Multiply 2 Digits by 1 Digit WORKSHEET
Multiply a whole number of up to four digits by a one-digit whole number, and multiply two two-digit numbers, using strategies based on place value and the properties of operations. Illustrate and explain the calculation by using equations, rectangular arrays, and/or area models.
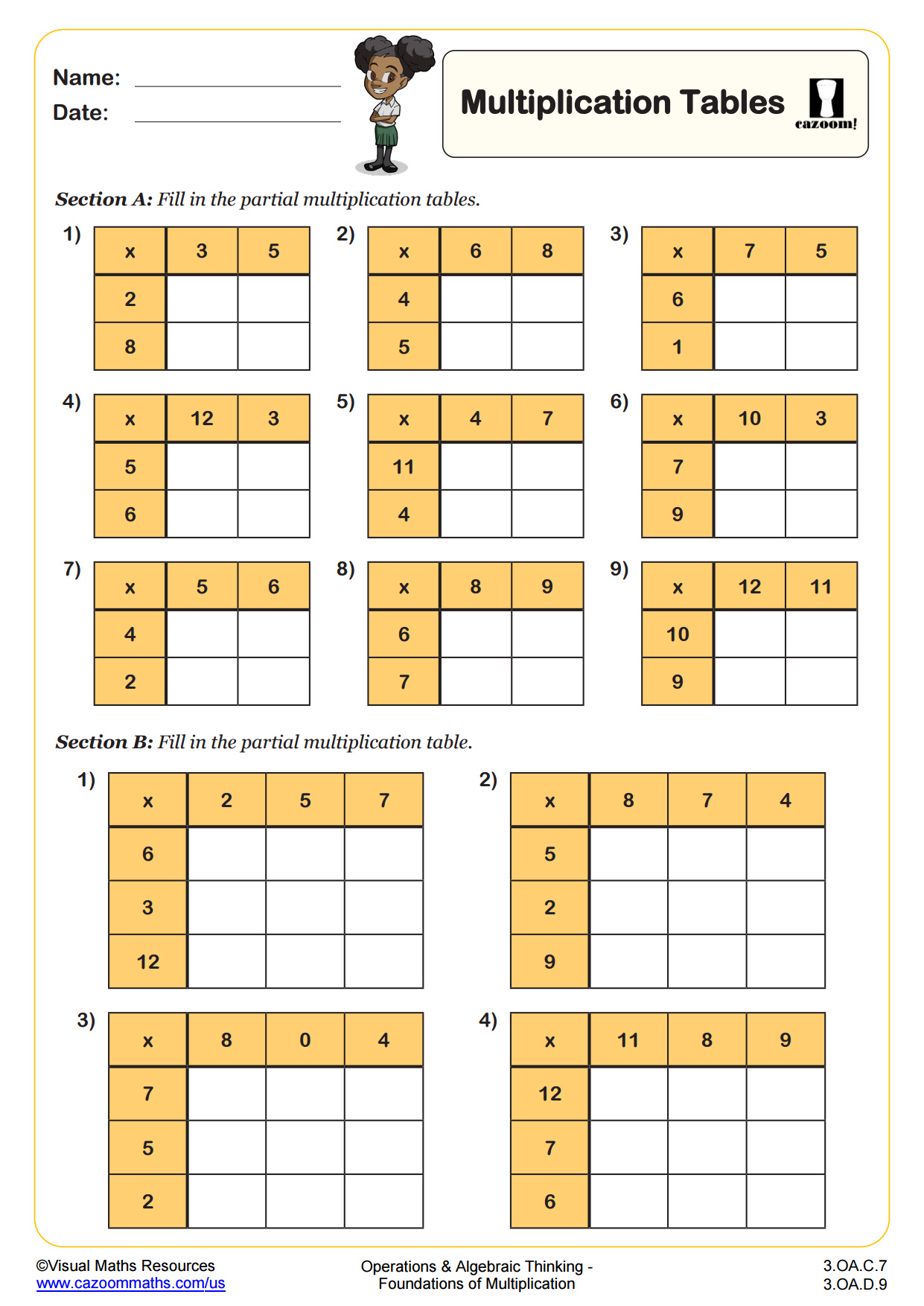
Multiply 2 Digits by 1 Digit WORKSHEET DESCRIPTION
Learners will use their knowledge of place value and the 2, 3, 4, 5, 8, and 10 times tables to multiply 2-digit numbers by single digits mentally throughout this worksheet.
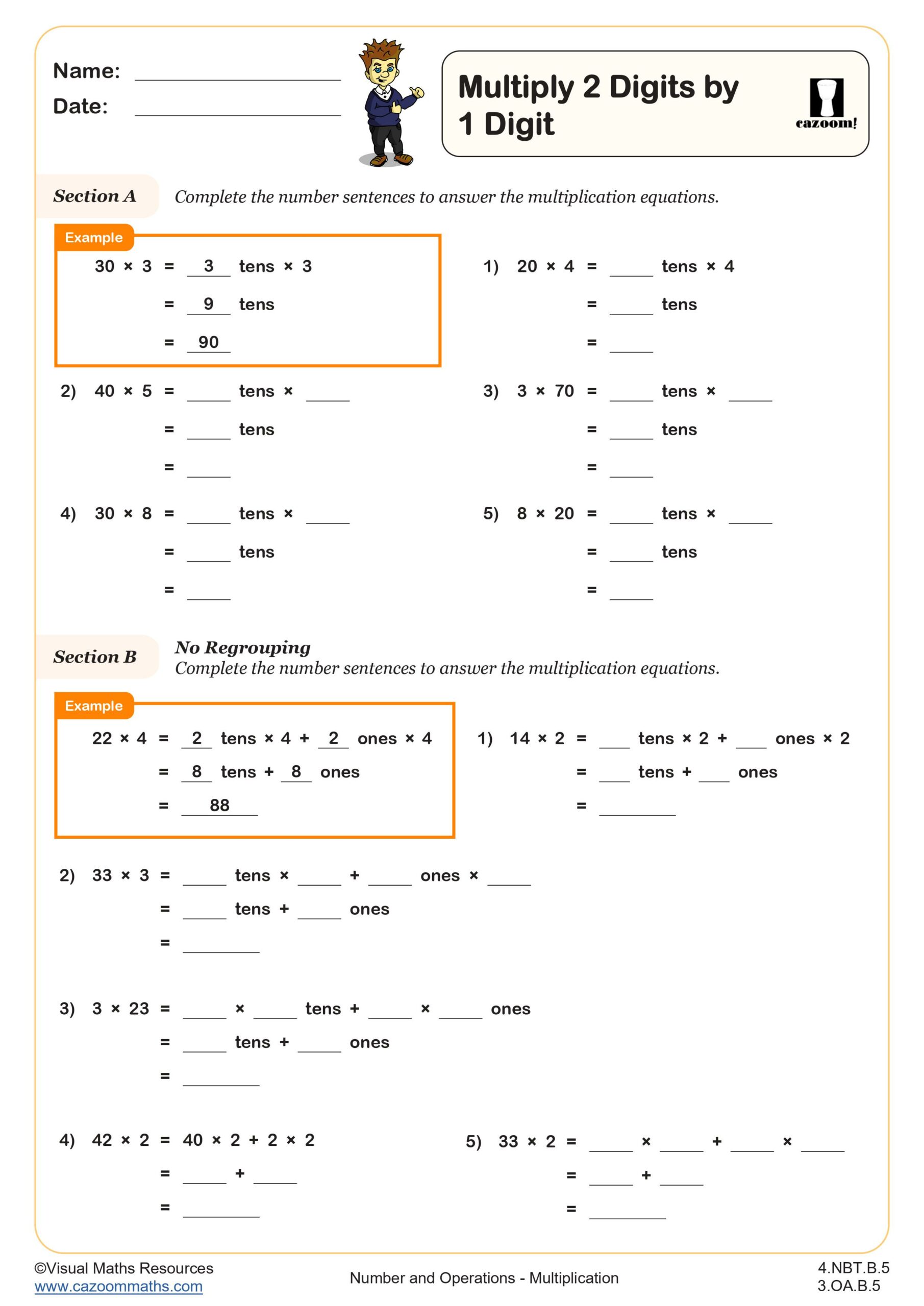
Students begin by multiplying multiples of 10 by a single digit in section A. Here, learners are encouraged to consider 30 as 3 tens before completing the multiplication.
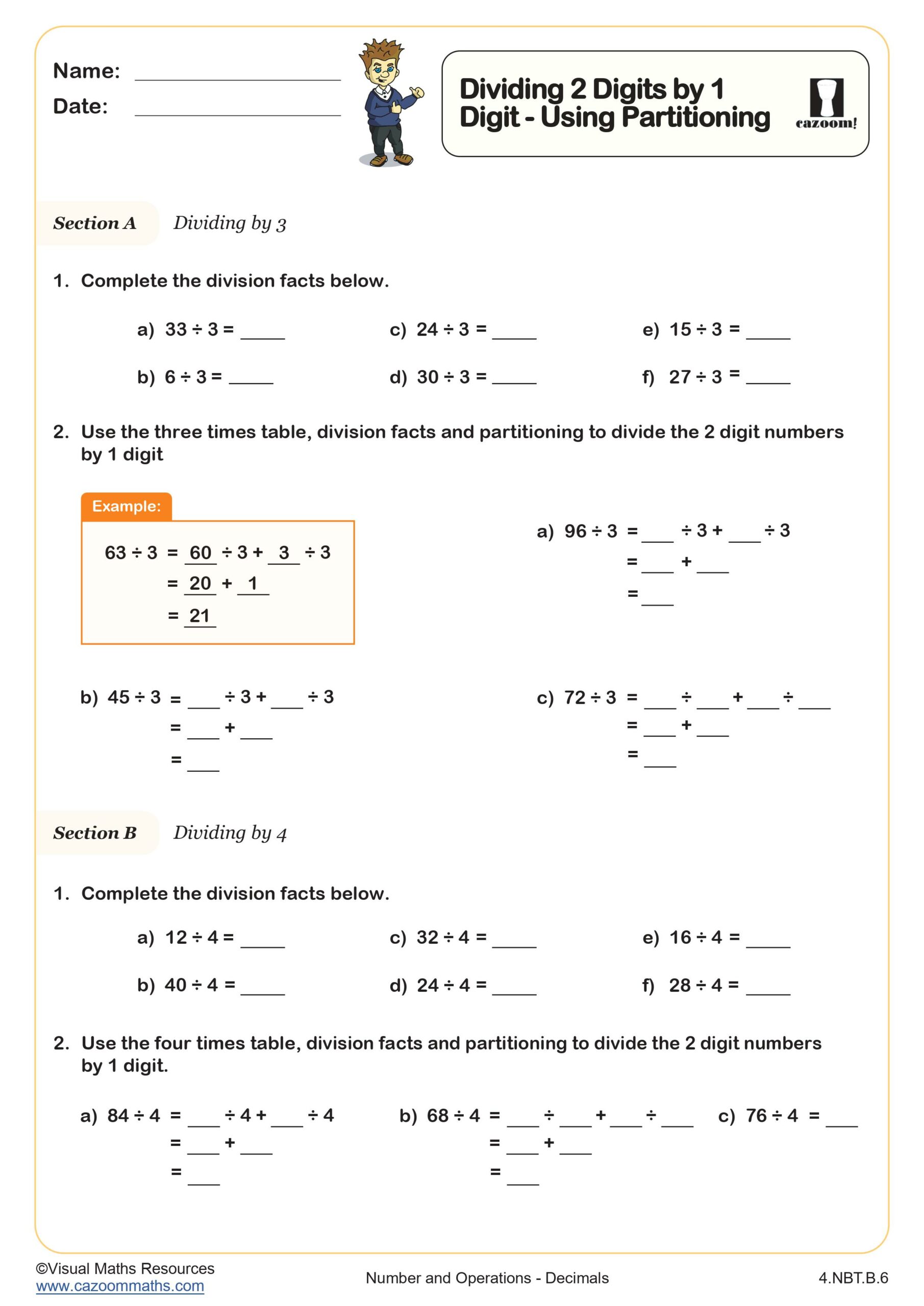
Next up, learners will answer multiplication questions that require no regrouping across sections B and C. Number sentences and partitioning are used throughout section B. Section C still encourages students to partition numbers into 10s and 1s but this time part part whole models are used for variation.
In section D, pupils will answer 6 multiplication questions that require regrouping.
RELATED TO Multiply 2 Digits by 1 Digit WORKSHEET
Frequently Asked Questions
This multiply 2 digits by 1 digit worksheet is designed for students in 4th Grade and 5th Grade and aligns with Common Core State Standards.