Back to:
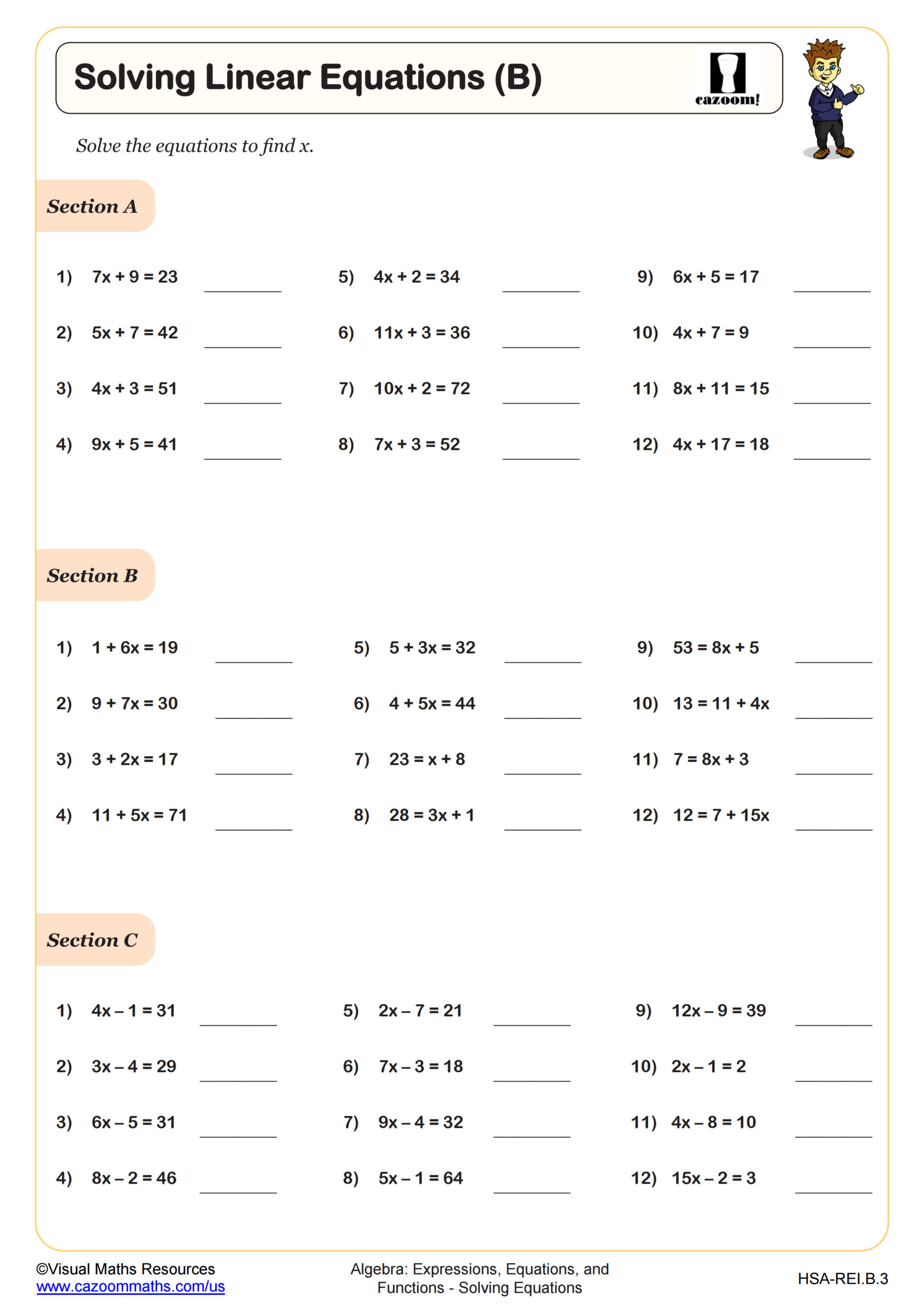
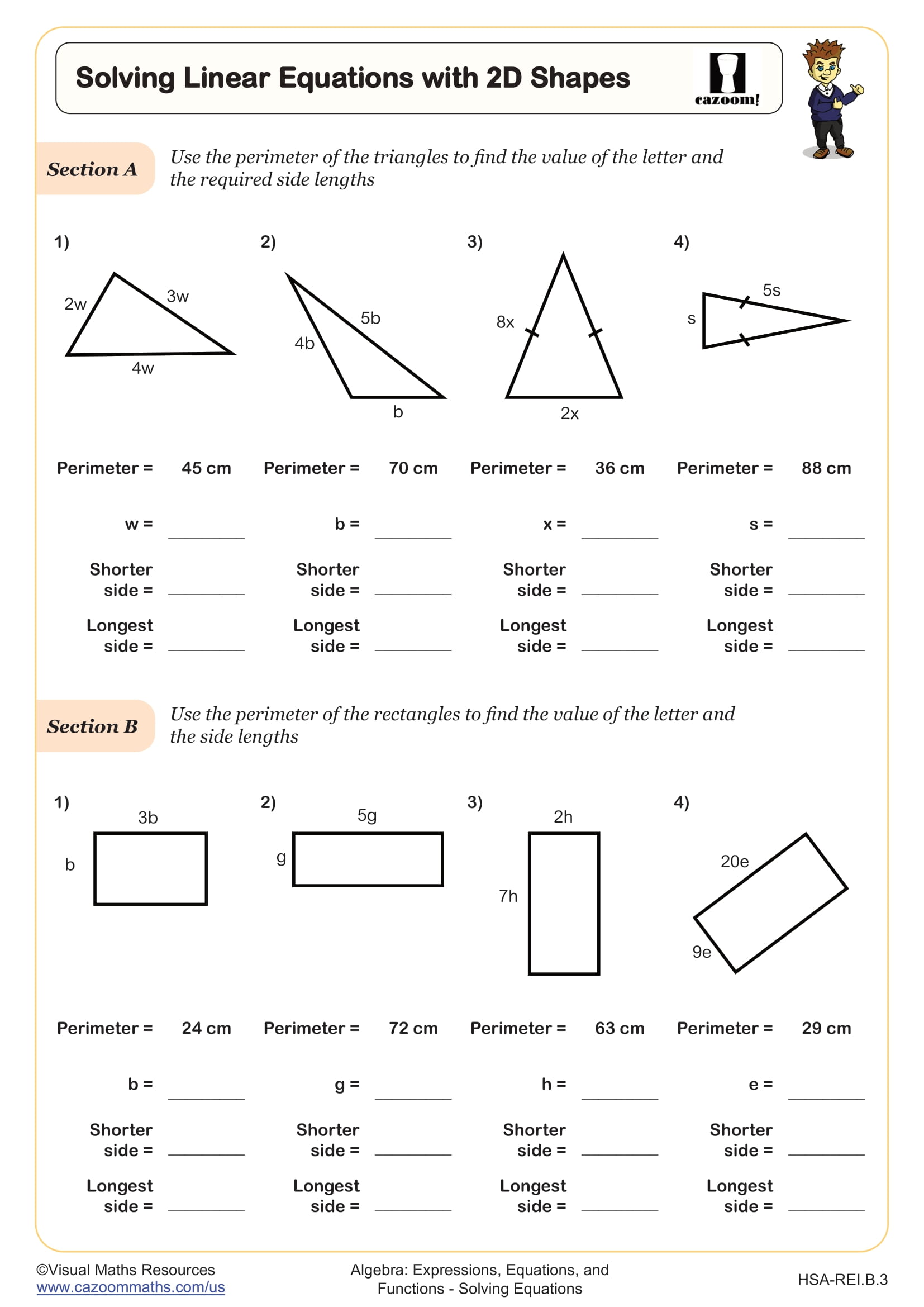
Solving Linear Equations with 2D Shapes WORKSHEET
Suitable for Grades: Algebra I, IM 1
CCSS: 6.EE.B.7, 7.EE.B.4, HSA.REI.B.3
CCSS Description: Solve real‑world and mathematical problems by writing and solving equations of the form x + p = q and p x = q for nonnegative rational numbers.
Use variables to represent quantities in a real-world or mathematical problem, and construct simple equations and inequalities to solve problems by reasoning about the quantities. a. Solve word problems leading to equations of the form px + q = r and p(x + q) = r, where p, q, and r are specific rational numbers. Solve equations of these forms fluently. Compare an algebraic solution to an arithmetic solution, identifying the sequence of the operations used in each approach. For example, the perimeter of a rectangle is 54 cm. Its length is 6 cm. What is its width? b. Solve word problems leading to inequalities of the form px + q > r or px + q < r, where p, q, and r are specific rational numbers. Graph the solution set of the inequality and interpret it in the context of the problem. For example: As a salesperson, you are paid $50 per week plus $3 per sale. This week you want your pay to be at least $100. Write an inequality for the number of sales you need to make, and describe the solutions.
Solve linear equations and inequalities in one variable, including equations with coefficients represented by letters.
Use variables to represent quantities in a real-world or mathematical problem, and construct simple equations and inequalities to solve problems by reasoning about the quantities. a. Solve word problems leading to equations of the form px + q = r and p(x + q) = r, where p, q, and r are specific rational numbers. Solve equations of these forms fluently. Compare an algebraic solution to an arithmetic solution, identifying the sequence of the operations used in each approach. For example, the perimeter of a rectangle is 54 cm. Its length is 6 cm. What is its width? b. Solve word problems leading to inequalities of the form px + q > r or px + q < r, where p, q, and r are specific rational numbers. Graph the solution set of the inequality and interpret it in the context of the problem. For example: As a salesperson, you are paid $50 per week plus $3 per sale. This week you want your pay to be at least $100. Write an inequality for the number of sales you need to make, and describe the solutions.
Solve linear equations and inequalities in one variable, including equations with coefficients represented by letters.
Solving Linear Equations with 2D Shapes WORKSHEET DESCRIPTION
This worksheet is designed to help learners apply their knowledge of solving equations to finding missing lengths of 2D shapes when given algebraic side lengths and a known perimeter. Section A provides some scalene and isosceles triangles with algebraic side lengths. Section B provides rectangles. Section C presents squares, and section D presents some other shapes with equal side lengths. Learners will need to find the unknown letter and side lengths.
RELATED TO Solving Linear Equations with 2D Shapes WORKSHEET
Frequently Asked Questions
This solving linear equations with 2d shapes worksheet is designed for students in Algebra I and IM 1 and aligns with Common Core State Standards.