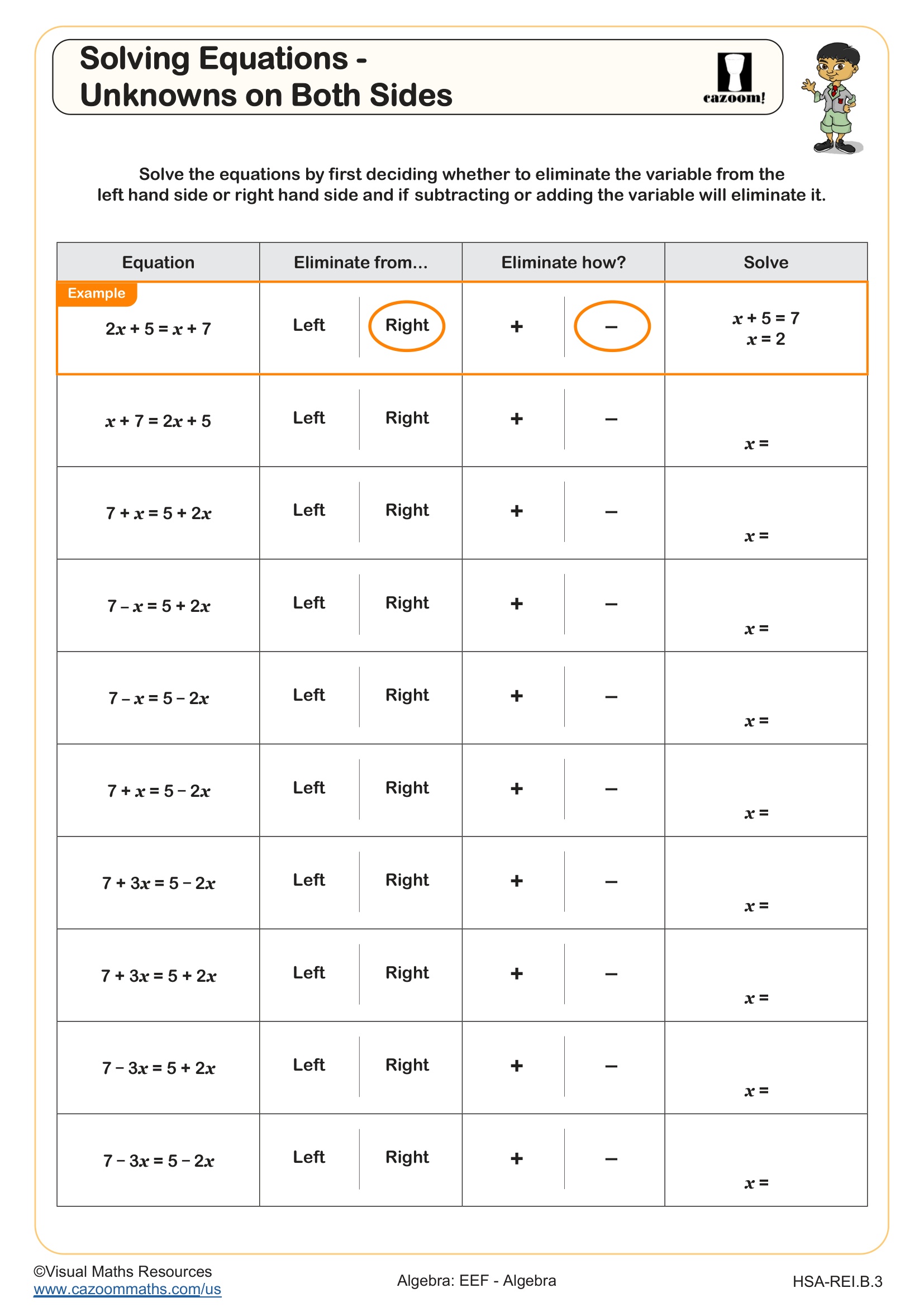
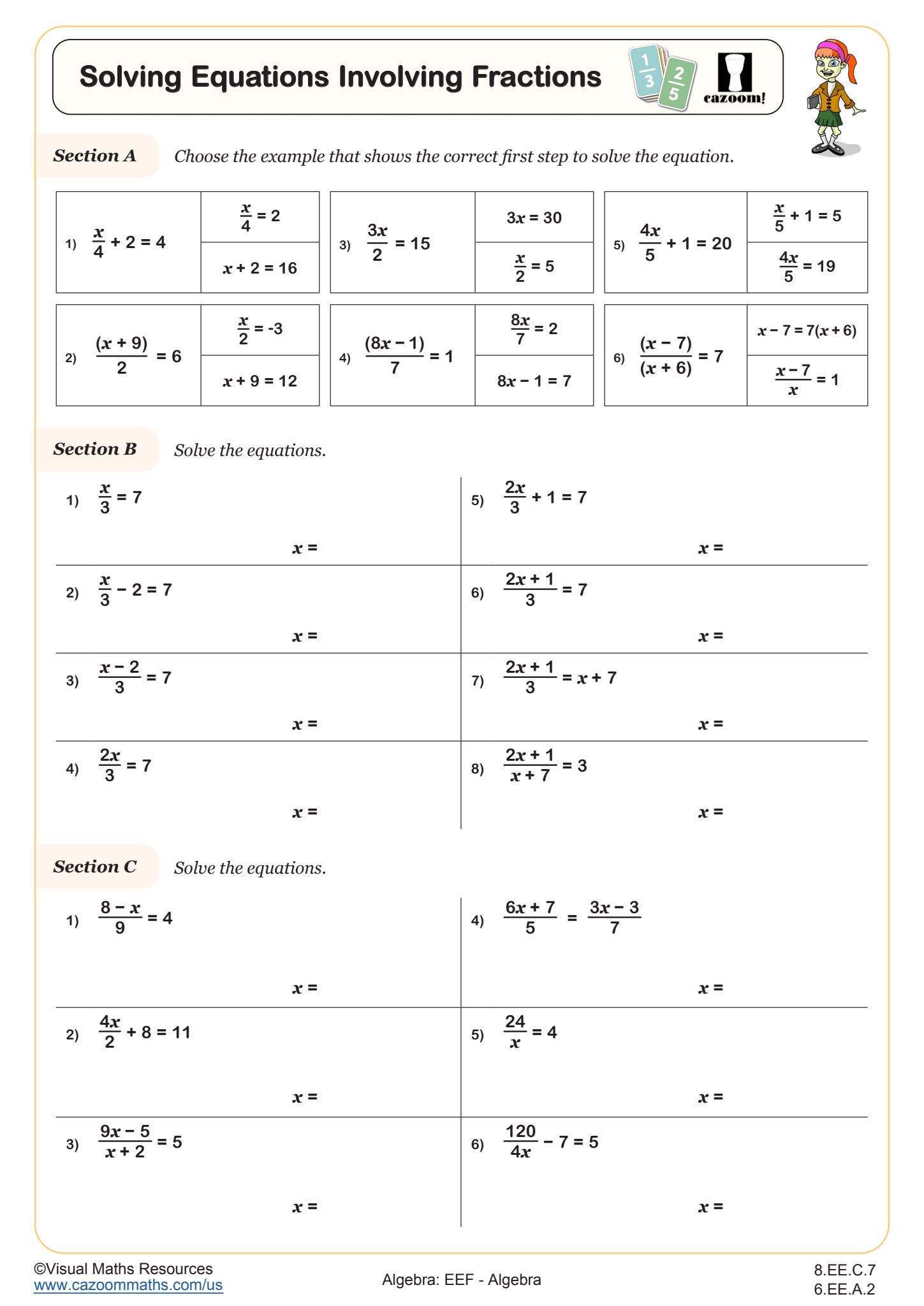
Solving Equations Involving Fractions WORKSHEET
Solve linear equations in one variable. a. Give examples of linear equations in one variable with one solution, infinitely many solutions, or no solutions. Show which of these possibilities is the case by successively transforming the given equation into simpler forms, until an equivalent equation of the form x = a, a = a, or a = b results (where a and b are different numbers). b. Solve linear equations with rational number coefficients, including equations whose solutions require expanding expressions using the distributive property and collecting like terms.
Solving Equations Involving Fractions WORKSHEET DESCRIPTION
This worksheet systematically develops students' skills in solving linear equations involving fractions.
Section A challenges students to identify the correct first step for various fractional equation types.
Section B consists of 8 minimally different and increasingly difficult equations to solve. This helps students to see how small changes affect the order of inverse operations and gradually builds confidence to solve complex equations.
There are a further 6 equations to be solved in Section C which do not follow the same structure as in Section B.
Solutions to equations are positive and negative throughout as well as integer, fractions and decimals numbers.
RELATED TO Solving Equations Involving Fractions WORKSHEET
Frequently Asked Questions
This solving equations involving fractions worksheet is designed for students in 6th Grade and 8th Grade and aligns with Common Core State Standards.