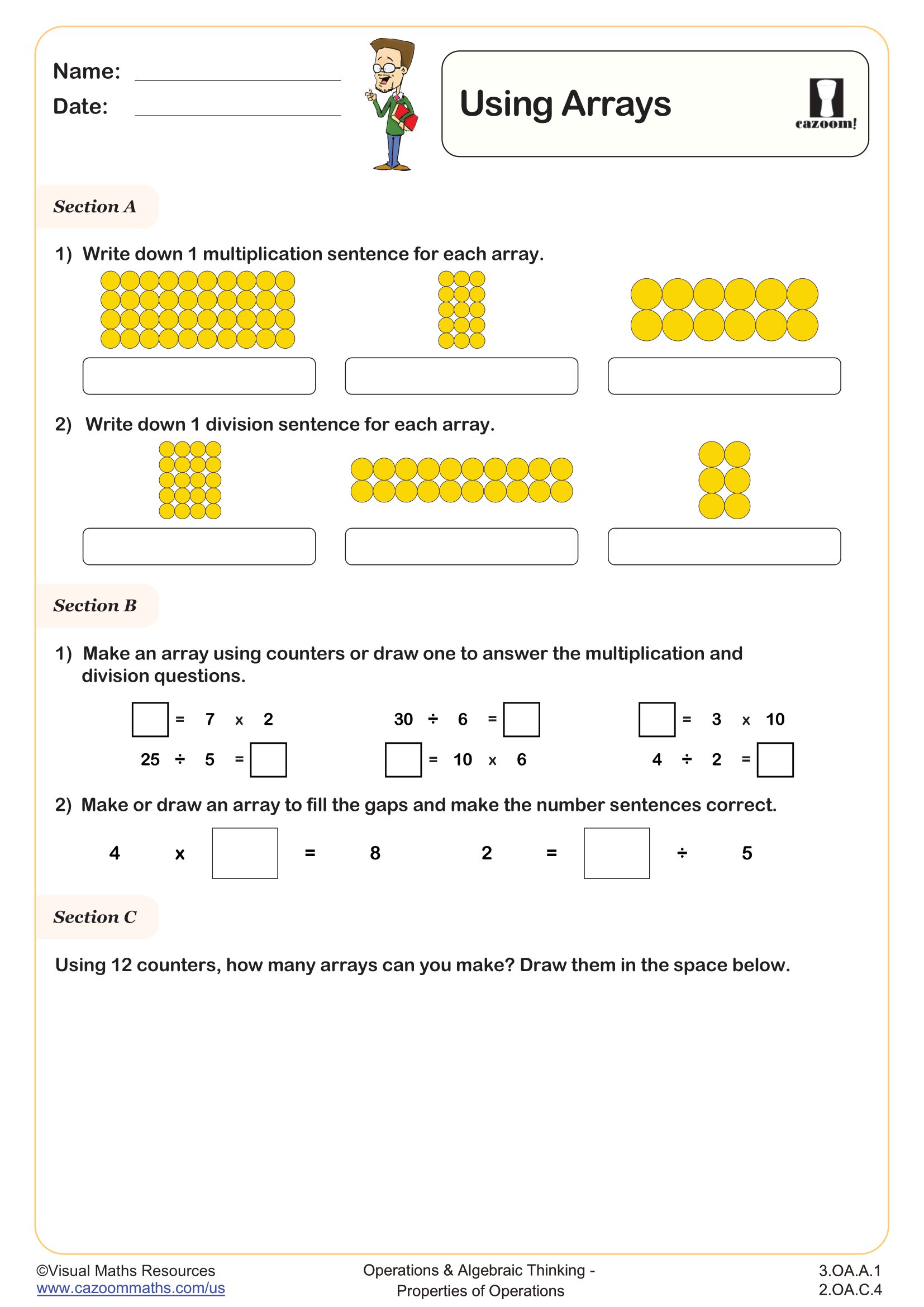
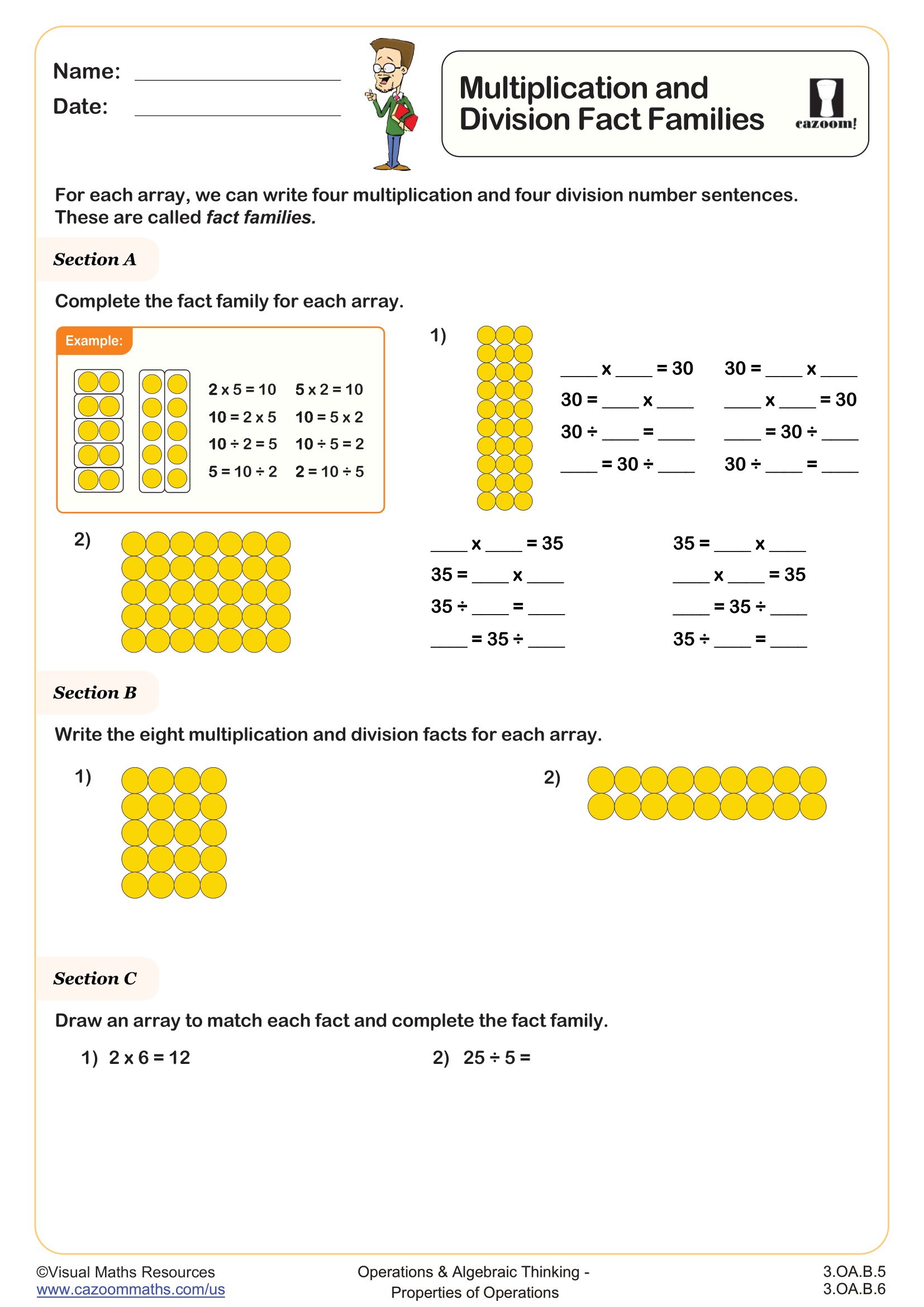
This worksheet introduces students to multiplication and division fact families using arrays.
In section A, students will complete fact families for two different arrays as they fill the gaps in number sentences.
Learners continue writing fact families in section B however this time the template of number sentences has been removed.
Then, in section C learners will draw arrays to match a given fact (one multiplication and one division fact) and use these arrays to complete the fact families.
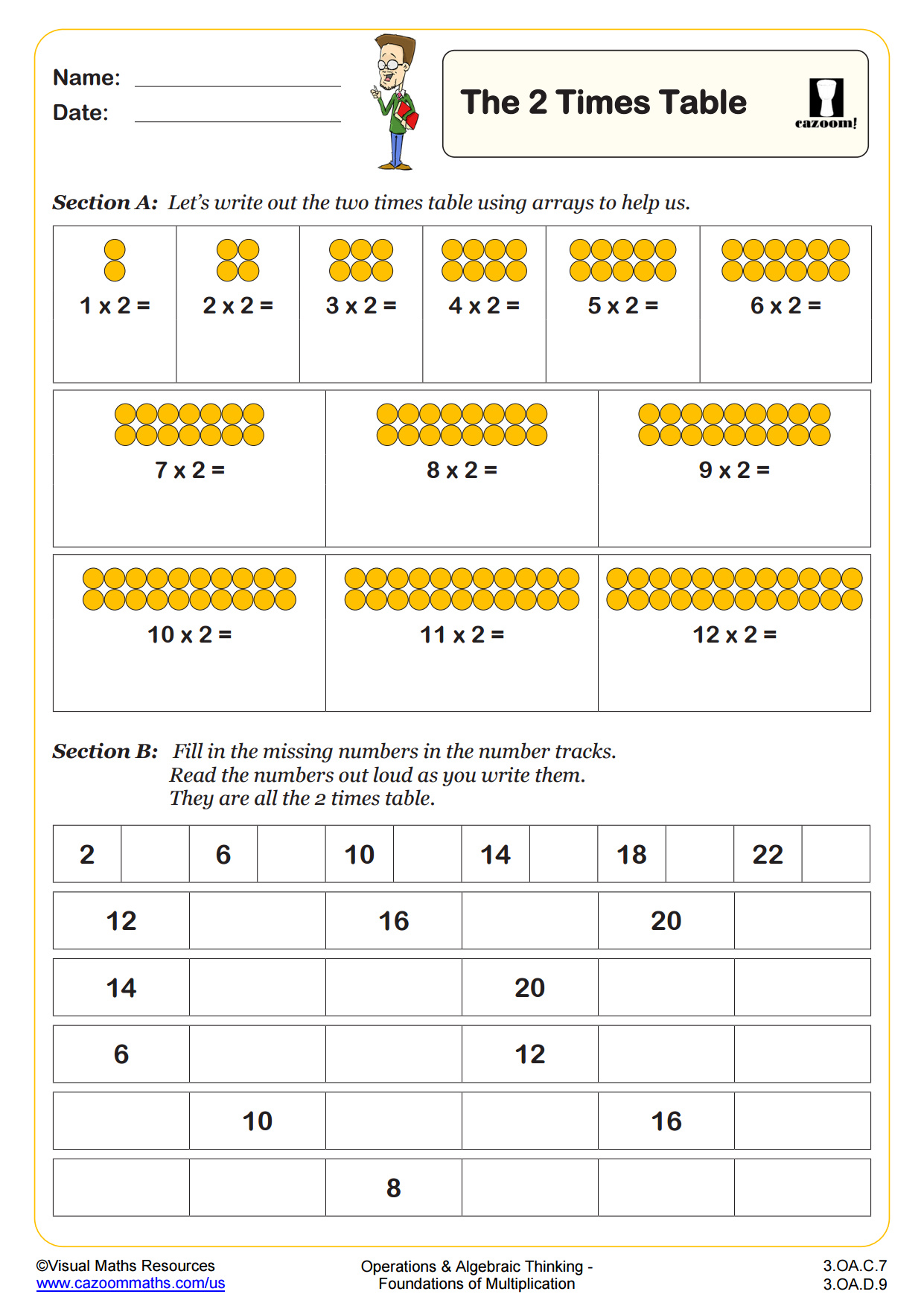
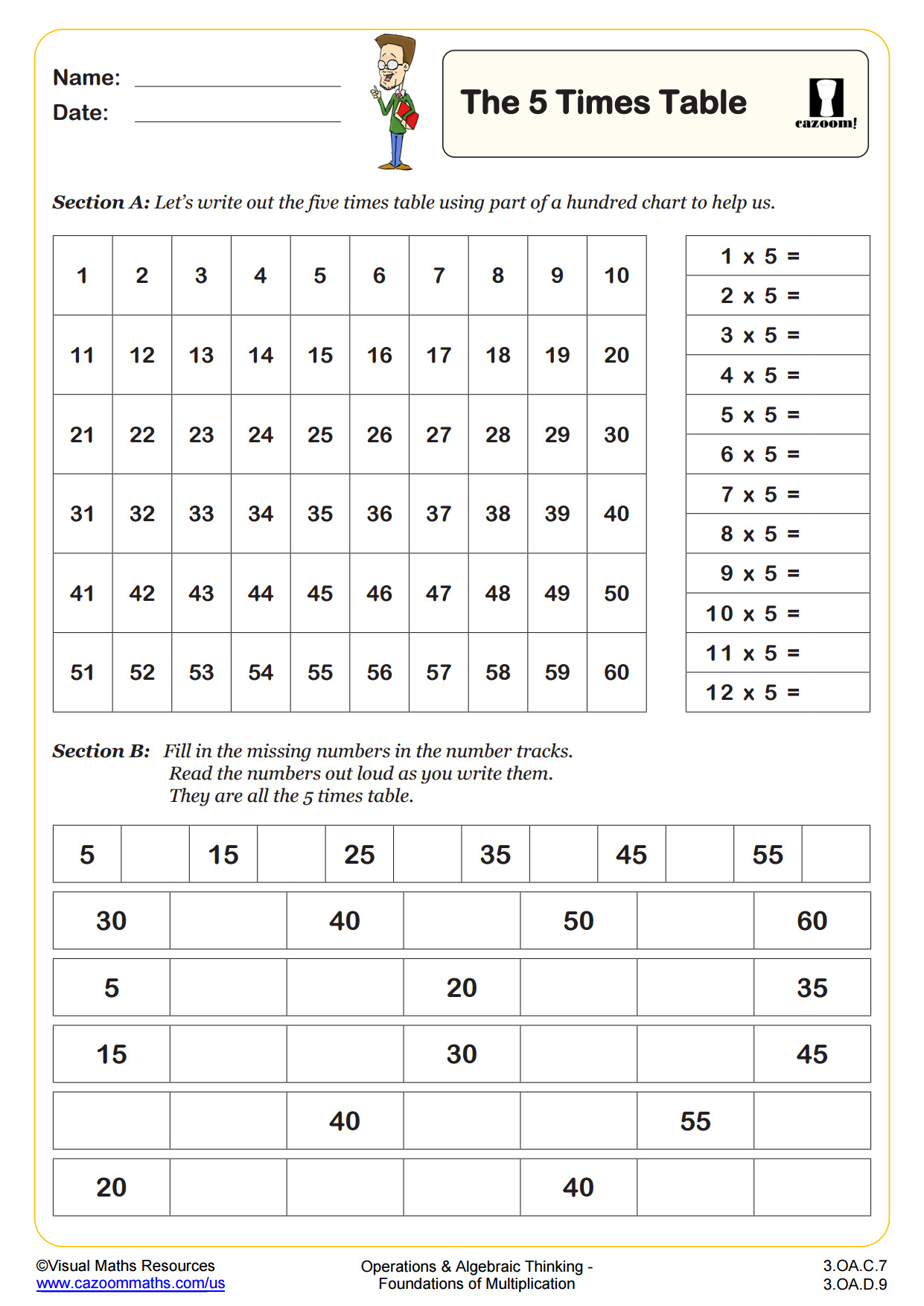
The 2, 5 and 10 times tables are used in line with the UK curriculum for year 2 learners.
RELATED TO Multiplication and Division Fact Families WORKSHEET
Frequently Asked Questions
This multiplication and division fact families worksheet is designed for students in 3rd Grade and aligns with Common Core State Standards.