Integrated Math 3 Algebra Worksheets
What Algebra Topics Are Covered in Integrated Math 3?
Integrated Math 3 algebra extends beyond solving equations to include advanced pattern analysis, with quadratic sequences representing a key concept. Students learn to identify when sequences follow quadratic patterns by examining constant second differences, then develop general nth term formulas in the form an² + bn + c. This connects their work with quadratic functions, completing the square, and polynomial operations from earlier in the curriculum.
A common error students make involves forgetting to test whether a sequence is linear or quadratic before applying formulas. Teachers often see students attempt to find a common difference when the sequence actually requires second difference analysis, leading to incorrect formulas. Establishing a systematic approach where students always calculate both first and second differences prevents this misconception and builds stronger mathematical reasoning habits.
How Do Quadratic Sequences Appear on the SAT and ACT?
Standardized tests include quadratic sequences in pattern recognition and function modeling questions, often within the Problem Solving and Data Analysis or Passport to Advanced Math sections. Students need to demonstrate they can identify the type of sequence, extend patterns logically, and sometimes connect sequences to explicit function notation. Questions may present sequences in tables, diagrams, or word problems requiring students to recognize the underlying quadratic relationship.
Students lose points when they rush to find patterns without verifying their formula works for all given terms. Many students correctly identify the sequence type but make arithmetic errors when calculating coefficients for the nth term formula. Teachers notice that students who check their formula against at least three terms from the original sequence catch these mistakes before submitting answers, significantly improving accuracy on timed assessments.
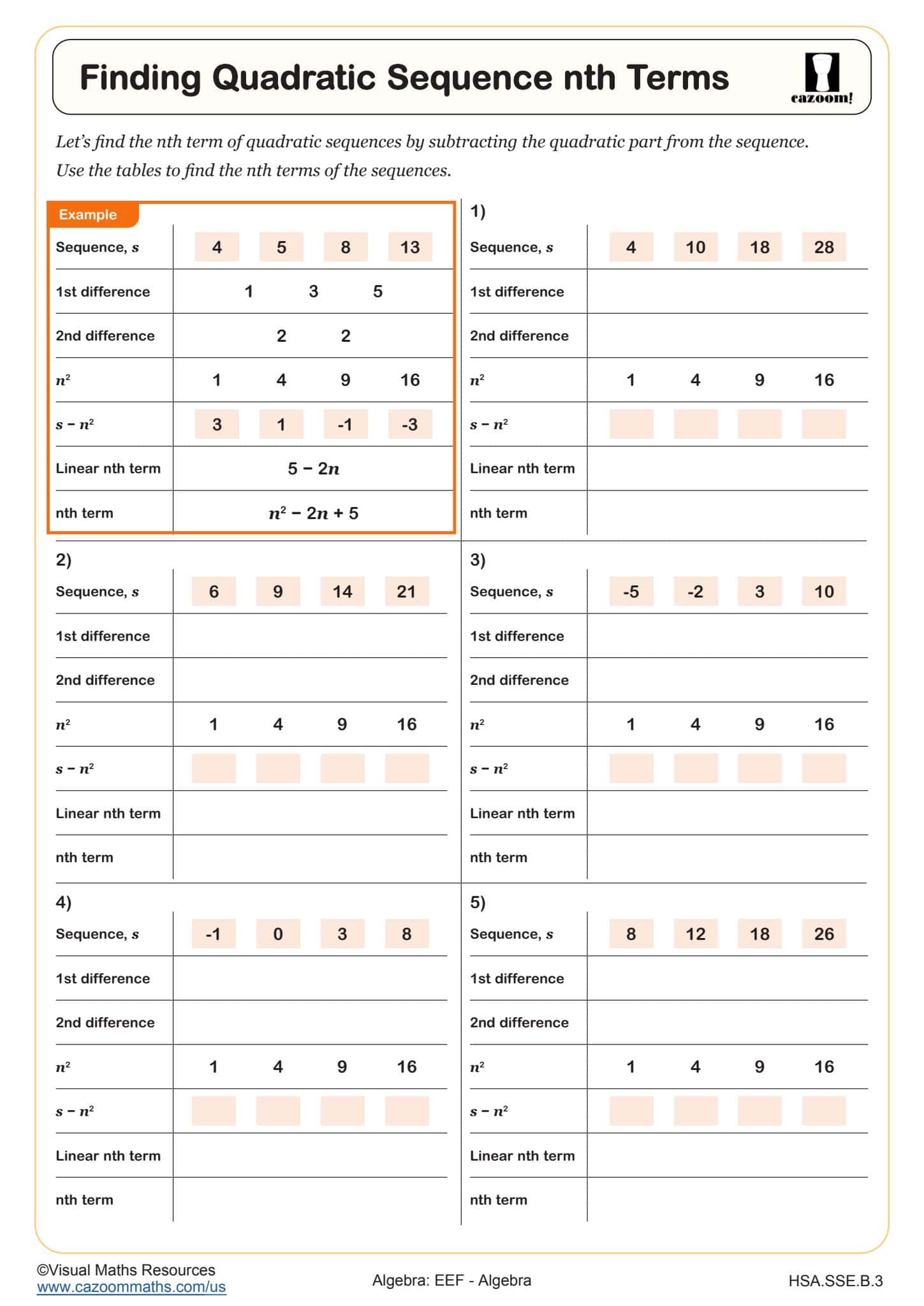
What Is the Method for Finding nth Terms of Quadratic Sequences?
Finding the nth term of a quadratic sequence involves a systematic process starting with calculating first differences between consecutive terms, then second differences. When second differences are constant, the sequence is quadratic, and that constant value equals 2a in the formula an² + bn + c. Students then solve for b and c by substituting known terms and their positions into the formula, creating a system that reveals all coefficients.
This skill connects directly to physics and engineering contexts where quadratic relationships model motion under constant acceleration. The distance an object falls under gravity follows a quadratic pattern with respect to time, making this more than abstract algebra. Students studying kinematics in physics courses recognize these same patterns, strengthening their ability to translate between mathematical models and physical phenomena across STEM disciplines.
How Can Teachers Use These Algebra Worksheets in Integrated Math 3?
These worksheets provide structured practice with quadratic sequences, moving students from recognizing patterns through calculating second differences to writing complete nth term formulas. The problems build progressively, allowing students to develop confidence with the procedural steps before tackling more complex sequences. With answer keys included, students can check their work immediately, identifying exactly where errors occur in their calculation process rather than wondering if their entire approach is wrong.
Many teachers use these worksheets during targeted review sessions before unit assessments or state testing, particularly when addressing gaps in pattern recognition skills. The format works well for paired work where one student calculates differences while the other sets up the formula, then they verify together. Teachers also assign portions as homework following initial instruction, using class time the next day to address common errors revealed by student work, making instruction more responsive to actual student needs.