Subtracting Integers with Counters WORKSHEET
Subtracting Integers with Counters WORKSHEET DESCRIPTION
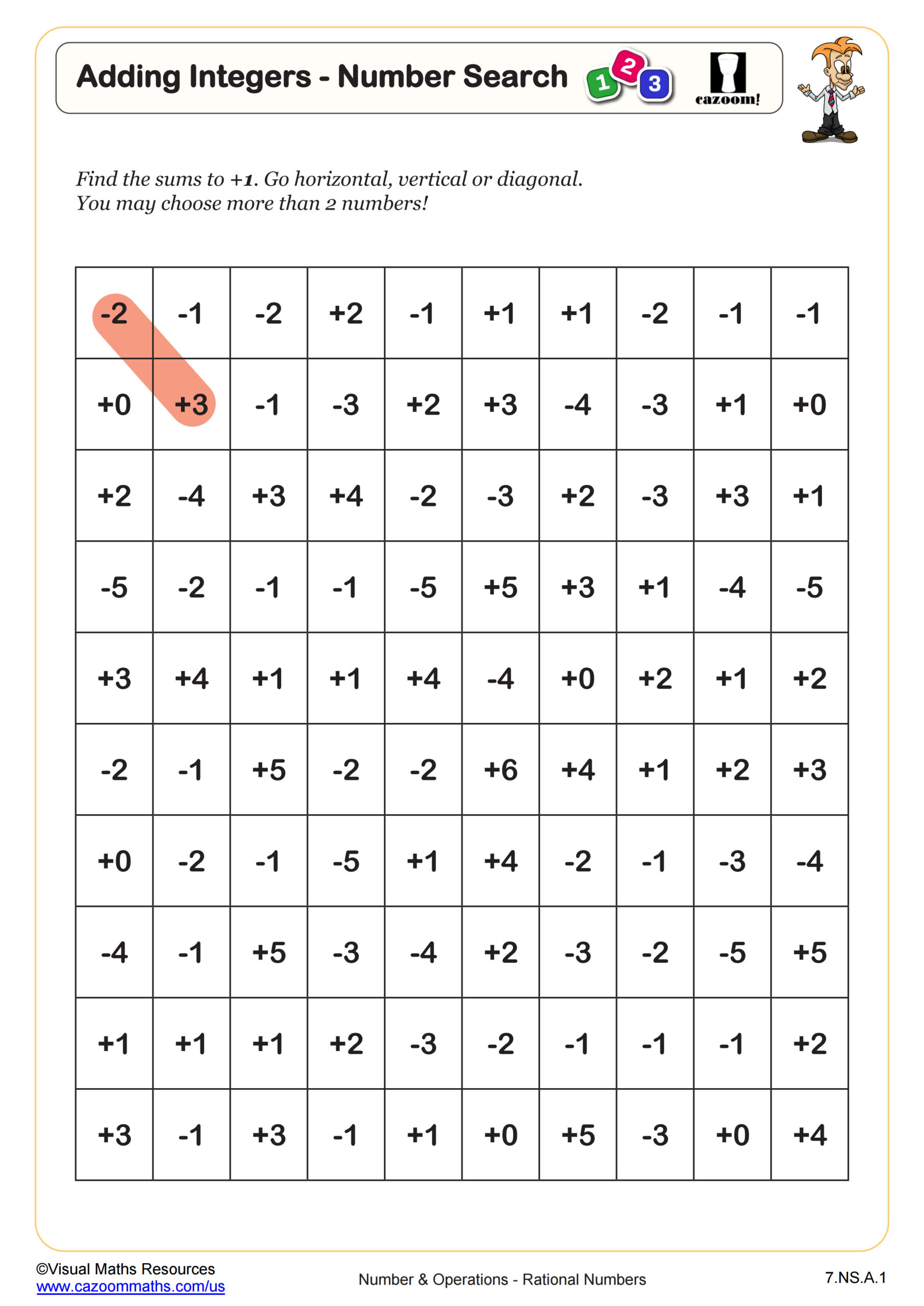
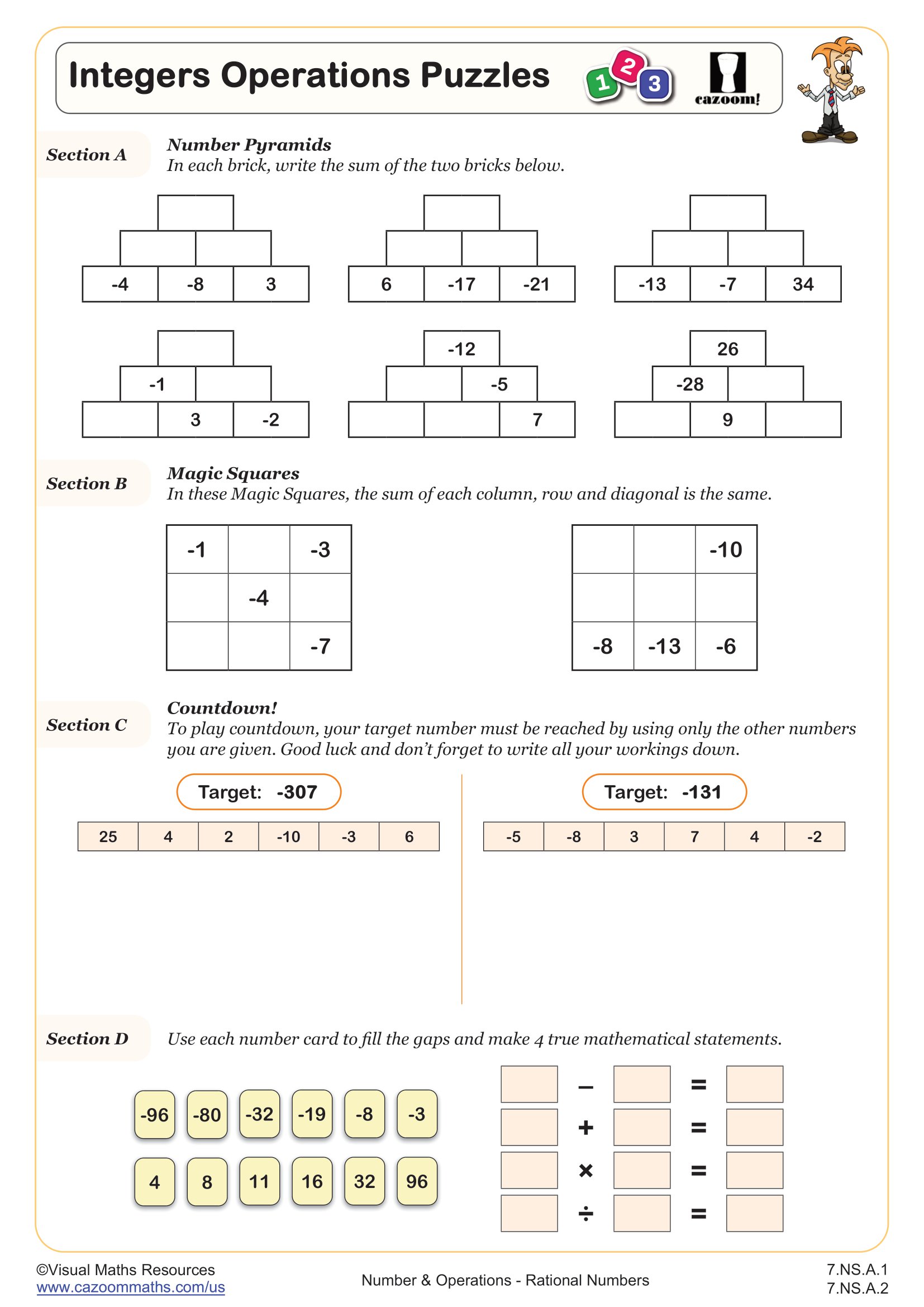
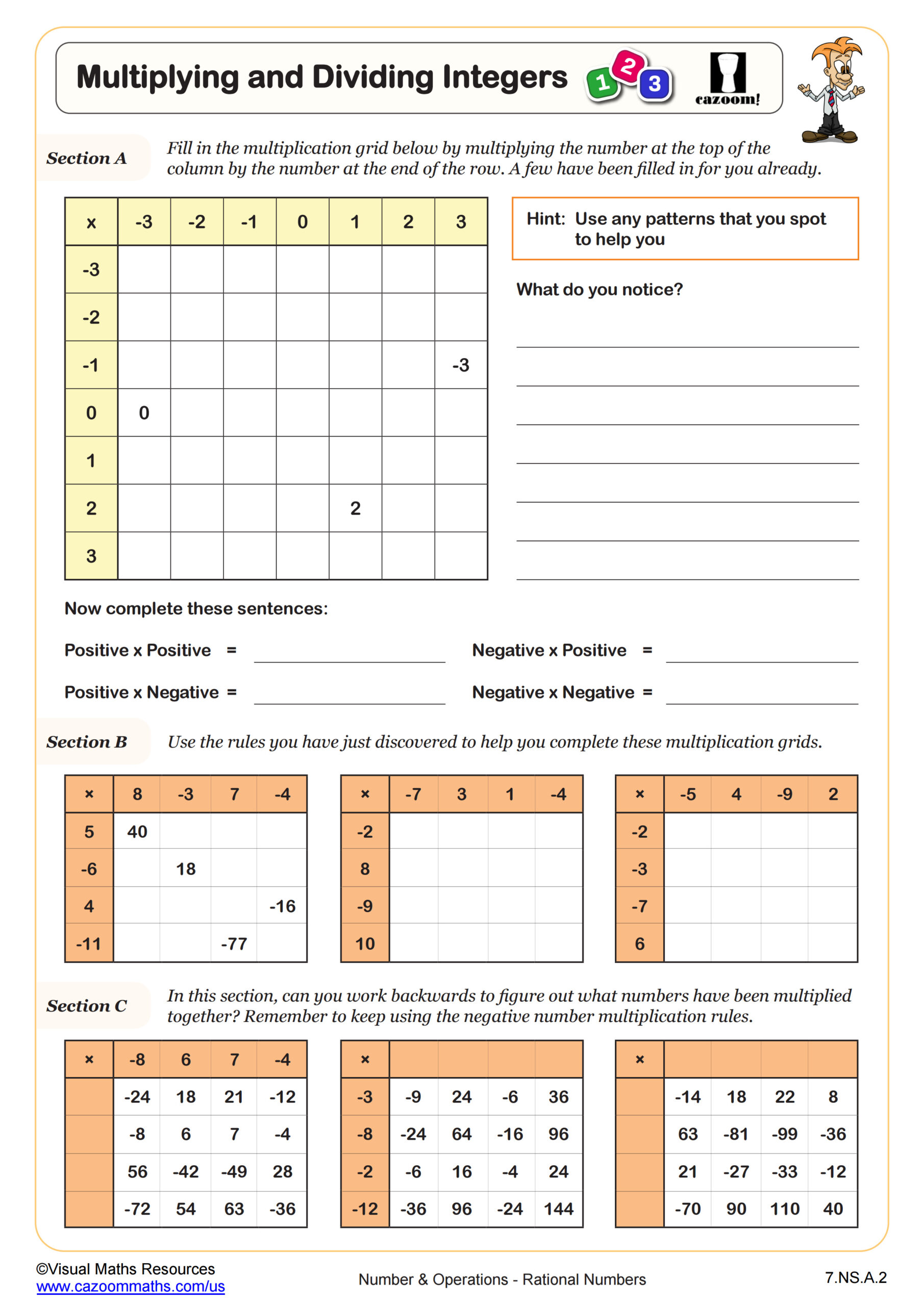
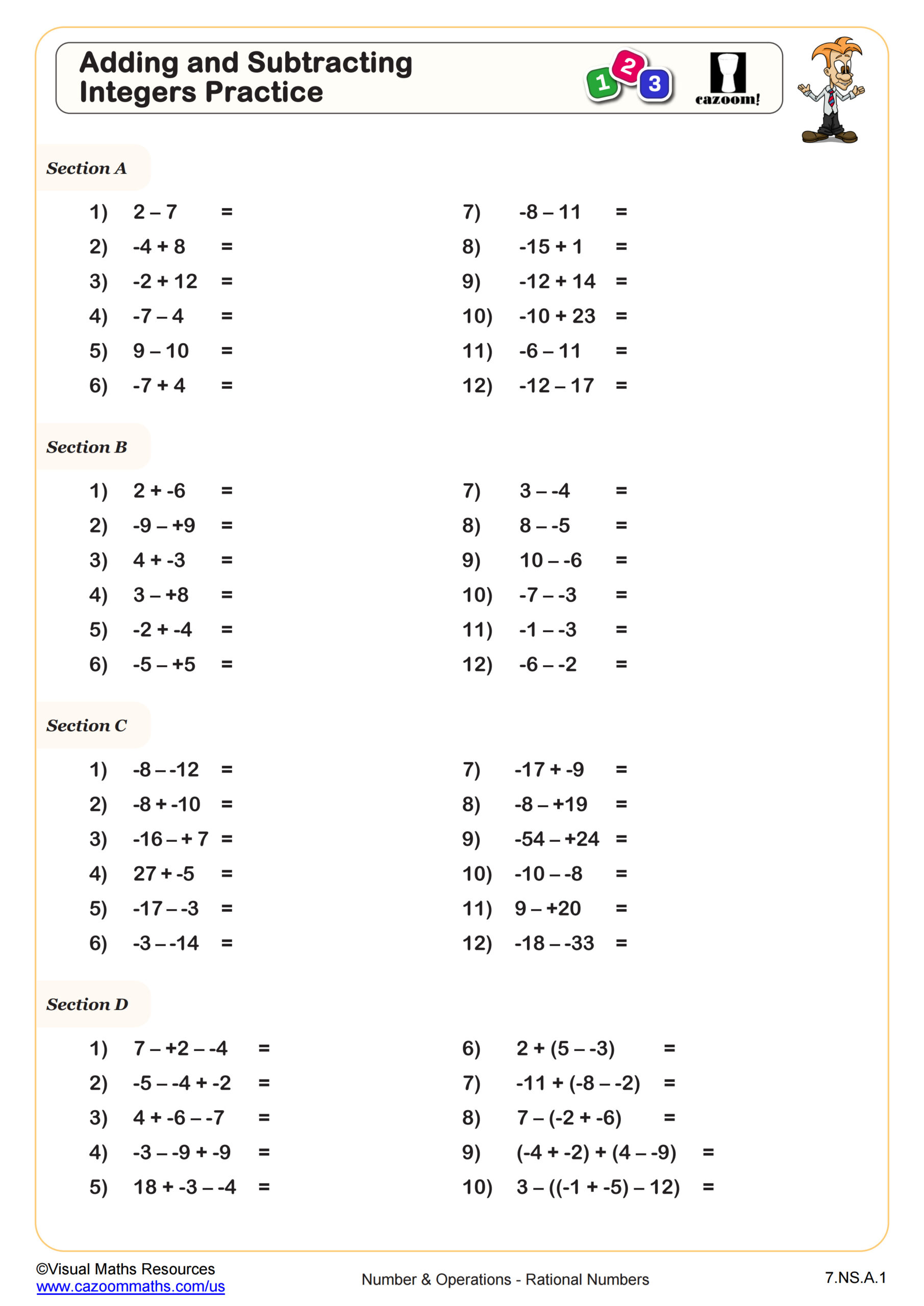
This worksheet uses directed number counters to make sense of subtraction with positive and negative numbers.
Starting with an example, section A requires students to state the calculation that an image of directed counters represents.
In section B, students will practice subtraction with directed numbers while drawing counters or using manipulatives to aid them.
Once students have articulated what they notice happens when negative numbers are subtracted, they are ready to answer the 20 questions in section C. Here, we encourage students to try without the use of manipulatives.
Our worksheet finishes with a puzzle where students will use a set of numbers to make eight correct subtraction statements.

RELATED TO Subtracting Integers with Counters WORKSHEET
Frequently Asked Questions
This subtracting integers with counters worksheet is designed for students in 7th Grade and aligns with Common Core State Standards.