High School Units and Dimensions Worksheets
What Are Units and Dimensions in High School Math?
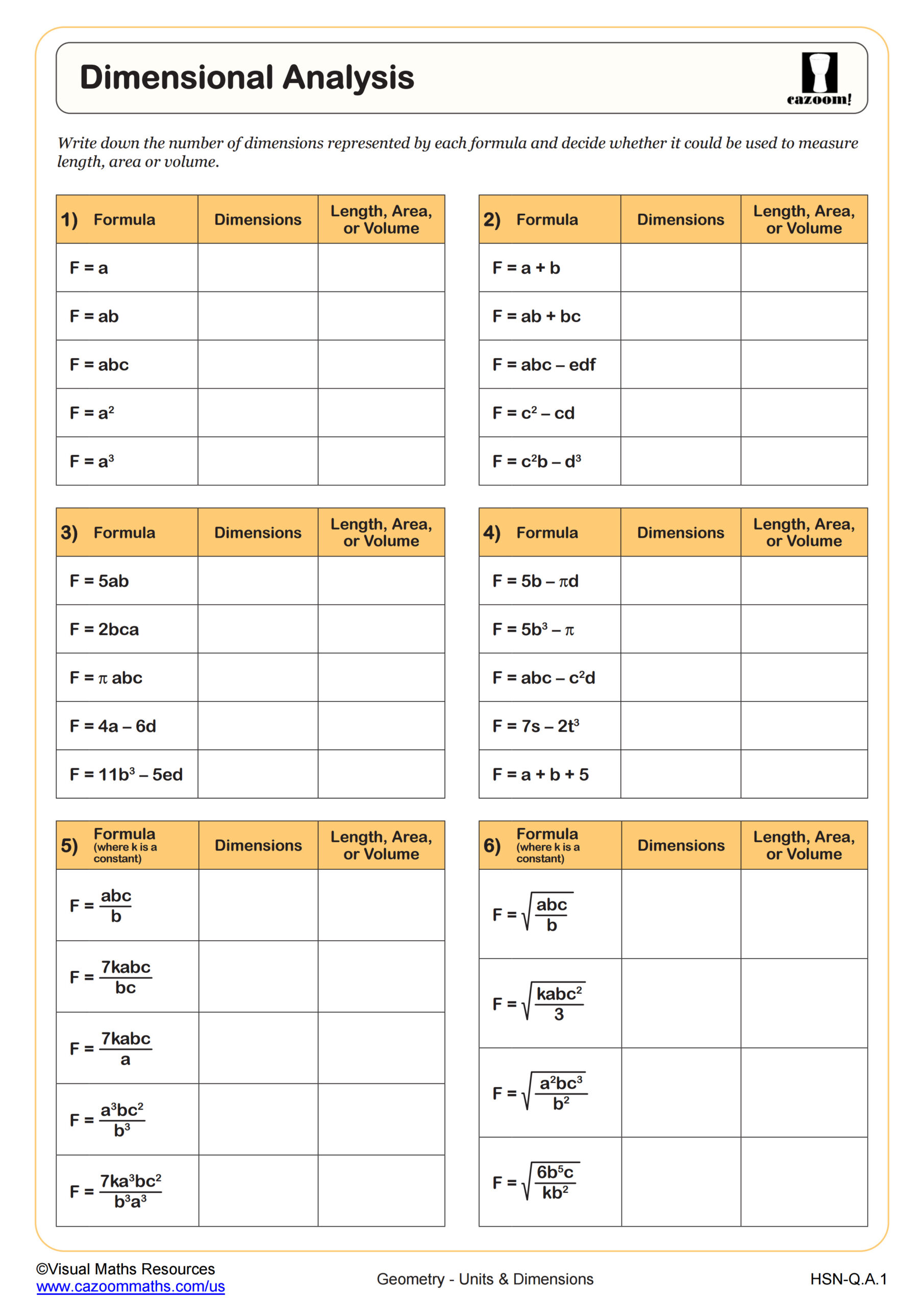
Units and dimensions refer to the measurements and their properties used to quantify physical quantities in mathematics and science. In high school math, this topic focuses on understanding metric system relationships, converting between different scales of measurement, and applying dimensional reasoning to real-world problems. Students learn to work with length conversions (millimeters to centimeters, centimeters to meters) and develop strategies for checking whether their answers make sense dimensionally.
A common error occurs when students multiply instead of divide during conversions, or vice versa. Teachers frequently notice that asking "Should the number get bigger or smaller?" before converting helps students self-correct. For example, when converting 350 centimeters to meters, students should recognize the answer must be smaller since meters are larger units. This simple checkpoint prevents many calculation mistakes and builds number sense alongside conversion skills.
Which Grade Levels Study Units and Dimensions?
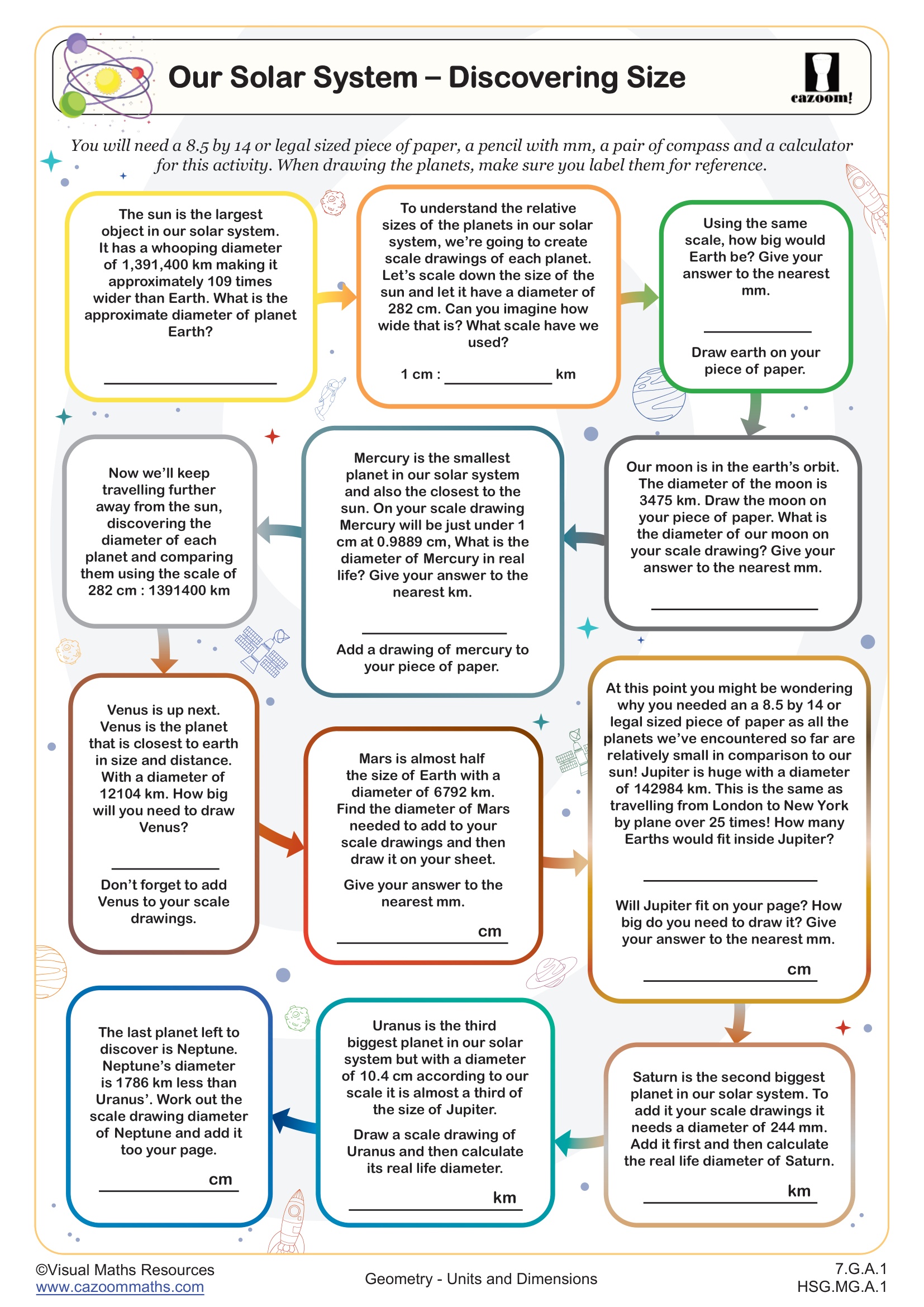
These worksheets align with high school curricula across Algebra I, Algebra II, Geometry, Precalculus, and Integrated Math 1, 2, and 3 courses. While measurement appears in earlier grades, high school treatment emphasizes precision, multi-step conversions, and applications within algebraic and scientific contexts. Students encounter units and dimensions when solving geometry problems involving perimeter and area, working with physics-based word problems, and analyzing functions with real-world parameters.
The progression moves from straightforward single-unit conversions in Algebra I to more complex applications in upper-level courses. Precalculus students apply dimensional reasoning to parametric equations and polar coordinates, while Integrated Math sequences build these skills incrementally across three years. Students confidently tackle compound units (like square centimeters or cubic meters) once they master linear measurement conversions, making the foundational practice essential for advanced problem-solving.
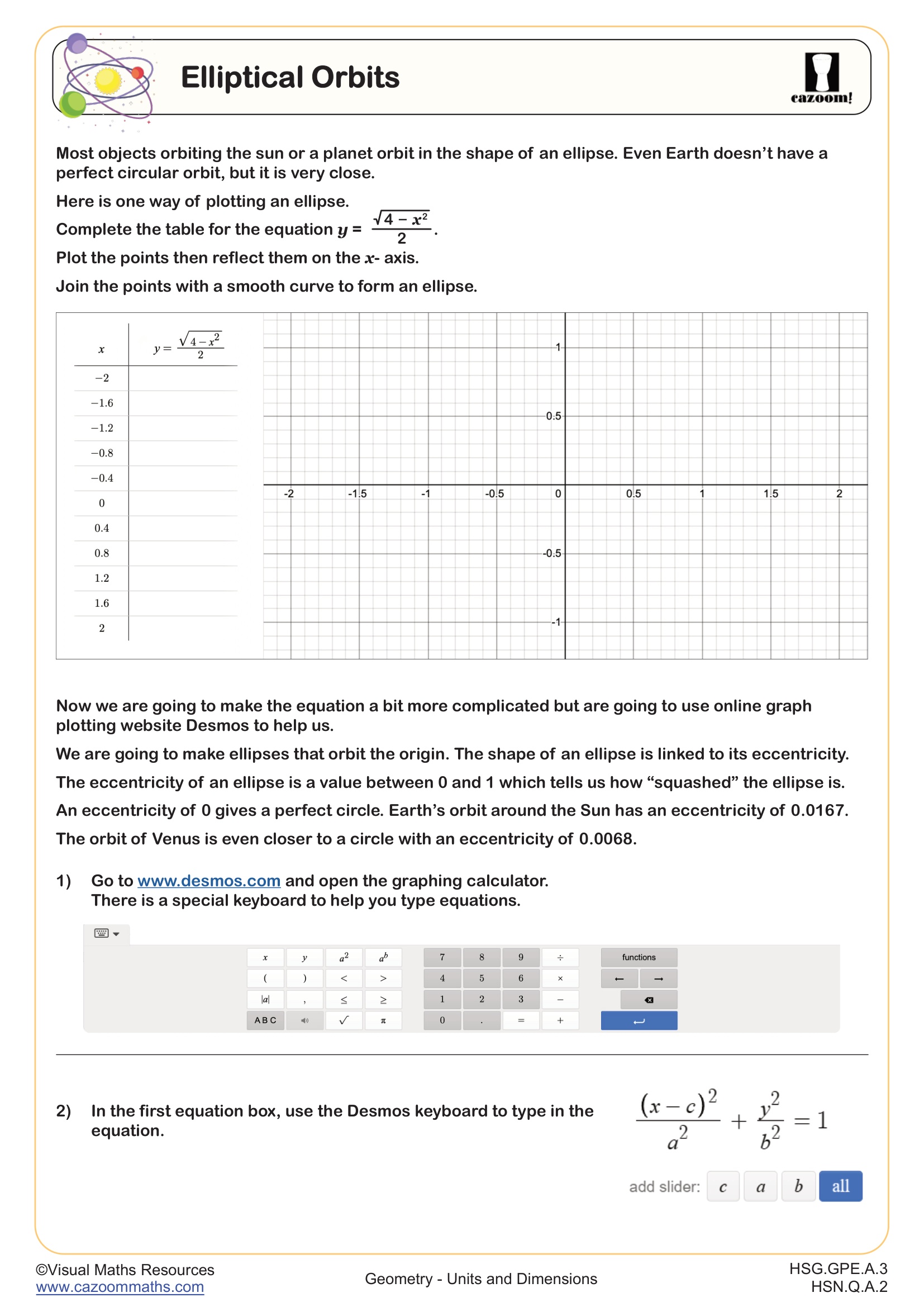
How Do Elliptical Orbits Connect to Units and Dimensions?
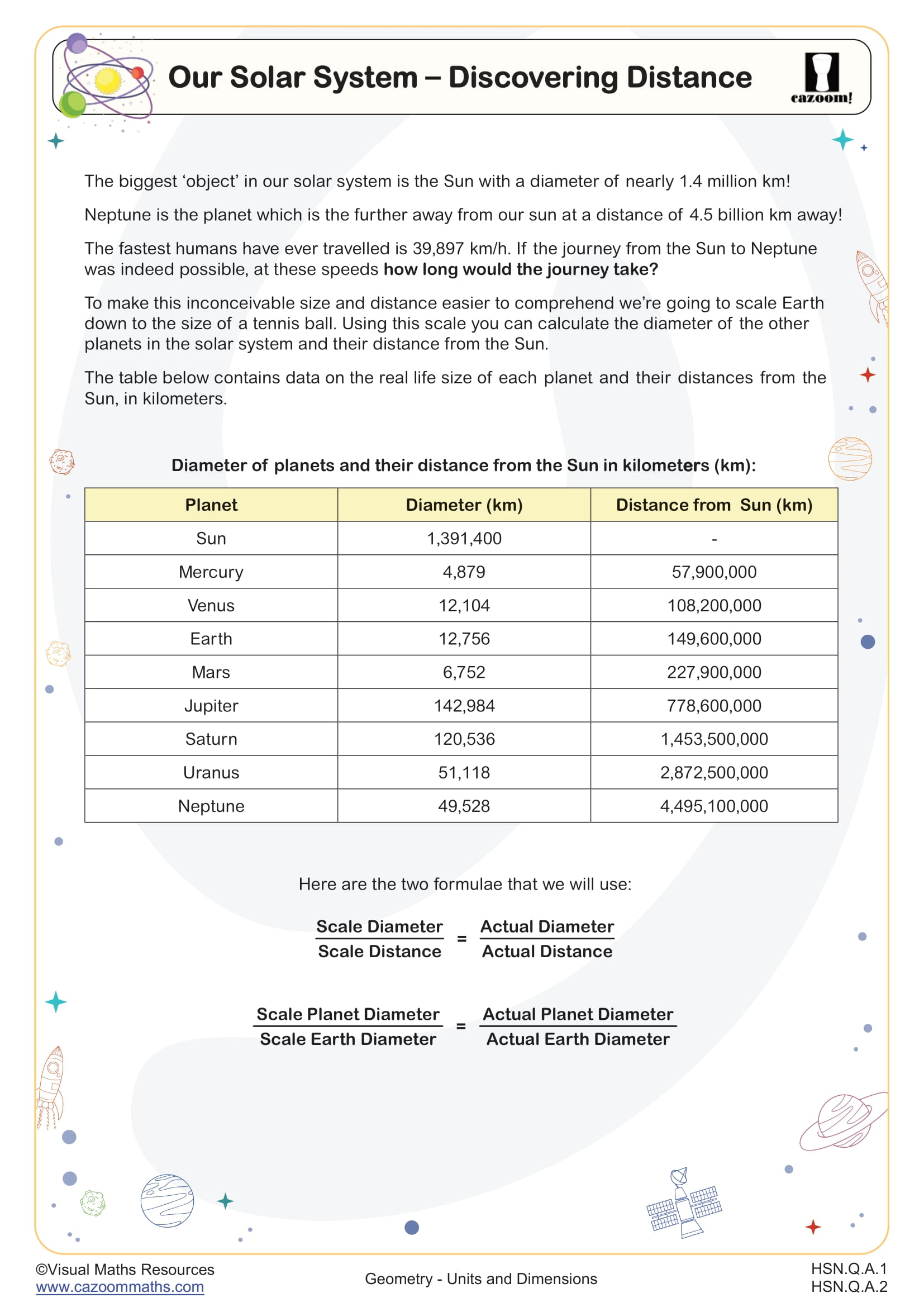
Elliptical orbits represent an advanced application where students use dimensional reasoning to describe planetary motion and satellite trajectories. This topic connects algebraic concepts (the equation of an ellipse) with physical measurements, requiring students to work with astronomical units, kilometers, and meters while maintaining dimensional consistency. Students analyze semi-major and semi-minor axes, calculate orbital periods, and explore Kepler's laws through mathematical models that demand careful attention to units.
This application directly supports STEM fields including aerospace engineering, astrophysics, and satellite communications. GPS satellites, for example, follow elliptical orbits calculated using precise unit conversions between Earth radii, kilometers, and meters. Engineers designing space missions must convert between metric and sometimes imperial units while accounting for extreme scales, from millimeter tolerances in spacecraft components to million-kilometer orbital distances. Understanding how dimensional consistency affects these calculations prepares students for careers requiring mathematical modeling of physical systems.
How Should Teachers Use These Units and Dimensions Worksheets?
The worksheets provide scaffolded practice that begins with straightforward conversions between adjacent metric units before progressing to multi-step problems and applied contexts. Answer keys allow students to check their work immediately, reinforcing correct methods and identifying misconceptions before they become ingrained. Teachers find that students benefit from working several problems of one type before moving to the next level of complexity, building confidence through incremental success.
These resources work effectively for differentiated instruction, intervention support, and homework assignments. Teachers often use simpler conversion worksheets as warm-up activities to activate prior knowledge before introducing new geometric or algebraic content. The elliptical orbit problems serve well as extension activities for advanced students or project-based learning connections. Paired work helps struggling students verbalize their reasoning about whether to multiply or divide, while independent practice solidifies skills needed for standardized assessments that expect fluency with metric conversions.