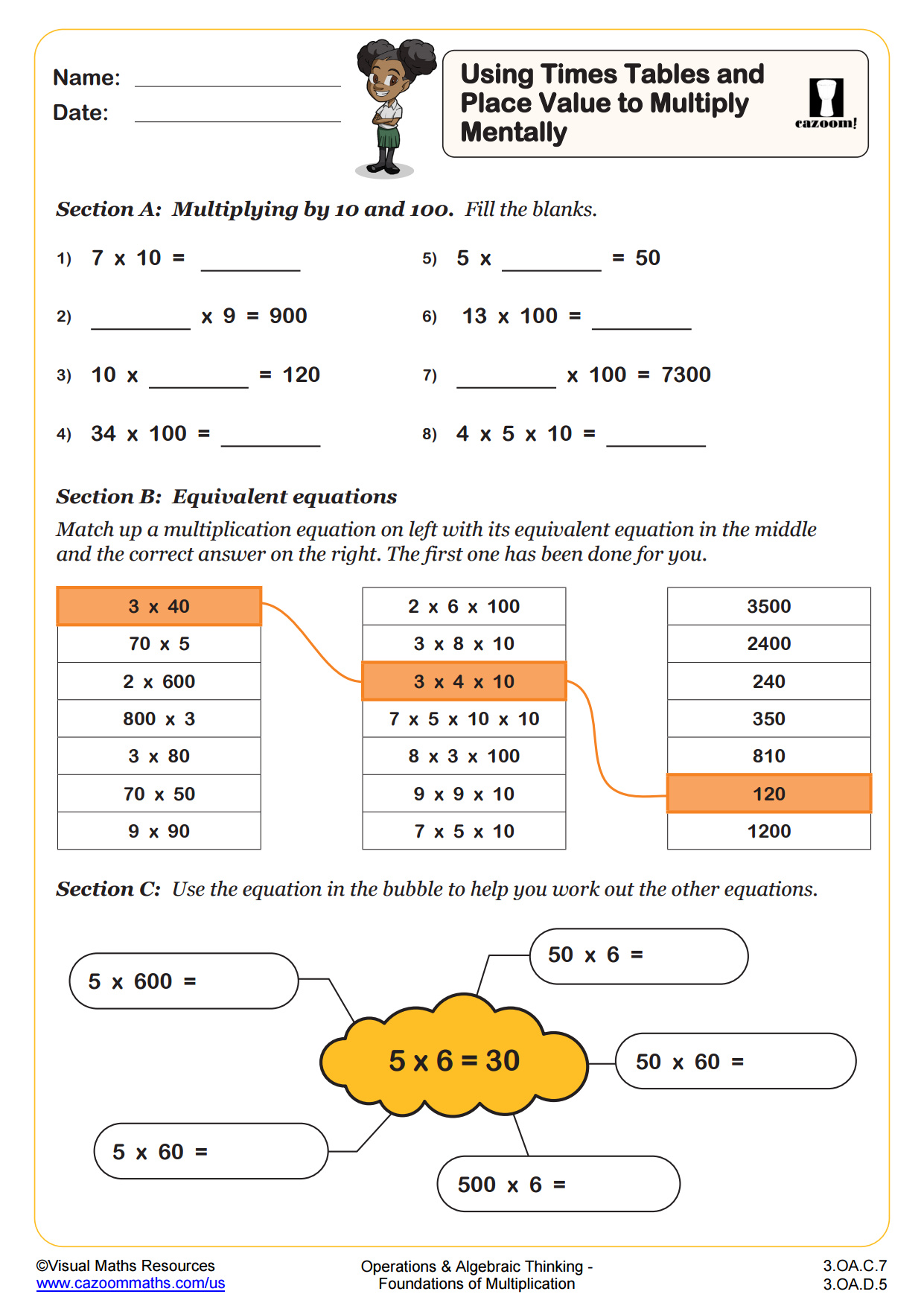
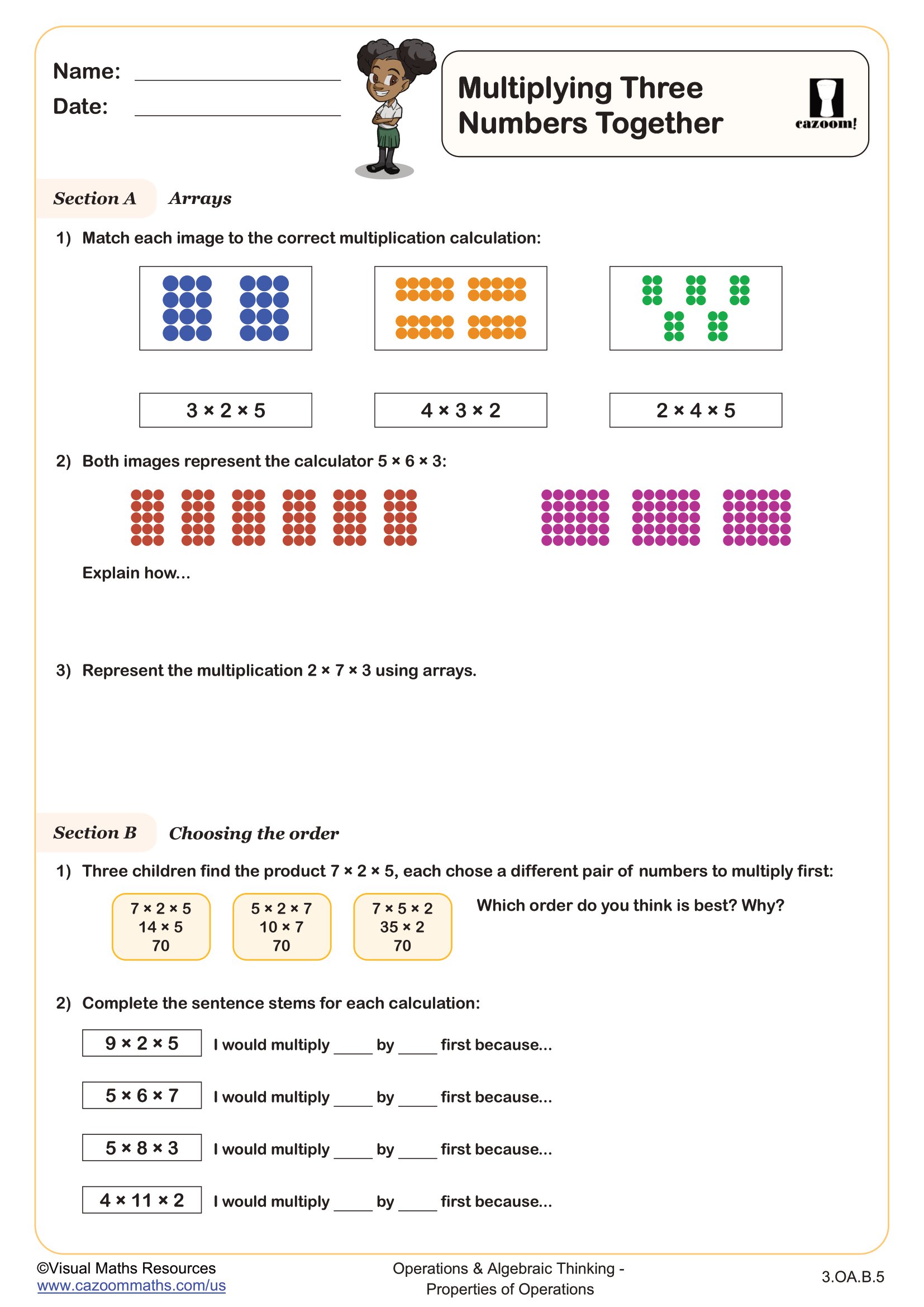
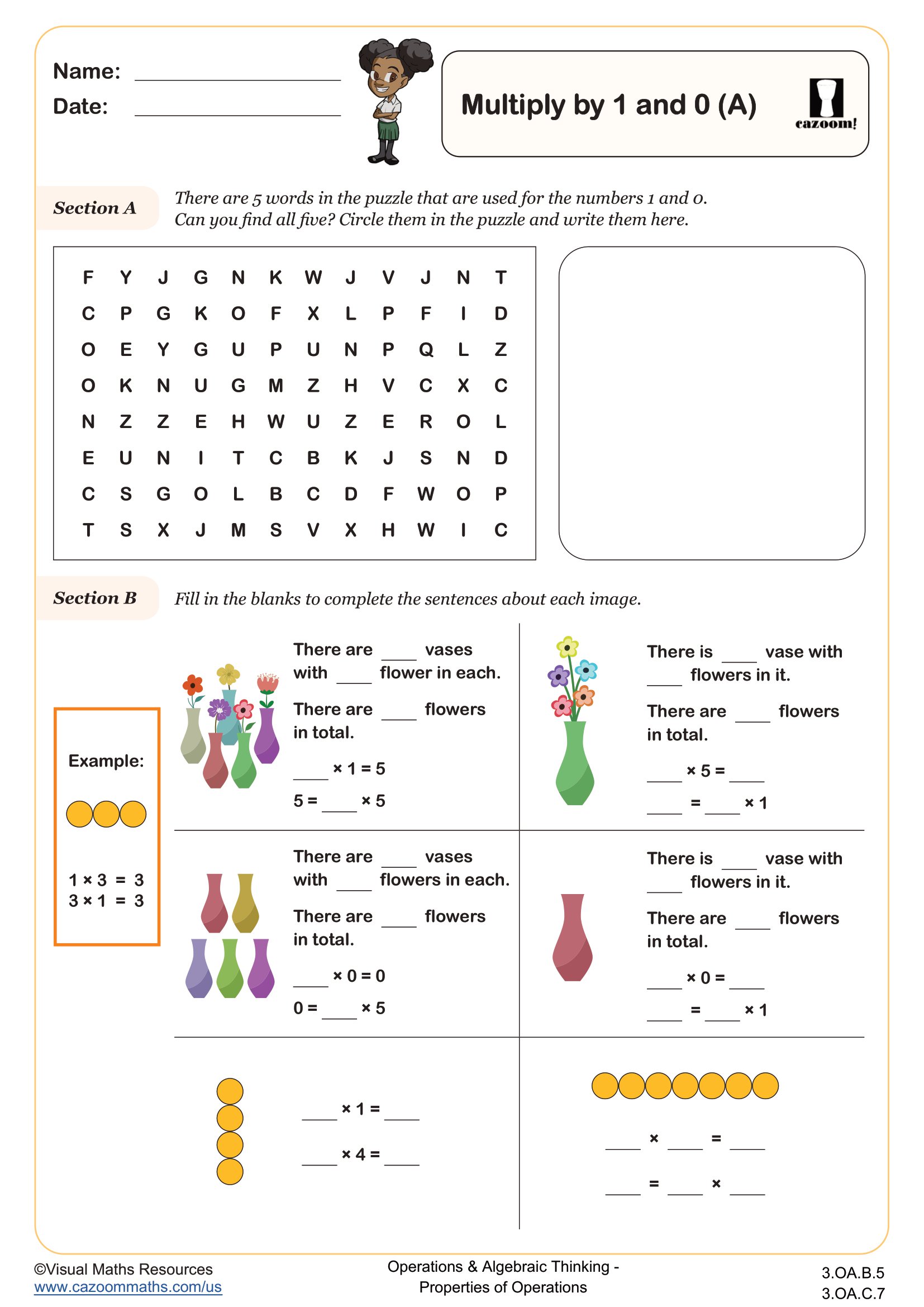
Back to:
Multiplying by 1 and 0 (B) WORKSHEET
Suitable for Grades: 3rd Grade
CCSS: 3.OA.B.5, 3.OA.C.7
CCSS Description: Apply properties of operations as strategies to multiply and divide.2 Examples: If 6 × 4 = 24 is known, then 4 × 6 = 24 is also known. (Commutative property of multiplication.) 3 × 5 × 2 can be found by 3 × 5 = 15, then 15 × 2 = 30, or by 5 × 2 = 10, then 3 × 10 = 30. (Associative property of multiplication.) Knowing that 8 × 5 = 40 and 8 × 2 = 16, one can find 8 × 7 as 8 × (5 + 2) = (8 × 5) + (8 × 2) = 40 + 16 = 56. (Distributive property.)
Fluently multiply and divide within 100, using strategies such as the relationship between multiplication and division (e.g., knowing that 8 × 5 = 40, one knows 40 ÷ 5 = 8) or properties of operations. By the end of Grade 3, know from memory all products of two one-digit numbers.
Fluently multiply and divide within 100, using strategies such as the relationship between multiplication and division (e.g., knowing that 8 × 5 = 40, one knows 40 ÷ 5 = 8) or properties of operations. By the end of Grade 3, know from memory all products of two one-digit numbers.
Multiplying by 1 and 0 (B) WORKSHEET DESCRIPTION
Part of students being able to multiply and divide mentally includes understanding the effects of multiplying by 1 and 0.
Imagery is used in section A to demonstrate the effects of multiplying by 1 and 0.
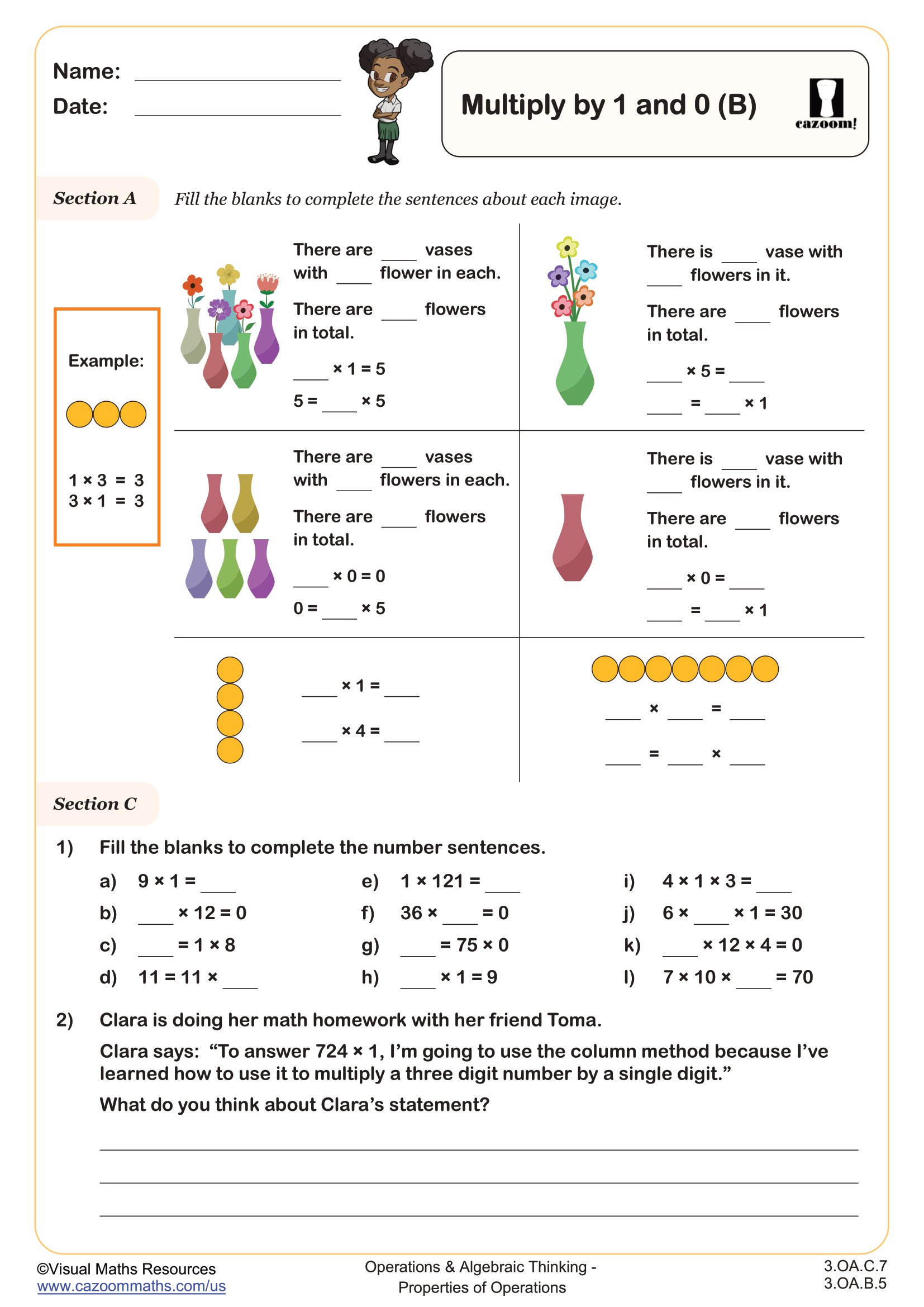
Students will fill gaps in number sentences in section B where numbers are multiplied by 1 and 0, as well as articulating themselves as they evaluate two statements regarding multiplying by 1 and 0.
In section C students will complete two multiplication pyramids before deciding whether three statements are always, sometimes or never true.
RELATED TO Multiplying by 1 and 0 (B) WORKSHEET
Frequently Asked Questions
This multiplying by 1 and 0 (b) worksheet is designed for students in 3rd Grade and aligns with Common Core State Standards.