Back to:
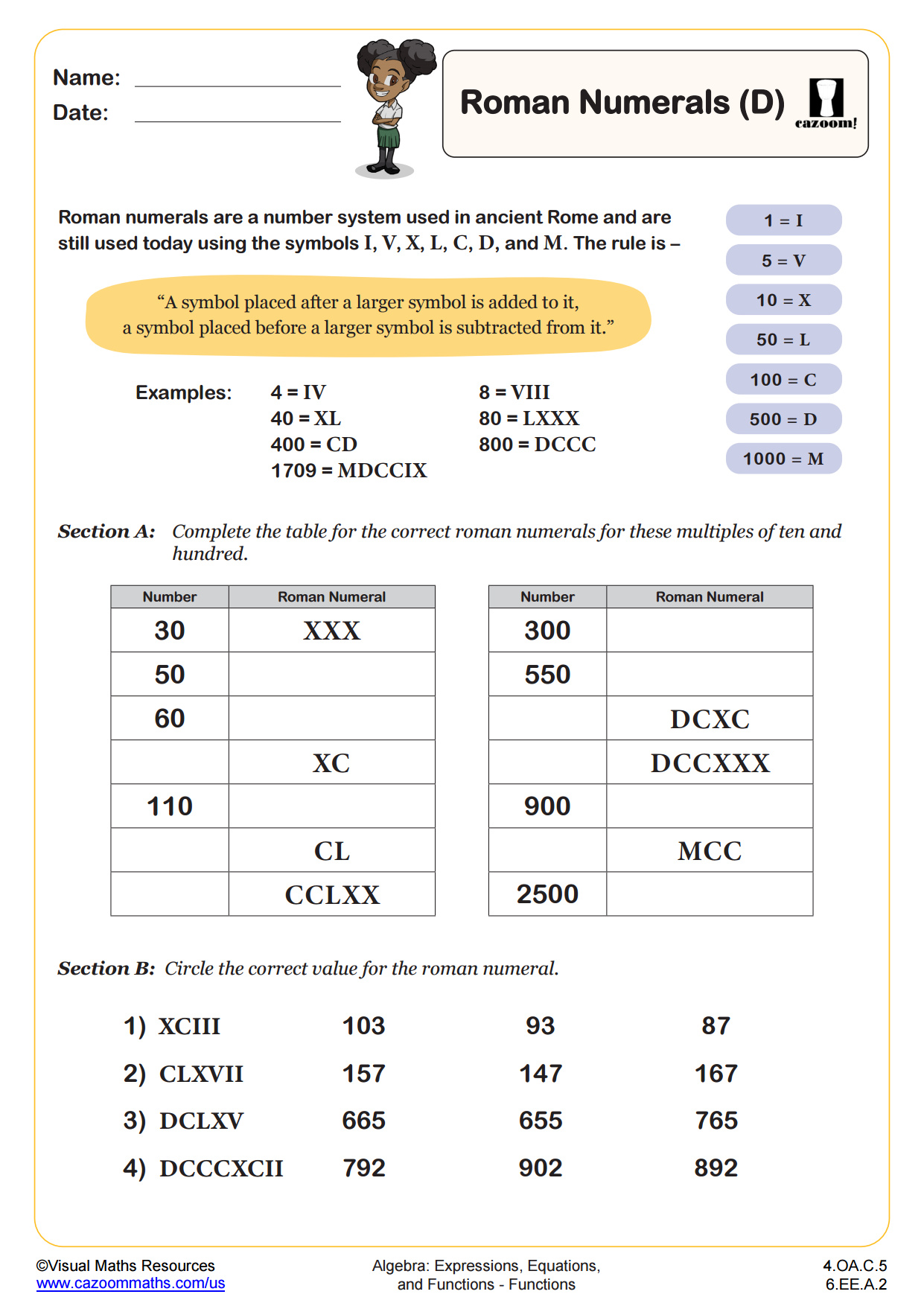
Roman Numerals (D) WORKSHEET
Suitable for Grades: 4th Grade, 6th Grade
CCSS: 4.OA.C.5, 6.EE.A.2
CCSS Description: Generate a number or shape pattern that follows a given rule. Identify apparent features of the pattern that were not explicit in the rule itself. For example, given the rule “Add 3” and the starting number 1, generate terms in the resulting sequence and observe that the terms appear to alternate between odd and even numbers. Explain informally why the numbers will continue to alternate in this way
Write, read, and evaluate expressions in which letters stand for numbers. a. Write expressions that record operations with numbers and with letters standing for numbers. For example, express the calculation “Subtract y from 5” as 5 – y.b. Identify parts of an expression using mathematical terms (sum, term, product, factor, quotient, coefficient); view one or more parts of an expression as a single entity. For example, describe the expression 2 (8 + 7) as a product of two factors; view (8 + 7) as both a single entity and a sum of two terms. c. Evaluate expressions at specific values of their variables. Include expressions that arise from formulas used in real-world problems. Perform arithmetic operations, including those involving whole-number exponents, in the conventional order when there are no parentheses to specify a particular order (Order of Operations). For example, use the formulas V = s3 and A = 6 s2 to find the volume and surface area of a cube with sides of length s = 1/2.
Write, read, and evaluate expressions in which letters stand for numbers. a. Write expressions that record operations with numbers and with letters standing for numbers. For example, express the calculation “Subtract y from 5” as 5 – y.b. Identify parts of an expression using mathematical terms (sum, term, product, factor, quotient, coefficient); view one or more parts of an expression as a single entity. For example, describe the expression 2 (8 + 7) as a product of two factors; view (8 + 7) as both a single entity and a sum of two terms. c. Evaluate expressions at specific values of their variables. Include expressions that arise from formulas used in real-world problems. Perform arithmetic operations, including those involving whole-number exponents, in the conventional order when there are no parentheses to specify a particular order (Order of Operations). For example, use the formulas V = s3 and A = 6 s2 to find the volume and surface area of a cube with sides of length s = 1/2.
Roman Numerals (D) WORKSHEET DESCRIPTION
This worksheet extends students' knowledge of roman numerals to numbers up to 1000 and beyond
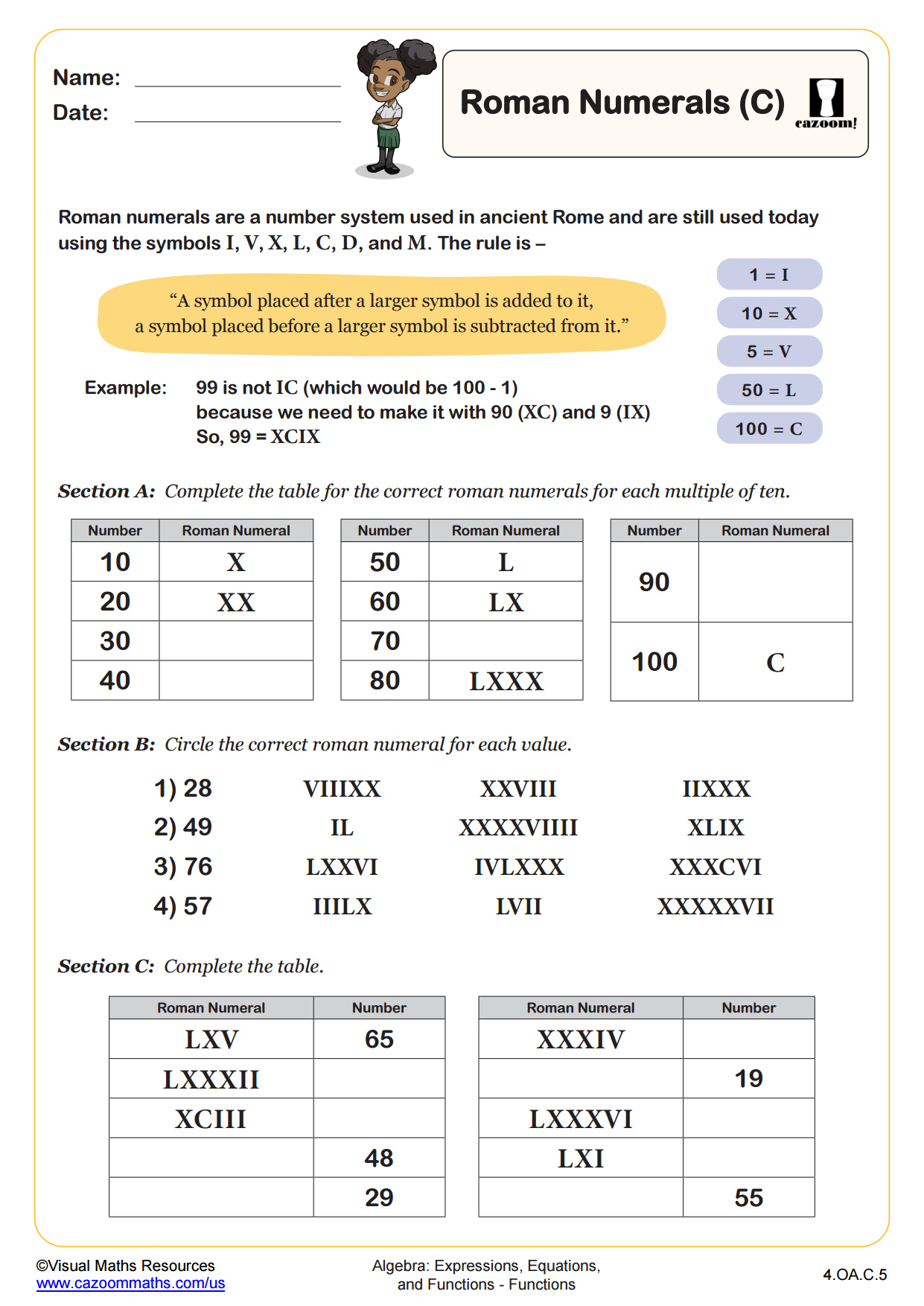
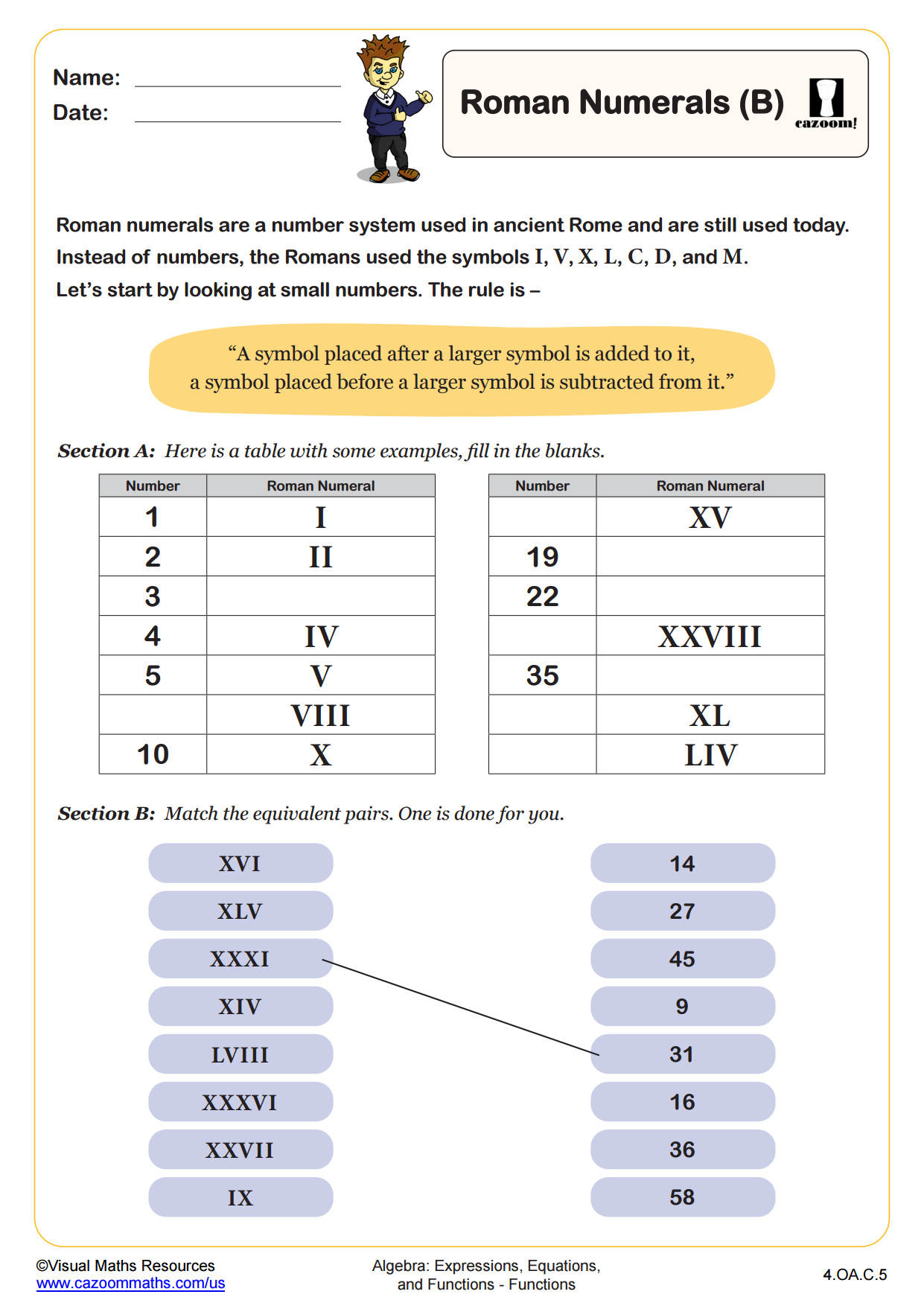
In section A children will either identify roman numerals or write numbers as roman numerals. All numbers here are multiples of 10 or 100. Section B is a multiple choice activity. students must correctly identify roman numerals in numerical form. Then in section C students have to match up 7 numbers in numerical form to the corresponding roman numeral. Sections D and E provide a challenge for your learners as they will find the sums of roman numerals.
RELATED TO Roman Numerals (D) WORKSHEET
Frequently Asked Questions
This roman numerals (d) worksheet is designed for students in 4th Grade and 6th Grade and aligns with Common Core State Standards.