Back to:
Polynomial Addition Pyramids (C) WORKSHEET
Suitable for Grades: Algebra I, IM 1
CCSS: 6.EE.A.4, HSA.APR.A.1, HSA.SSE.B.3
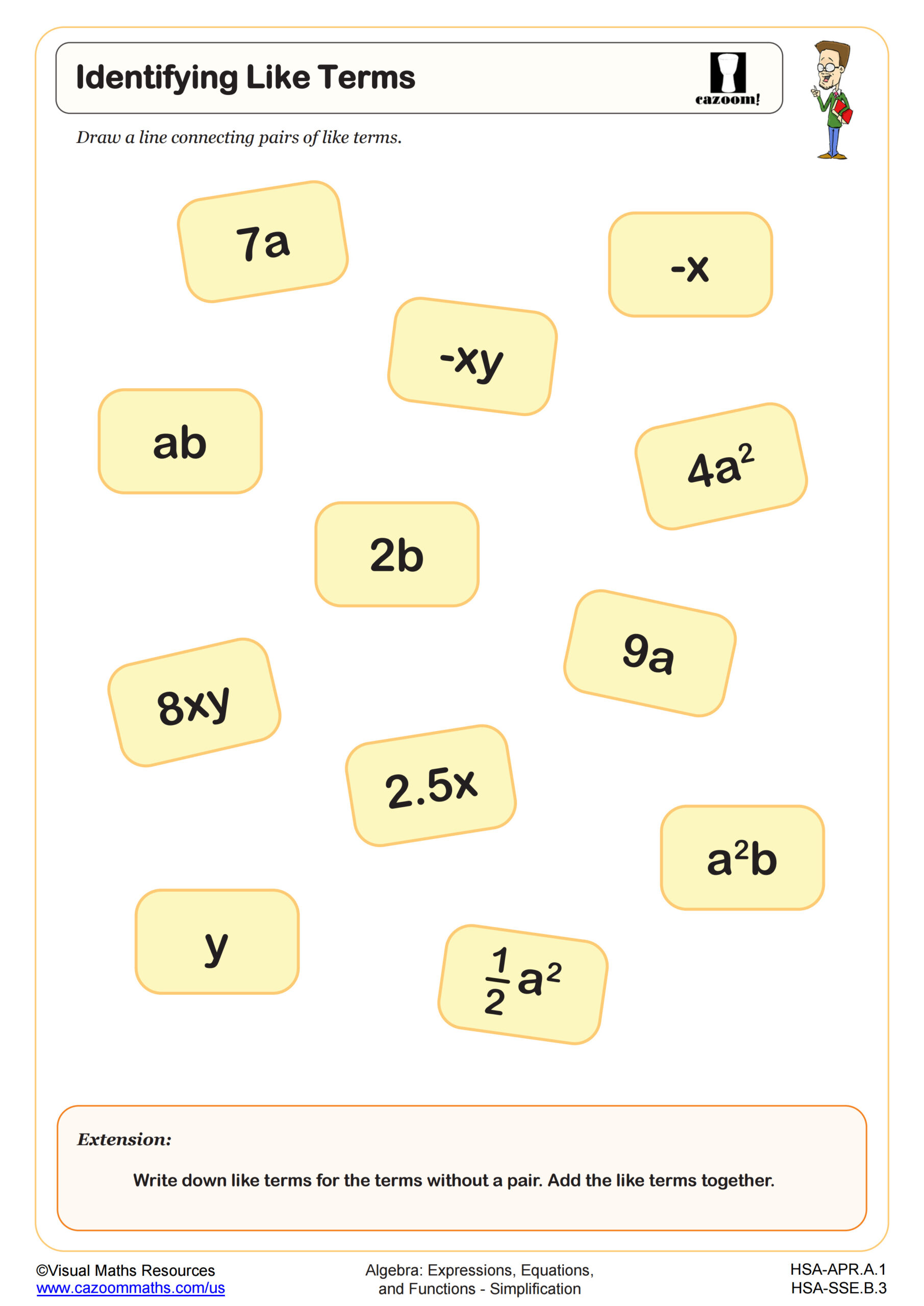
CCSS Description: Identify when two expressions are equivalent (i.e., when the two expressions name the same number regardless of which value is substituted into them). For example, the expressions y + y + y and 3y are equivalent because they name the same number regardless of which number y stands for.
Understand that polynomials form a system analogous to the integers, namely, they are closed under the operations of addition, subtraction, and multiplication; add, subtract, and multiply polynomials.
Choose and produce an equivalent form of an expression to reveal and explain properties of the quantity represented by the expression.★ a. Factor a quadratic expression to reveal the zeros of the function it defines. b. Complete the square in a quadratic expression to reveal the maximum or minimum value of the function it defines. c. Use the properties of exponents to transform expressions for exponential functions. For example the expression 1.15t can be rewritten as (1.151/12)12t ≈ 1.01212t to reveal the approximate equivalent monthly interest rate if the annual rate is 15%
Understand that polynomials form a system analogous to the integers, namely, they are closed under the operations of addition, subtraction, and multiplication; add, subtract, and multiply polynomials.
Choose and produce an equivalent form of an expression to reveal and explain properties of the quantity represented by the expression.★ a. Factor a quadratic expression to reveal the zeros of the function it defines. b. Complete the square in a quadratic expression to reveal the maximum or minimum value of the function it defines. c. Use the properties of exponents to transform expressions for exponential functions. For example the expression 1.15t can be rewritten as (1.151/12)12t ≈ 1.01212t to reveal the approximate equivalent monthly interest rate if the annual rate is 15%
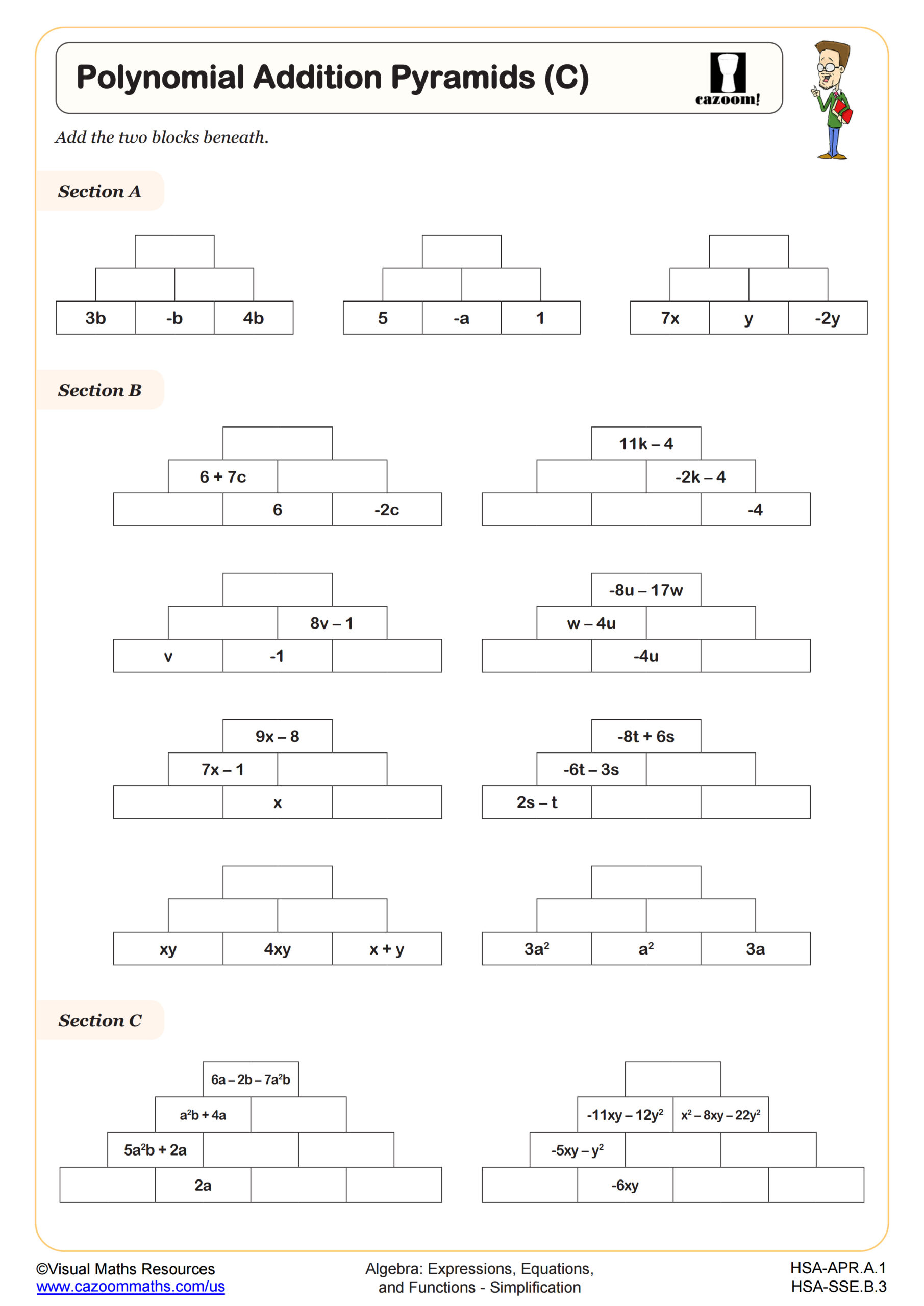
Polynomial Addition Pyramids (C) WORKSHEET DESCRIPTION
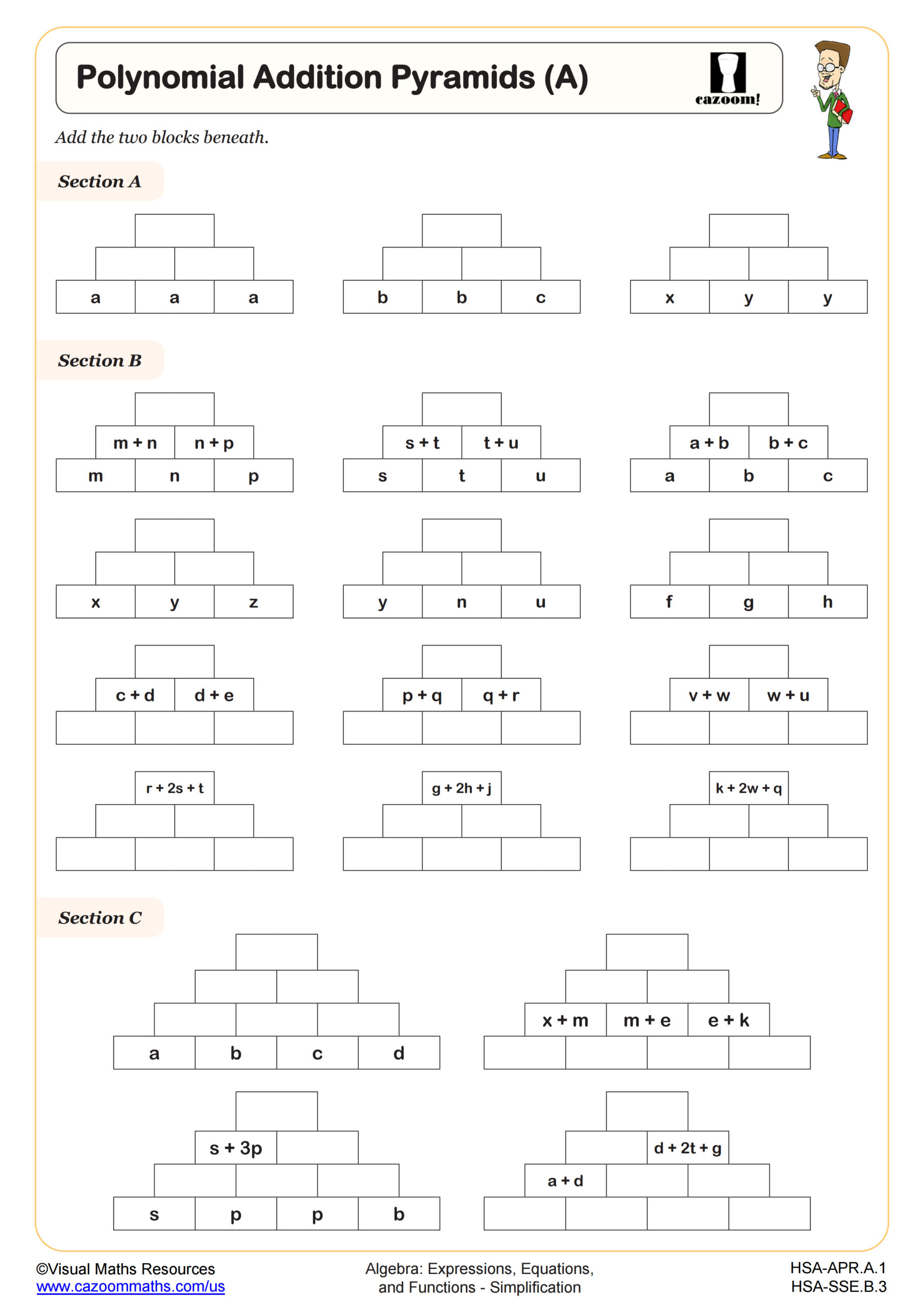
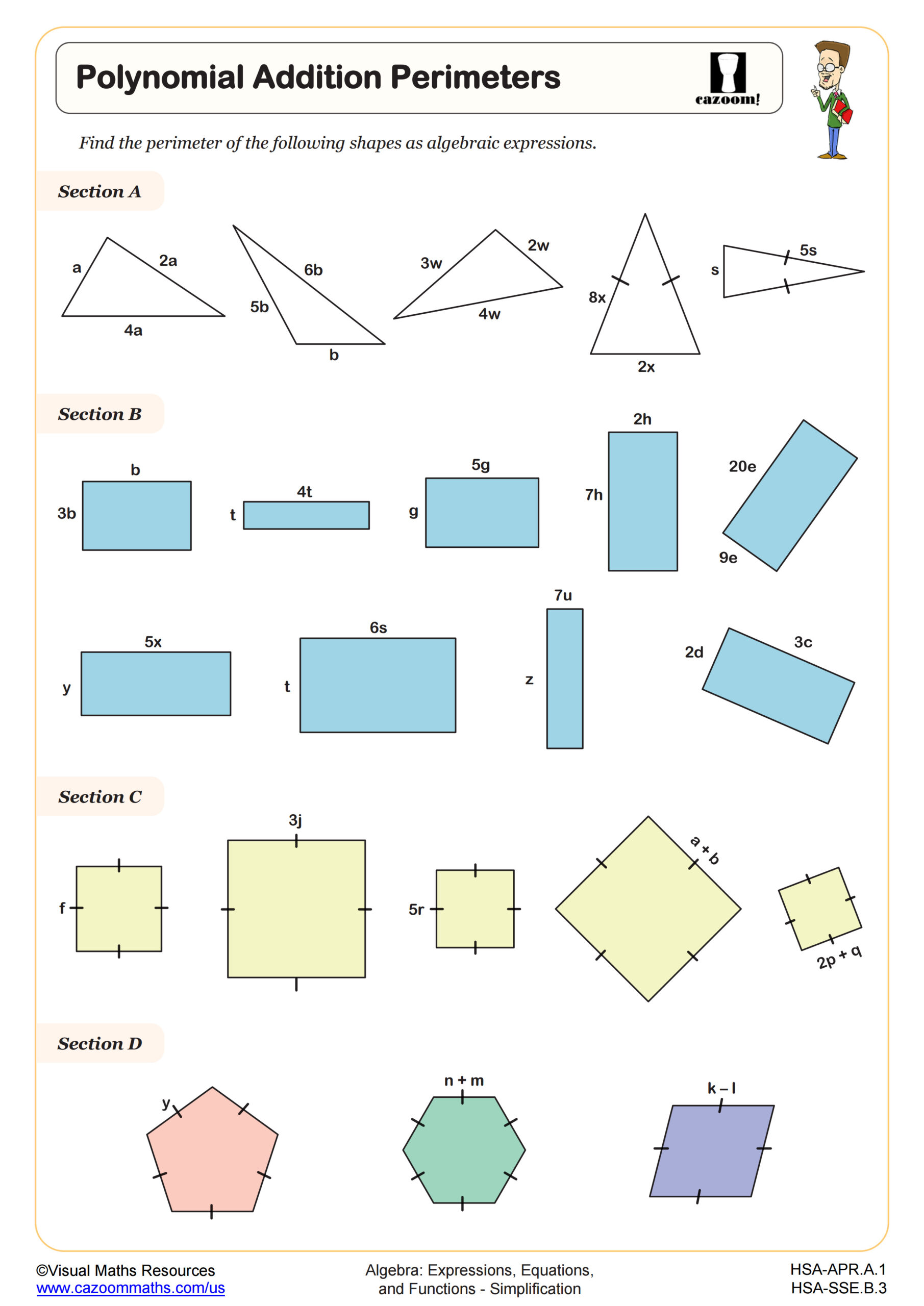
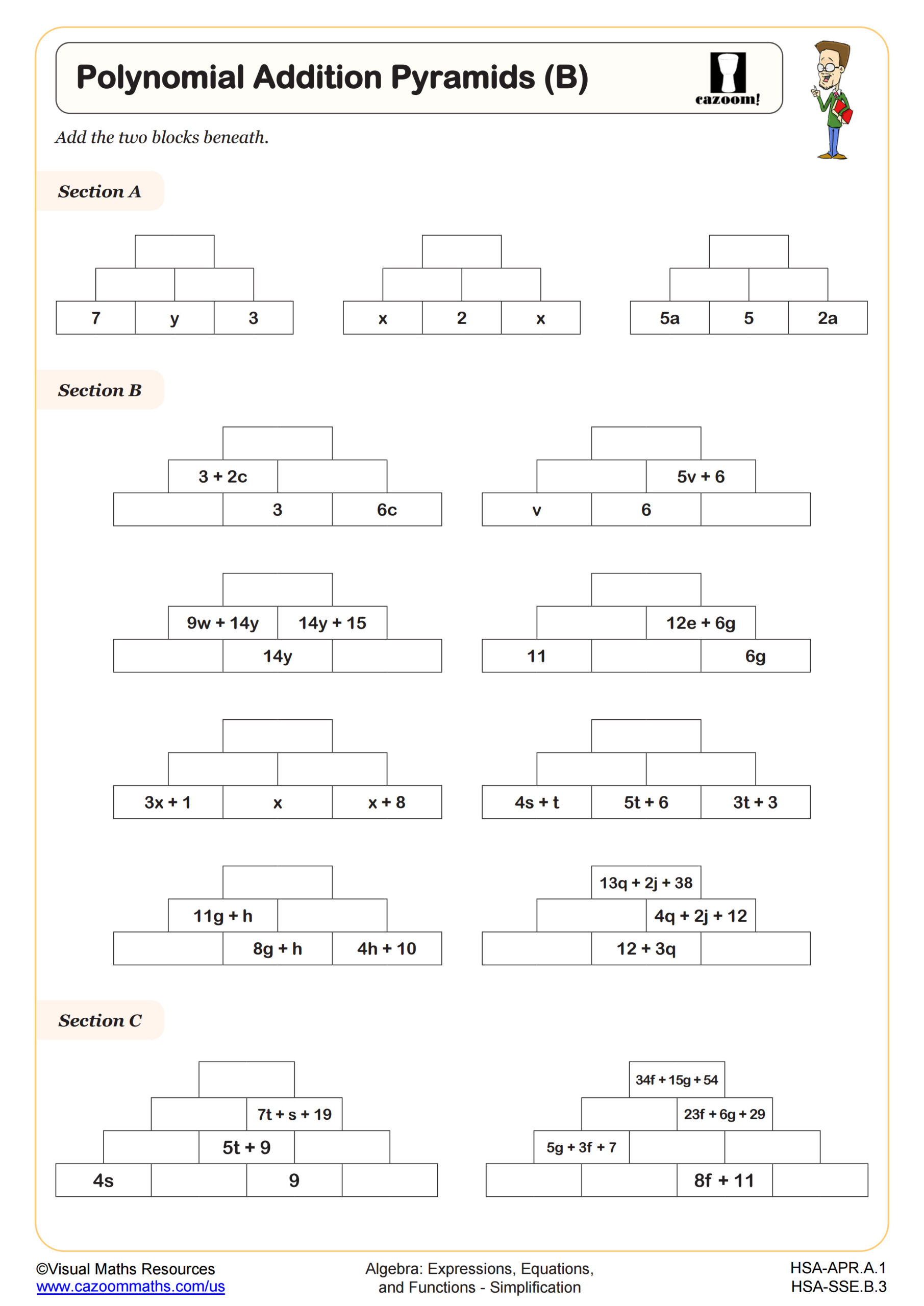
The worksheet provides a familiar activity for synthesizing the skills of combining like terms and simplifying expressions. The worksheet has three sections that give an increasing level of difficulty. The addition pyramids begin with three rows and then progress to four rows with more complicated expressions to add. This worksheet extends on Polynomial Addition Pyramids (B) by including negative terms and exponents.
RELATED TO Polynomial Addition Pyramids (C) WORKSHEET
Frequently Asked Questions
This polynomial addition pyramids (c) worksheet is designed for students in Algebra I and IM 1 and aligns with Common Core State Standards.