Algebra I Linear Functions Worksheets
Drawing Gradients (A)
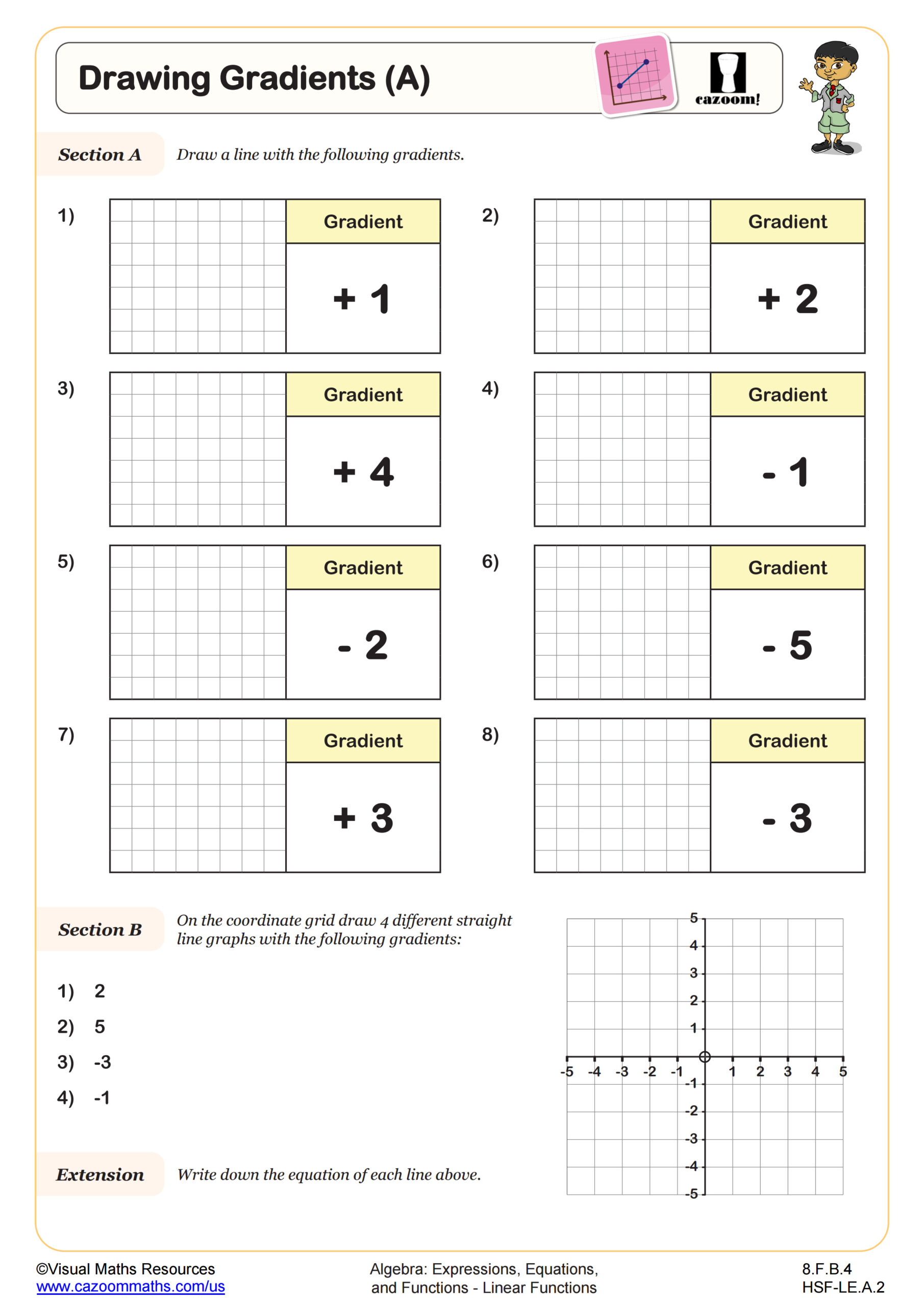
Drawing Gradients (B)
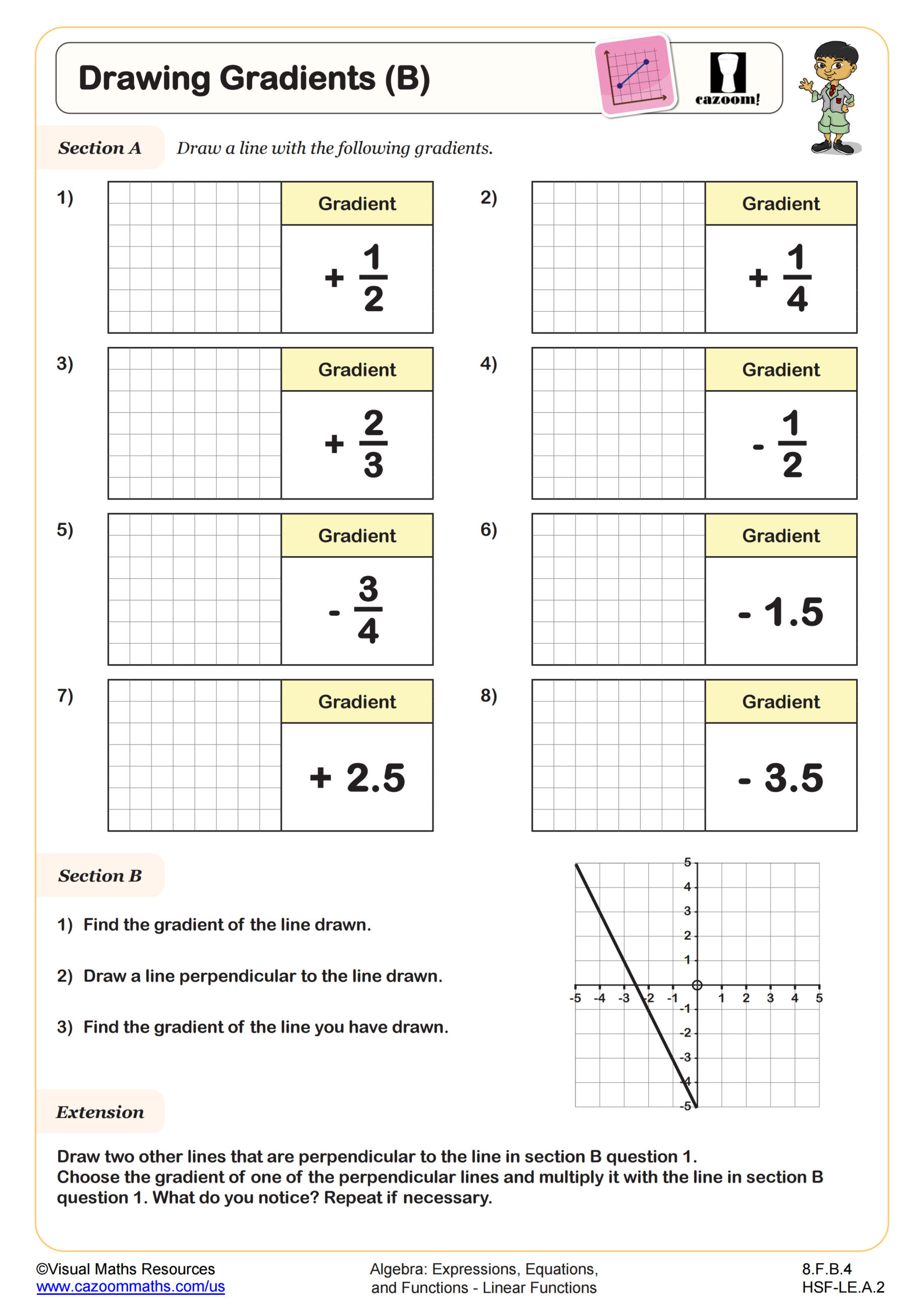
Equations of Parallel Lines
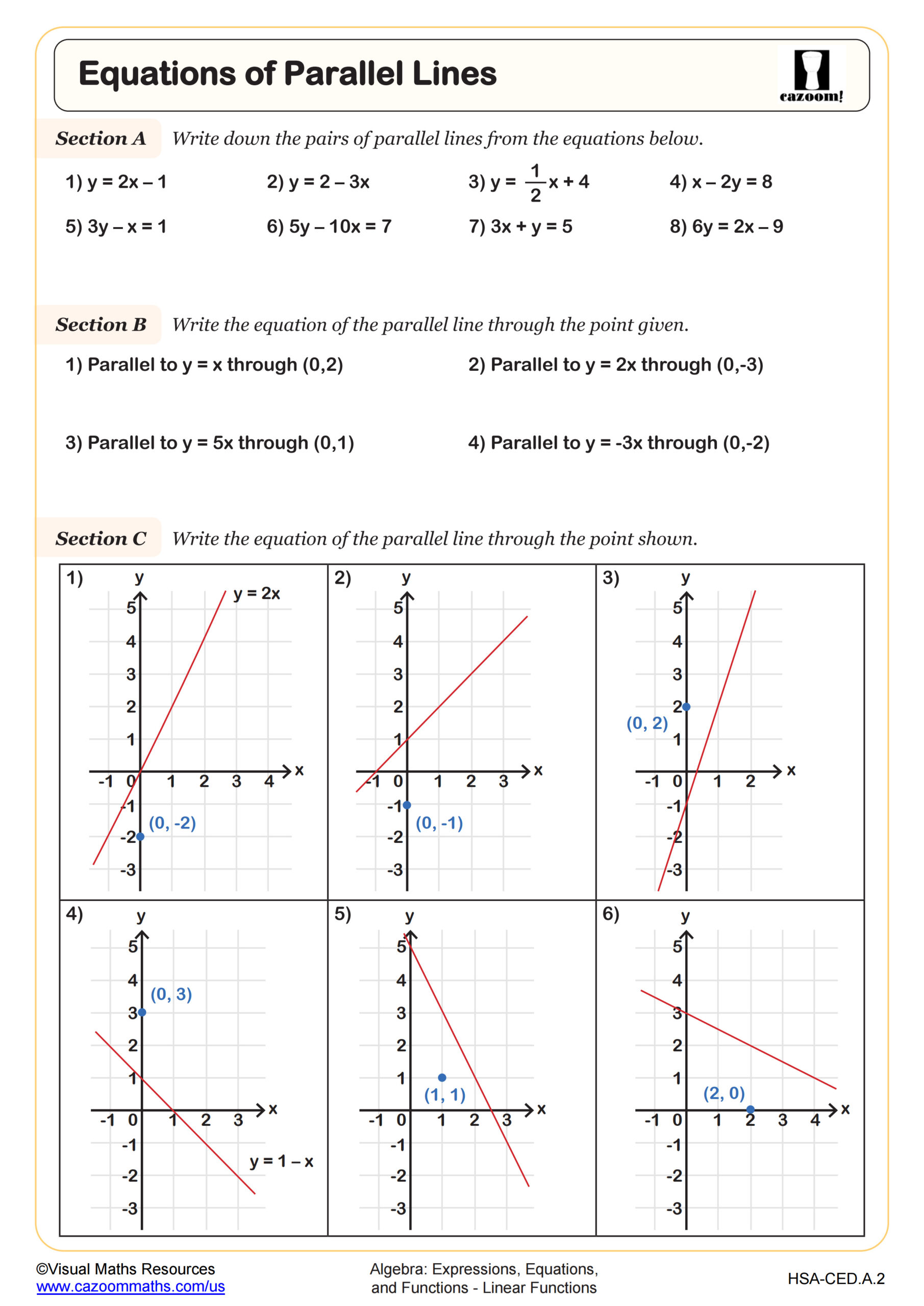
Equations of Perpendicular Lines
Finding Gradients
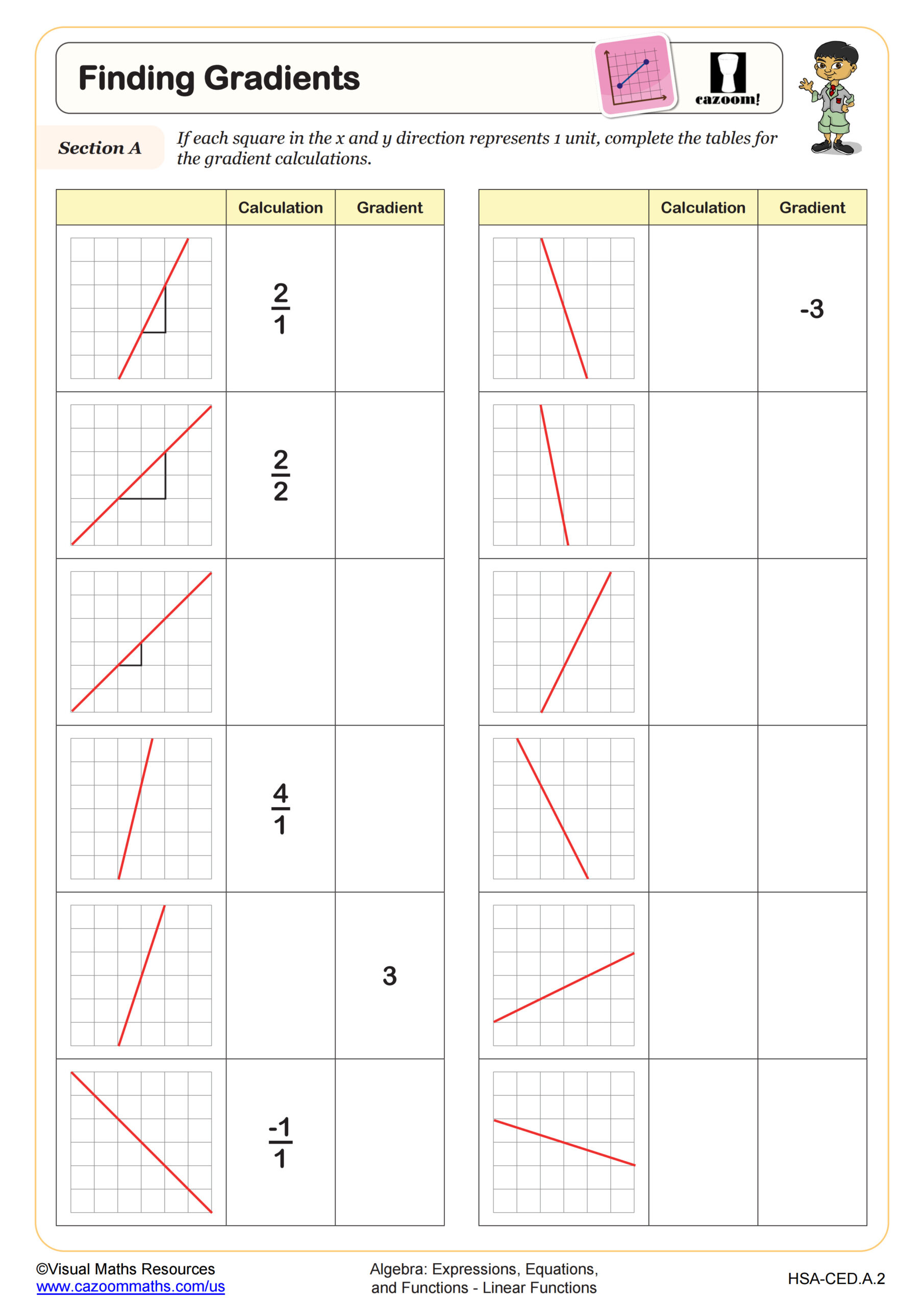
Introduction to Graphing Linear Functions
Investigating Linear Functions

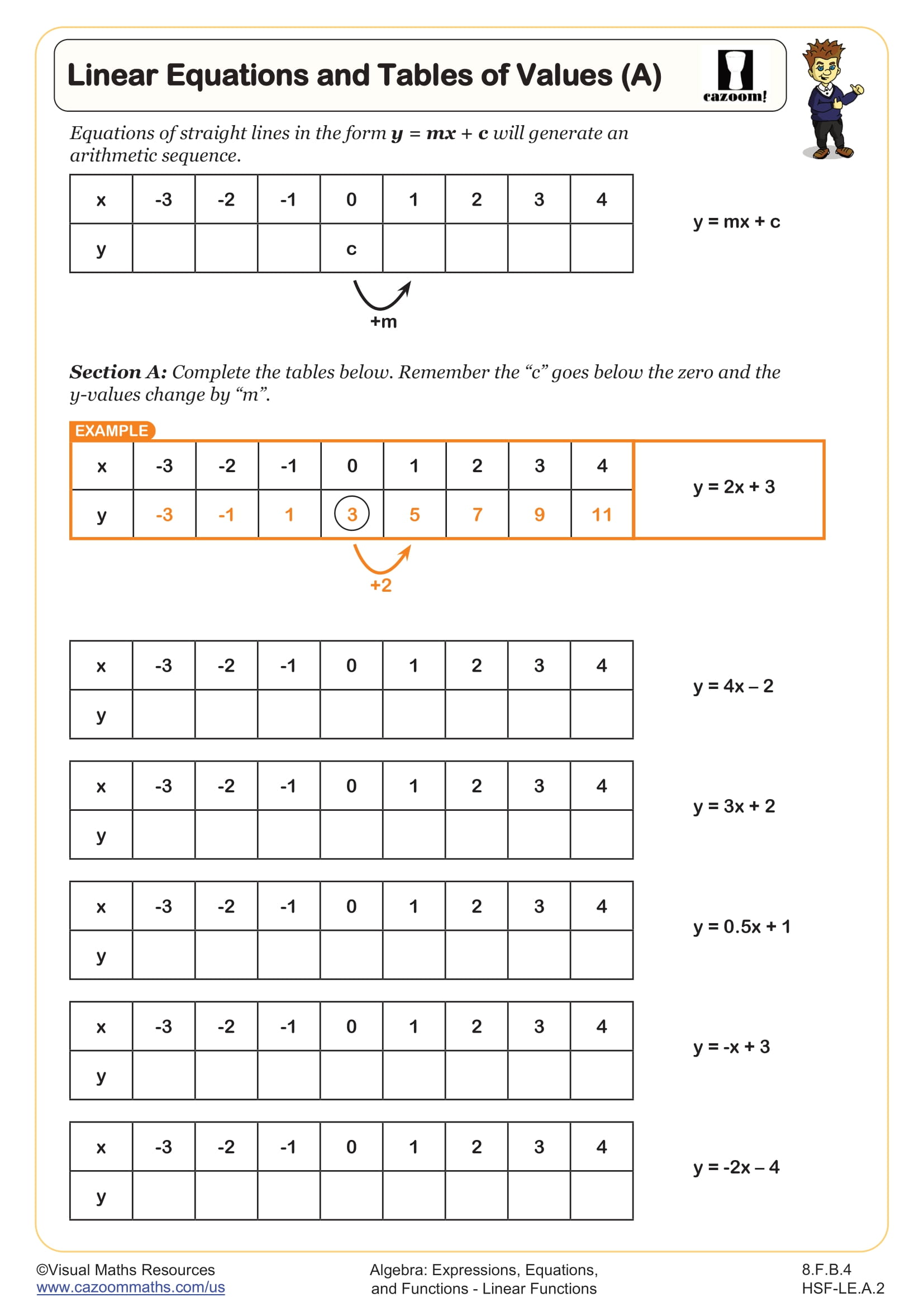
Linear Equations and Tables of Values (A)
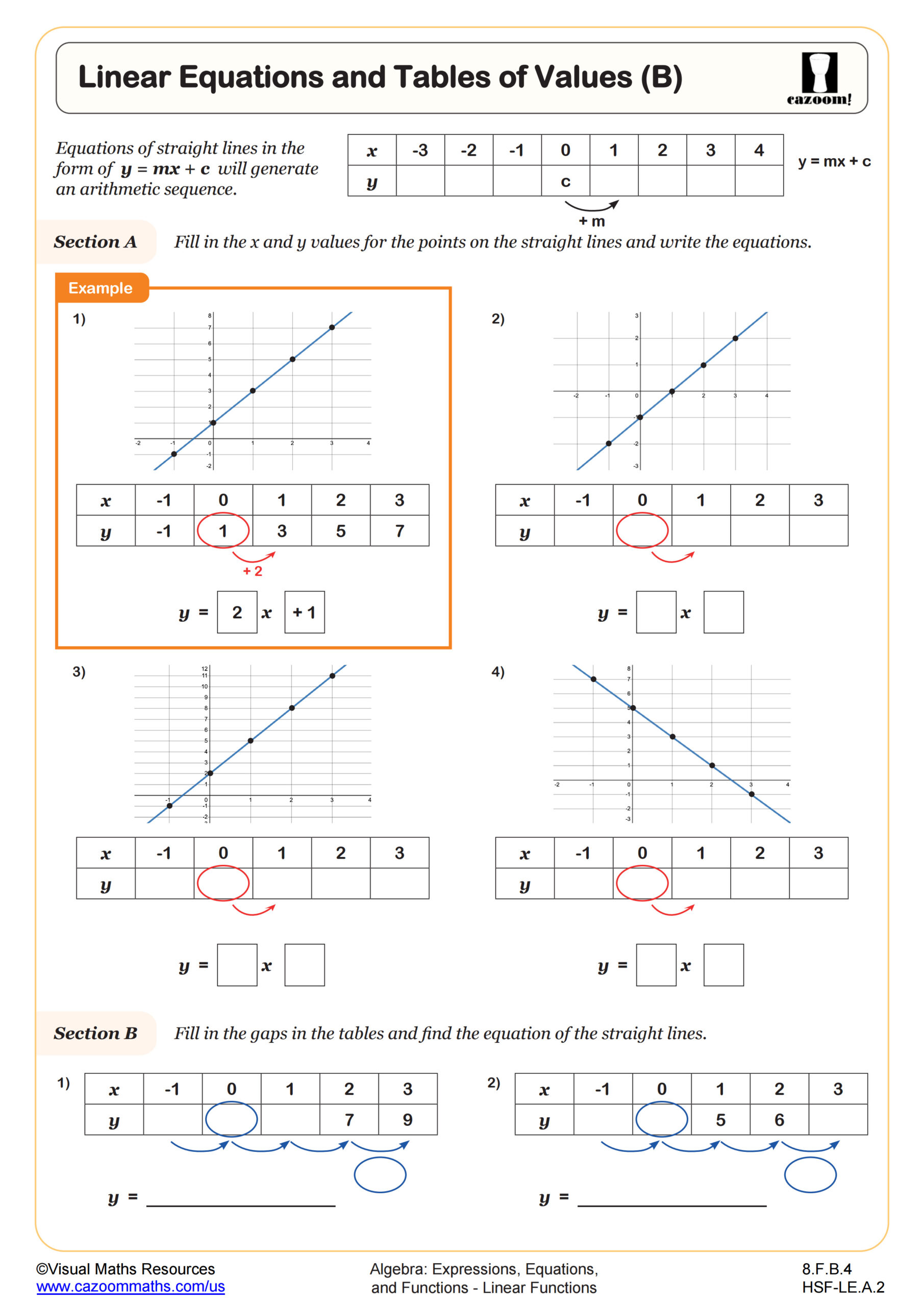
Linear Equations and Tables of Values (B)
Linear Functions (A)
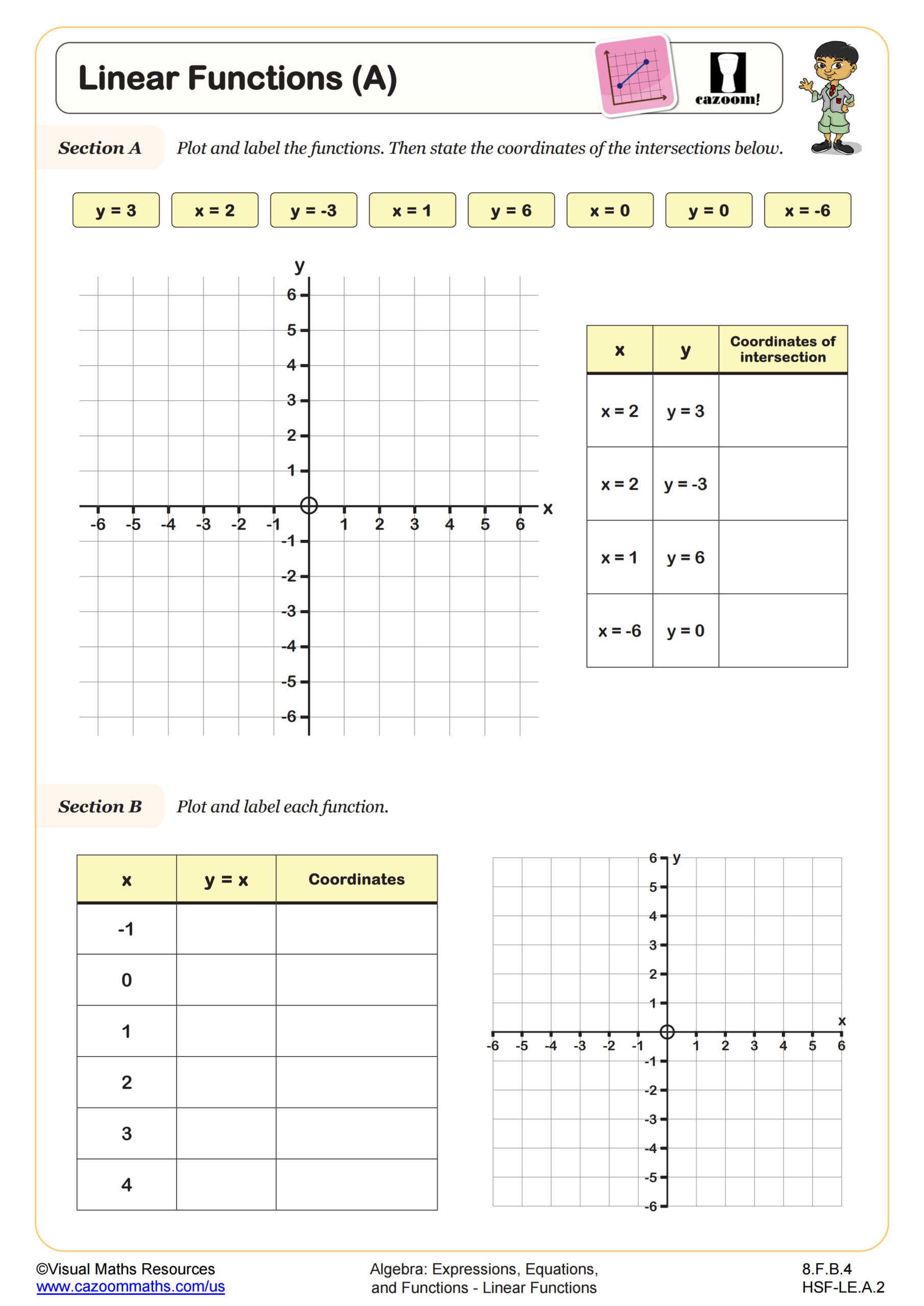
Linear Functions (B)
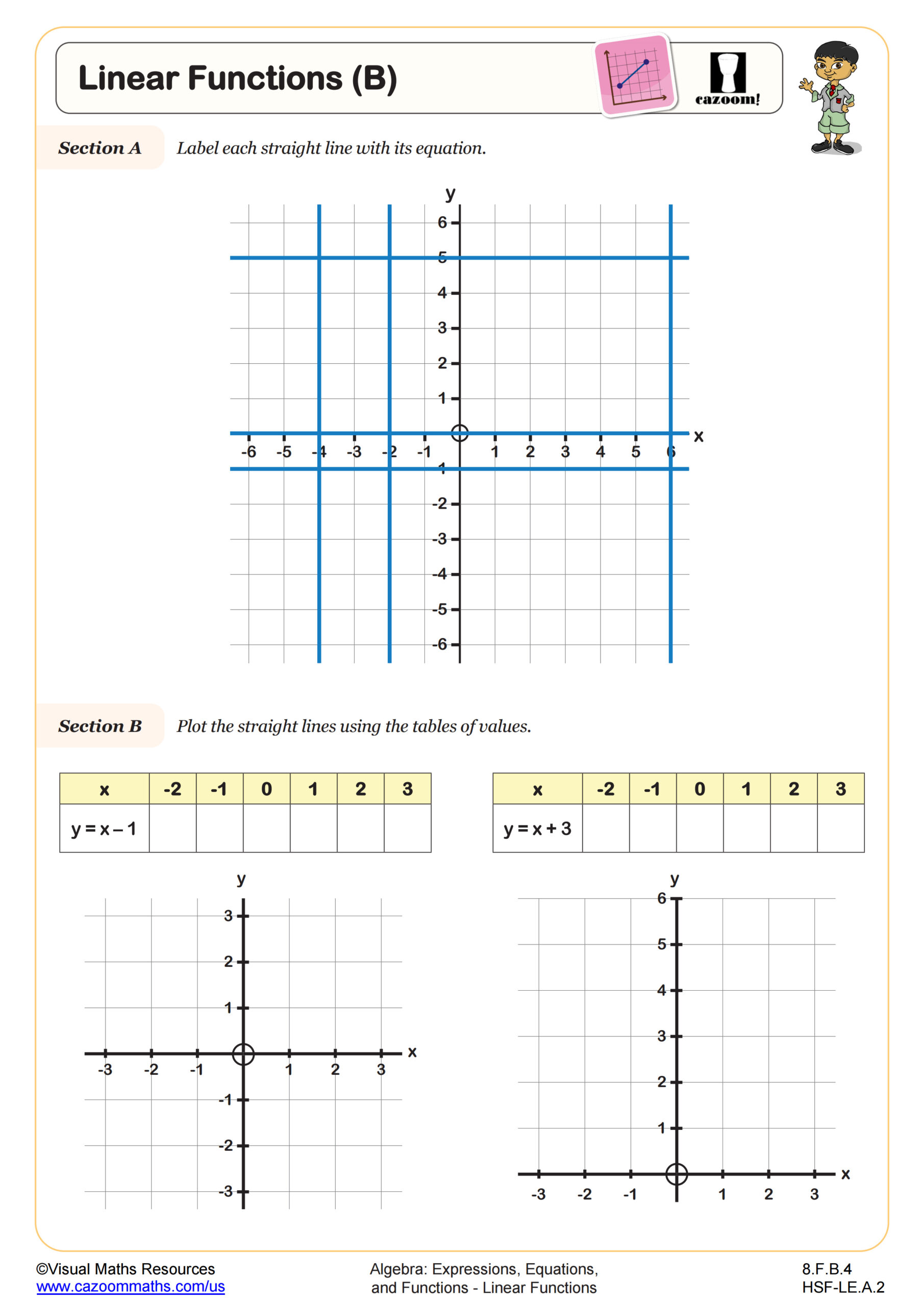
Plotting Exponential Graphs
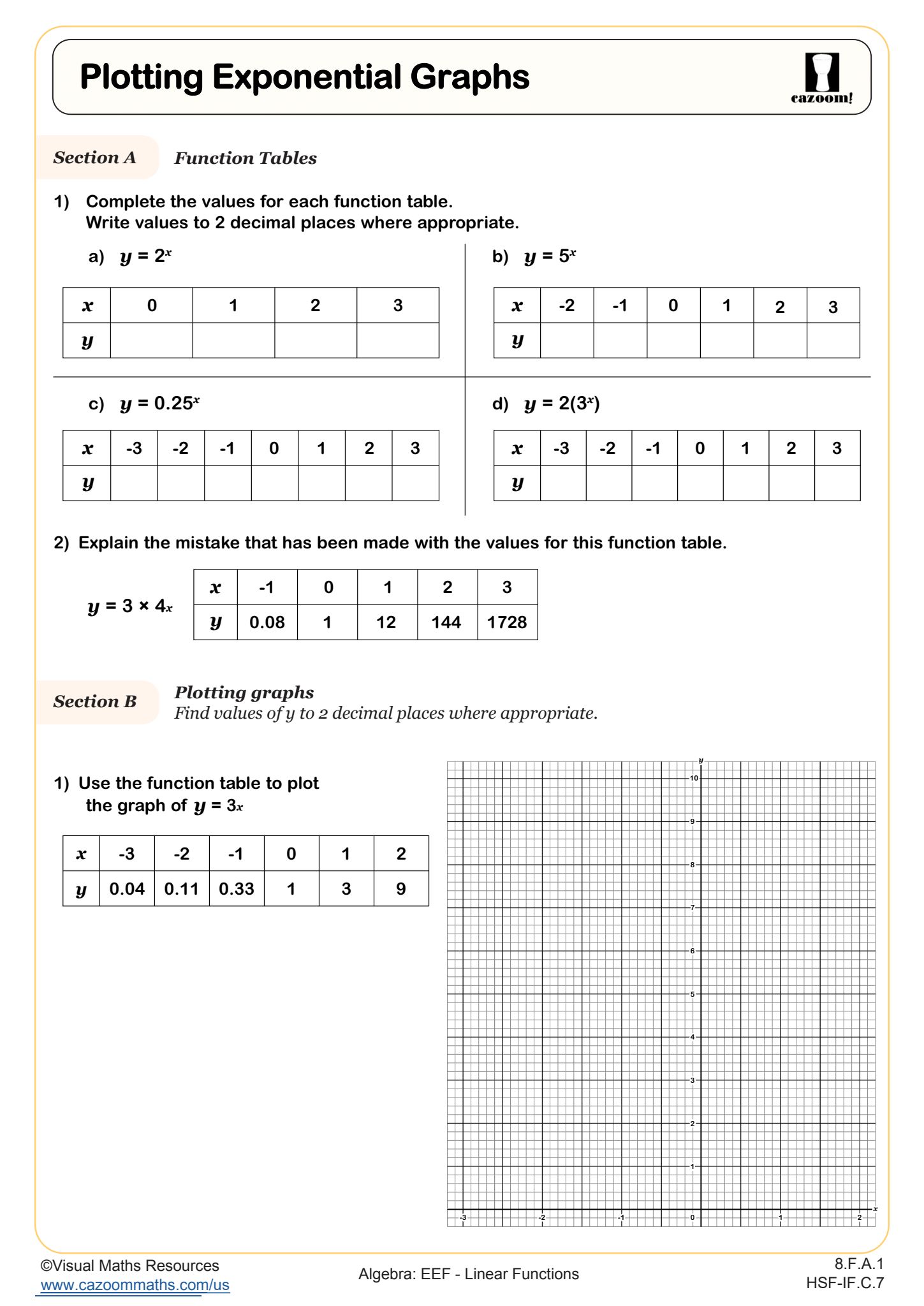
Solving Simultaneous Equations Graphically (B)
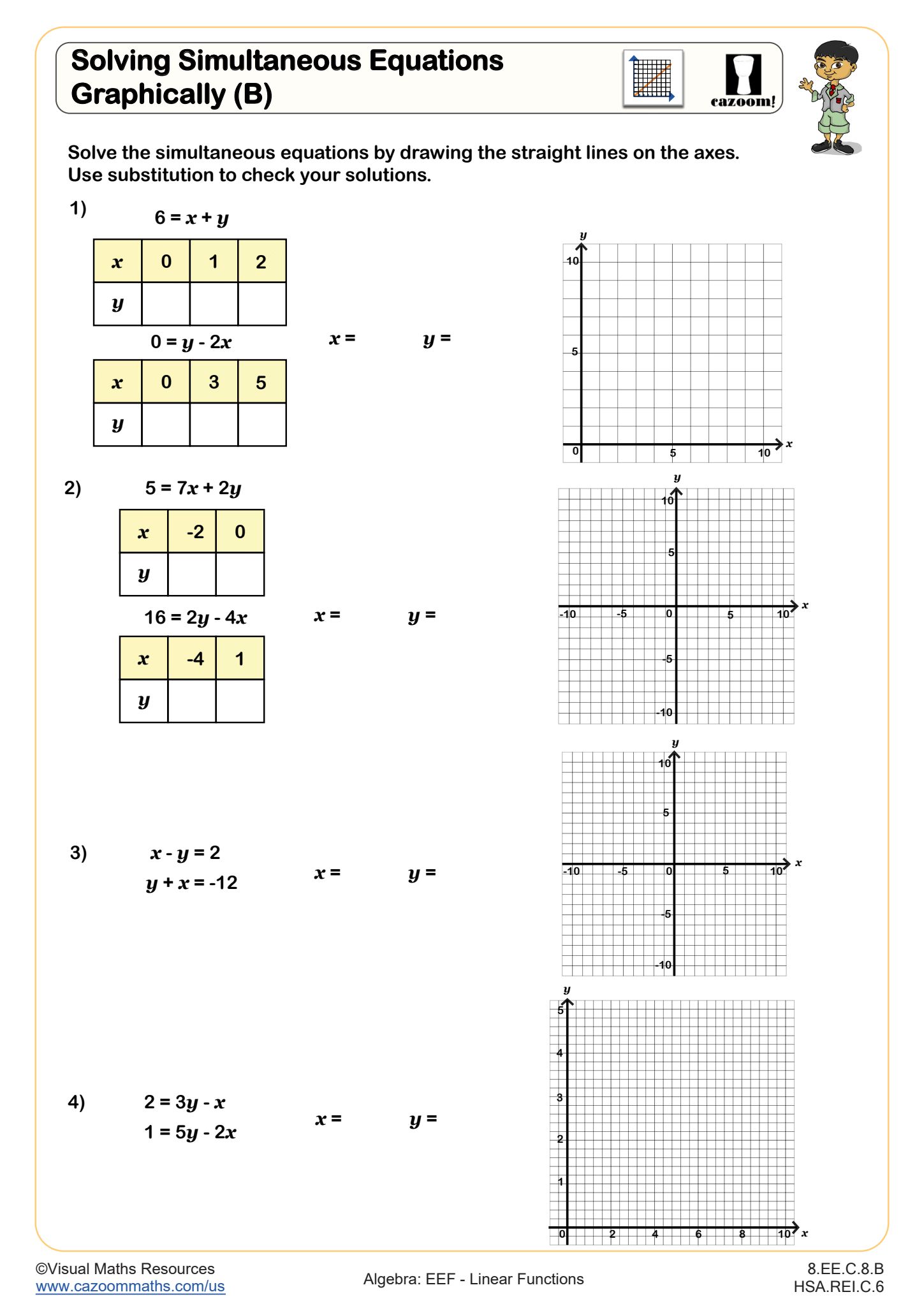
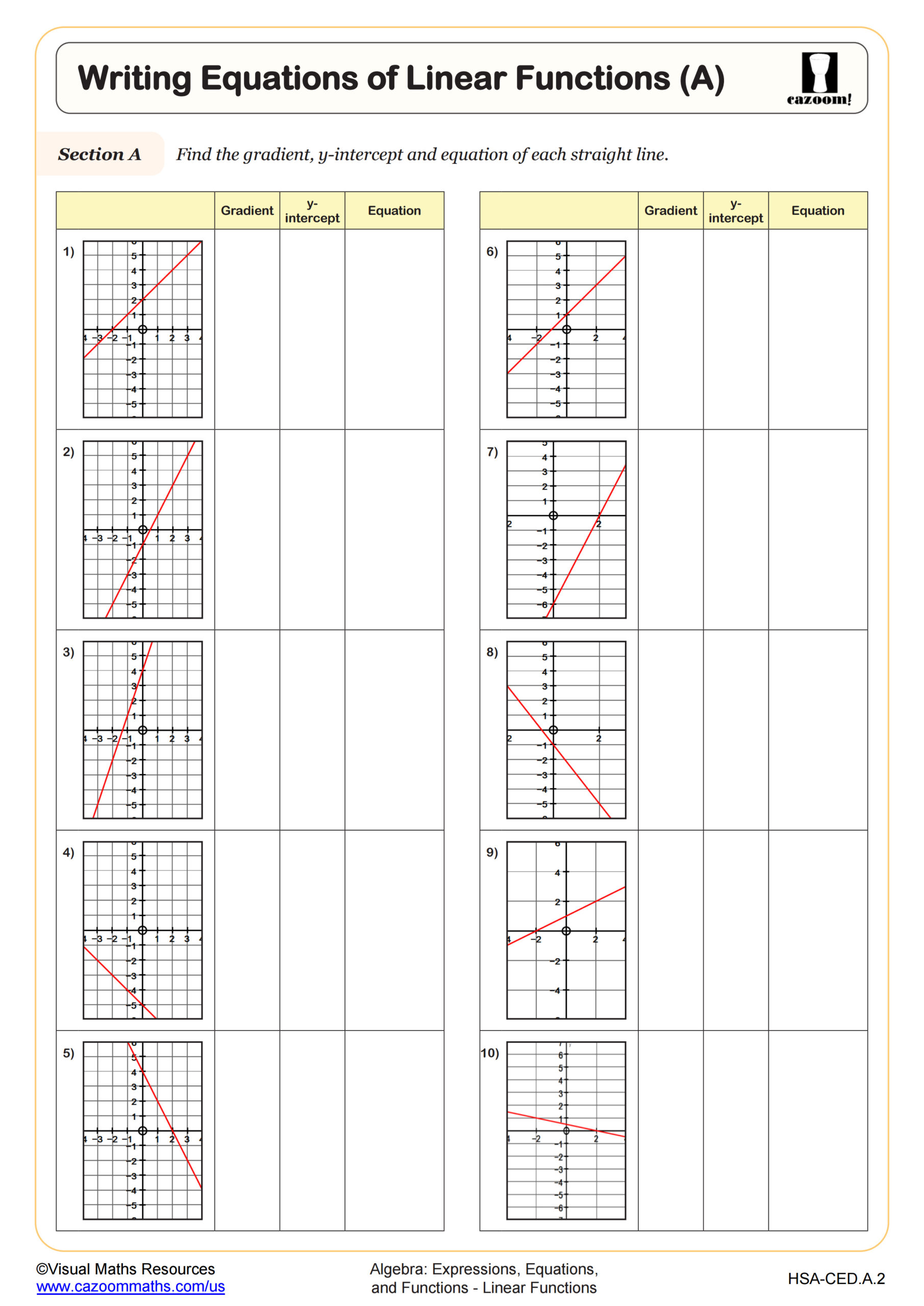
Writing Equations of Linear Functions (A)
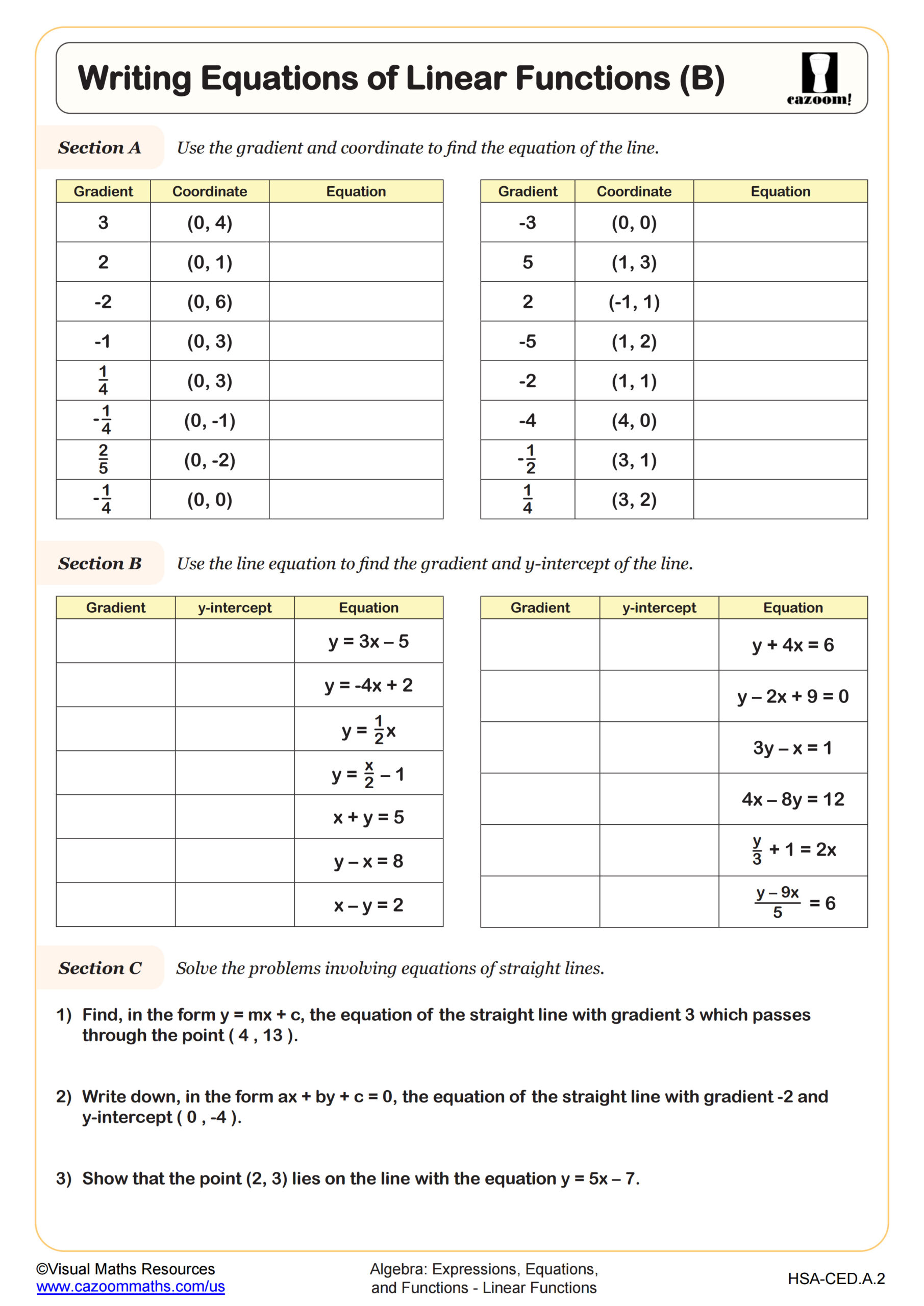
Writing Equations of Linear Functions (B)
What Linear Functions Skills Do Algebra I Students Practice?
Algebra I students work with linear functions across multiple representations: equations, graphs, tables, and verbal descriptions. The curriculum covers slope-intercept form (y = mx + b), point-slope form, standard form, identifying slopes and y-intercepts, graphing from equations, writing equations from graphs or two points, and understanding parallel lines (same slope) and perpendicular lines (opposite reciprocal slopes). Students also practice connecting tables of values to linear equations and recognizing constant rates of change.
Teachers frequently notice that students lose points when they confuse the slope formula with point-slope form, writing (y - y₁)/(x - x₁) instead of the correct equation format. Another common error occurs when finding perpendicular slopes: students often forget the negative sign when taking the reciprocal. Worksheets that explicitly practice these distinctions help students avoid these predictable mistakes on assessments.
How Do Linear Functions Appear on the SAT and State Tests?
Standardized tests like the SAT and ACT expect students to interpret linear functions in context, not just manipulate equations mechanically. Questions often present real-world scenarios involving constant rates, asking students to write equations from verbal descriptions, identify what slope and y-intercept represent in a situation, or predict values. The SAT calculator section frequently includes multi-step problems where students must extract information from graphs or tables and apply linear function concepts.
Students lose significant points when they correctly calculate slope but then write the wrong equation because they substitute values incorrectly into point-slope form. Another assessment pitfall happens with perpendicular lines: students may identify perpendicular slopes correctly but fail to use given points to write the complete equation. State assessments also test whether students recognize that linear functions have constant rates of change, distinguishing them from exponential or quadratic patterns.
Why Do Perpendicular Line Equations Challenge Students?
Finding equations of perpendicular lines requires students to combine multiple skills: calculating slopes, finding reciprocals, applying negative signs, and using point-slope or slope-intercept form. Students must recognize that if one line has slope m, a perpendicular line has slope -1/m. Many students correctly identify that perpendicular slopes are opposite reciprocals but then struggle to use a given point to write the actual equation, often substituting coordinates into the wrong variables.
This skill connects directly to geometry and engineering applications. Urban planners use perpendicular lines when designing street grids, ensuring intersections meet at right angles. Civil engineers apply perpendicular slopes when calculating drainage systems, where water runoff channels must meet roads at specific angles for proper flow. In physics and calculus, perpendicular lines represent relationships between position and velocity vectors, making this Algebra I foundation critical for STEM-bound students.
How Can Teachers Use These Linear Function Worksheets in Algebra I?
The worksheets provide scaffolded practice that builds from basic graphing skills to more complex applications like perpendicular lines and multi-step problems. The collection includes differentiated levels (indicated by A and B versions) that allow teachers to match practice to student readiness. Answer keys enable students to check their work during independent practice, helping them identify specific error patterns before summative assessments. Teachers find that having worked solutions helps students understand not just what the answer is, but why their approach may have been incorrect.
Many teachers use these worksheets for targeted intervention when formative assessments reveal gaps in linear function understanding. The table-to-equation worksheets work particularly well for paired activities, where one student generates tables and the partner writes equations, then they verify using answer keys. The perpendicular and parallel line worksheets serve as effective test prep since these concepts consistently appear on state assessments and college entrance exams. Some teachers assign specific worksheets as homework before unit reviews, then use class time to address common errors revealed by the answer keys.